Home Blog Design Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)

Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)

In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey. Different types of visualizations serve distinct purposes. Whether you’re dealing with how to develop a report or simply trying to communicate complex information, how you present data influences how well your audience understands and engages with it. This extensive guide leads you through the different ways of data presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Data Presentation?
What should a data presentation include, line graphs, treemap chart, scatter plot, how to choose a data presentation type, recommended data presentation templates, common mistakes done in data presentation.
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. This process requires a series of tools, such as charts, graphs, tables, infographics, dashboards, and so on, supported by concise textual explanations to improve understanding and boost retention rate.
Data presentations require us to cull data in a format that allows the presenter to highlight trends, patterns, and insights so that the audience can act upon the shared information. In a few words, the goal of data presentations is to enable viewers to grasp complicated concepts or trends quickly, facilitating informed decision-making or deeper analysis.
Data presentations go beyond the mere usage of graphical elements. Seasoned presenters encompass visuals with the art of data storytelling , so the speech skillfully connects the points through a narrative that resonates with the audience. Depending on the purpose – inspire, persuade, inform, support decision-making processes, etc. – is the data presentation format that is better suited to help us in this journey.
To nail your upcoming data presentation, ensure to count with the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Understand the intent of your presentation before selecting the graphical layout and metaphors to make content easier to grasp.
- Engaging introduction: Use a powerful hook from the get-go. For instance, you can ask a big question or present a problem that your data will answer. Take a look at our guide on how to start a presentation for tips & insights.
- Structured Narrative: Your data presentation must tell a coherent story. This means a beginning where you present the context, a middle section in which you present the data, and an ending that uses a call-to-action. Check our guide on presentation structure for further information.
- Visual Elements: These are the charts, graphs, and other elements of visual communication we ought to use to present data. This article will cover one by one the different types of data representation methods we can use, and provide further guidance on choosing between them.
- Insights and Analysis: This is not just showcasing a graph and letting people get an idea about it. A proper data presentation includes the interpretation of that data, the reason why it’s included, and why it matters to your research.
- Conclusion & CTA: Ending your presentation with a call to action is necessary. Whether you intend to wow your audience into acquiring your services, inspire them to change the world, or whatever the purpose of your presentation, there must be a stage in which you convey all that you shared and show the path to staying in touch. Plan ahead whether you want to use a thank-you slide, a video presentation, or which method is apt and tailored to the kind of presentation you deliver.
- Q&A Session: After your speech is concluded, allocate 3-5 minutes for the audience to raise any questions about the information you disclosed. This is an extra chance to establish your authority on the topic. Check our guide on questions and answer sessions in presentations here.
Bar charts are a graphical representation of data using rectangular bars to show quantities or frequencies in an established category. They make it easy for readers to spot patterns or trends. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, although the vertical format is commonly known as a column chart. They display categorical, discrete, or continuous variables grouped in class intervals [1] . They include an axis and a set of labeled bars horizontally or vertically. These bars represent the frequencies of variable values or the values themselves. Numbers on the y-axis of a vertical bar chart or the x-axis of a horizontal bar chart are called the scale.

Real-Life Application of Bar Charts
Let’s say a sales manager is presenting sales to their audience. Using a bar chart, he follows these steps.
Step 1: Selecting Data
The first step is to identify the specific data you will present to your audience.
The sales manager has highlighted these products for the presentation.
- Product A: Men’s Shoes
- Product B: Women’s Apparel
- Product C: Electronics
- Product D: Home Decor
Step 2: Choosing Orientation
Opt for a vertical layout for simplicity. Vertical bar charts help compare different categories in case there are not too many categories [1] . They can also help show different trends. A vertical bar chart is used where each bar represents one of the four chosen products. After plotting the data, it is seen that the height of each bar directly represents the sales performance of the respective product.
It is visible that the tallest bar (Electronics – Product C) is showing the highest sales. However, the shorter bars (Women’s Apparel – Product B and Home Decor – Product D) need attention. It indicates areas that require further analysis or strategies for improvement.
Step 3: Colorful Insights
Different colors are used to differentiate each product. It is essential to show a color-coded chart where the audience can distinguish between products.
- Men’s Shoes (Product A): Yellow
- Women’s Apparel (Product B): Orange
- Electronics (Product C): Violet
- Home Decor (Product D): Blue

Bar charts are straightforward and easily understandable for presenting data. They are versatile when comparing products or any categorical data [2] . Bar charts adapt seamlessly to retail scenarios. Despite that, bar charts have a few shortcomings. They cannot illustrate data trends over time. Besides, overloading the chart with numerous products can lead to visual clutter, diminishing its effectiveness.
For more information, check our collection of bar chart templates for PowerPoint .
Line graphs help illustrate data trends, progressions, or fluctuations by connecting a series of data points called ‘markers’ with straight line segments. This provides a straightforward representation of how values change [5] . Their versatility makes them invaluable for scenarios requiring a visual understanding of continuous data. In addition, line graphs are also useful for comparing multiple datasets over the same timeline. Using multiple line graphs allows us to compare more than one data set. They simplify complex information so the audience can quickly grasp the ups and downs of values. From tracking stock prices to analyzing experimental results, you can use line graphs to show how data changes over a continuous timeline. They show trends with simplicity and clarity.
Real-life Application of Line Graphs
To understand line graphs thoroughly, we will use a real case. Imagine you’re a financial analyst presenting a tech company’s monthly sales for a licensed product over the past year. Investors want insights into sales behavior by month, how market trends may have influenced sales performance and reception to the new pricing strategy. To present data via a line graph, you will complete these steps.
First, you need to gather the data. In this case, your data will be the sales numbers. For example:
- January: $45,000
- February: $55,000
- March: $45,000
- April: $60,000
- May: $ 70,000
- June: $65,000
- July: $62,000
- August: $68,000
- September: $81,000
- October: $76,000
- November: $87,000
- December: $91,000
After choosing the data, the next step is to select the orientation. Like bar charts, you can use vertical or horizontal line graphs. However, we want to keep this simple, so we will keep the timeline (x-axis) horizontal while the sales numbers (y-axis) vertical.
Step 3: Connecting Trends
After adding the data to your preferred software, you will plot a line graph. In the graph, each month’s sales are represented by data points connected by a line.

Step 4: Adding Clarity with Color
If there are multiple lines, you can also add colors to highlight each one, making it easier to follow.
Line graphs excel at visually presenting trends over time. These presentation aids identify patterns, like upward or downward trends. However, too many data points can clutter the graph, making it harder to interpret. Line graphs work best with continuous data but are not suitable for categories.
For more information, check our collection of line chart templates for PowerPoint and our article about how to make a presentation graph .
A data dashboard is a visual tool for analyzing information. Different graphs, charts, and tables are consolidated in a layout to showcase the information required to achieve one or more objectives. Dashboards help quickly see Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). You don’t make new visuals in the dashboard; instead, you use it to display visuals you’ve already made in worksheets [3] .
Keeping the number of visuals on a dashboard to three or four is recommended. Adding too many can make it hard to see the main points [4]. Dashboards can be used for business analytics to analyze sales, revenue, and marketing metrics at a time. They are also used in the manufacturing industry, as they allow users to grasp the entire production scenario at the moment while tracking the core KPIs for each line.
Real-Life Application of a Dashboard
Consider a project manager presenting a software development project’s progress to a tech company’s leadership team. He follows the following steps.
Step 1: Defining Key Metrics
To effectively communicate the project’s status, identify key metrics such as completion status, budget, and bug resolution rates. Then, choose measurable metrics aligned with project objectives.
Step 2: Choosing Visualization Widgets
After finalizing the data, presentation aids that align with each metric are selected. For this project, the project manager chooses a progress bar for the completion status and uses bar charts for budget allocation. Likewise, he implements line charts for bug resolution rates.

Step 3: Dashboard Layout
Key metrics are prominently placed in the dashboard for easy visibility, and the manager ensures that it appears clean and organized.
Dashboards provide a comprehensive view of key project metrics. Users can interact with data, customize views, and drill down for detailed analysis. However, creating an effective dashboard requires careful planning to avoid clutter. Besides, dashboards rely on the availability and accuracy of underlying data sources.
For more information, check our article on how to design a dashboard presentation , and discover our collection of dashboard PowerPoint templates .
Treemap charts represent hierarchical data structured in a series of nested rectangles [6] . As each branch of the ‘tree’ is given a rectangle, smaller tiles can be seen representing sub-branches, meaning elements on a lower hierarchical level than the parent rectangle. Each one of those rectangular nodes is built by representing an area proportional to the specified data dimension.
Treemaps are useful for visualizing large datasets in compact space. It is easy to identify patterns, such as which categories are dominant. Common applications of the treemap chart are seen in the IT industry, such as resource allocation, disk space management, website analytics, etc. Also, they can be used in multiple industries like healthcare data analysis, market share across different product categories, or even in finance to visualize portfolios.
Real-Life Application of a Treemap Chart
Let’s consider a financial scenario where a financial team wants to represent the budget allocation of a company. There is a hierarchy in the process, so it is helpful to use a treemap chart. In the chart, the top-level rectangle could represent the total budget, and it would be subdivided into smaller rectangles, each denoting a specific department. Further subdivisions within these smaller rectangles might represent individual projects or cost categories.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy
While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project.
- Top-level rectangle: Total Budget
- Second-level rectangles: Departments (Engineering, Marketing, Sales)
- Third-level rectangles: Projects within each department
- Fourth-level rectangles: Cost categories for each project (Personnel, Marketing Expenses, Equipment)
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Tool
It’s time to select a data visualization tool supporting Treemaps. Popular choices include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, PowerPoint, or even coding with libraries like D3.js. It is vital to ensure that the chosen tool provides customization options for colors, labels, and hierarchical structures.
Here, the team uses PowerPoint for this guide because of its user-friendly interface and robust Treemap capabilities.
Step 3: Make a Treemap Chart with PowerPoint
After opening the PowerPoint presentation, they chose “SmartArt” to form the chart. The SmartArt Graphic window has a “Hierarchy” category on the left. Here, you will see multiple options. You can choose any layout that resembles a Treemap. The “Table Hierarchy” or “Organization Chart” options can be adapted. The team selects the Table Hierarchy as it looks close to a Treemap.
Step 5: Input Your Data
After that, a new window will open with a basic structure. They add the data one by one by clicking on the text boxes. They start with the top-level rectangle, representing the total budget.

Step 6: Customize the Treemap
By clicking on each shape, they customize its color, size, and label. At the same time, they can adjust the font size, style, and color of labels by using the options in the “Format” tab in PowerPoint. Using different colors for each level enhances the visual difference.
Treemaps excel at illustrating hierarchical structures. These charts make it easy to understand relationships and dependencies. They efficiently use space, compactly displaying a large amount of data, reducing the need for excessive scrolling or navigation. Additionally, using colors enhances the understanding of data by representing different variables or categories.
In some cases, treemaps might become complex, especially with deep hierarchies. It becomes challenging for some users to interpret the chart. At the same time, displaying detailed information within each rectangle might be constrained by space. It potentially limits the amount of data that can be shown clearly. Without proper labeling and color coding, there’s a risk of misinterpretation.
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that uses color coding to represent values across a two-dimensional surface. In these, colors replace numbers to indicate the magnitude of each cell. This color-shaded matrix display is valuable for summarizing and understanding data sets with a glance [7] . The intensity of the color corresponds to the value it represents, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and variations in the data.
As a tool, heatmaps help businesses analyze website interactions, revealing user behavior patterns and preferences to enhance overall user experience. In addition, companies use heatmaps to assess content engagement, identifying popular sections and areas of improvement for more effective communication. They excel at highlighting patterns and trends in large datasets, making it easy to identify areas of interest.
We can implement heatmaps to express multiple data types, such as numerical values, percentages, or even categorical data. Heatmaps help us easily spot areas with lots of activity, making them helpful in figuring out clusters [8] . When making these maps, it is important to pick colors carefully. The colors need to show the differences between groups or levels of something. And it is good to use colors that people with colorblindness can easily see.
Check our detailed guide on how to create a heatmap here. Also discover our collection of heatmap PowerPoint templates .
Pie charts are circular statistical graphics divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole, making it easy to visualize the contribution of each component to the total.
The size of the pie charts is influenced by the value of data points within each pie. The total of all data points in a pie determines its size. The pie with the highest data points appears as the largest, whereas the others are proportionally smaller. However, you can present all pies of the same size if proportional representation is not required [9] . Sometimes, pie charts are difficult to read, or additional information is required. A variation of this tool can be used instead, known as the donut chart , which has the same structure but a blank center, creating a ring shape. Presenters can add extra information, and the ring shape helps to declutter the graph.
Pie charts are used in business to show percentage distribution, compare relative sizes of categories, or present straightforward data sets where visualizing ratios is essential.
Real-Life Application of Pie Charts
Consider a scenario where you want to represent the distribution of the data. Each slice of the pie chart would represent a different category, and the size of each slice would indicate the percentage of the total portion allocated to that category.
Step 1: Define Your Data Structure
Imagine you are presenting the distribution of a project budget among different expense categories.
- Column A: Expense Categories (Personnel, Equipment, Marketing, Miscellaneous)
- Column B: Budget Amounts ($40,000, $30,000, $20,000, $10,000) Column B represents the values of your categories in Column A.
Step 2: Insert a Pie Chart
Using any of the accessible tools, you can create a pie chart. The most convenient tools for forming a pie chart in a presentation are presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Google Slides. You will notice that the pie chart assigns each expense category a percentage of the total budget by dividing it by the total budget.
For instance:
- Personnel: $40,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 40%
- Equipment: $30,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 30%
- Marketing: $20,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 20%
- Miscellaneous: $10,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 10%
You can make a chart out of this or just pull out the pie chart from the data.

3D pie charts and 3D donut charts are quite popular among the audience. They stand out as visual elements in any presentation slide, so let’s take a look at how our pie chart example would look in 3D pie chart format.

Step 03: Results Interpretation
The pie chart visually illustrates the distribution of the project budget among different expense categories. Personnel constitutes the largest portion at 40%, followed by equipment at 30%, marketing at 20%, and miscellaneous at 10%. This breakdown provides a clear overview of where the project funds are allocated, which helps in informed decision-making and resource management. It is evident that personnel are a significant investment, emphasizing their importance in the overall project budget.
Pie charts provide a straightforward way to represent proportions and percentages. They are easy to understand, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. These charts work well for small datasets with a limited number of categories.
However, a pie chart can become cluttered and less effective in situations with many categories. Accurate interpretation may be challenging, especially when dealing with slight differences in slice sizes. In addition, these charts are static and do not effectively convey trends over time.
For more information, check our collection of pie chart templates for PowerPoint .
Histograms present the distribution of numerical variables. Unlike a bar chart that records each unique response separately, histograms organize numeric responses into bins and show the frequency of reactions within each bin [10] . The x-axis of a histogram shows the range of values for a numeric variable. At the same time, the y-axis indicates the relative frequencies (percentage of the total counts) for that range of values.
Whenever you want to understand the distribution of your data, check which values are more common, or identify outliers, histograms are your go-to. Think of them as a spotlight on the story your data is telling. A histogram can provide a quick and insightful overview if you’re curious about exam scores, sales figures, or any numerical data distribution.
Real-Life Application of a Histogram
In the histogram data analysis presentation example, imagine an instructor analyzing a class’s grades to identify the most common score range. A histogram could effectively display the distribution. It will show whether most students scored in the average range or if there are significant outliers.
Step 1: Gather Data
He begins by gathering the data. The scores of each student in class are gathered to analyze exam scores.
After arranging the scores in ascending order, bin ranges are set.
Step 2: Define Bins
Bins are like categories that group similar values. Think of them as buckets that organize your data. The presenter decides how wide each bin should be based on the range of the values. For instance, the instructor sets the bin ranges based on score intervals: 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
Step 3: Count Frequency
Now, he counts how many data points fall into each bin. This step is crucial because it tells you how often specific ranges of values occur. The result is the frequency distribution, showing the occurrences of each group.
Here, the instructor counts the number of students in each category.
- 60-69: 1 student (Kate)
- 70-79: 4 students (David, Emma, Grace, Jack)
- 80-89: 7 students (Alice, Bob, Frank, Isabel, Liam, Mia, Noah)
- 90-100: 3 students (Clara, Henry, Olivia)
Step 4: Create the Histogram
It’s time to turn the data into a visual representation. Draw a bar for each bin on a graph. The width of the bar should correspond to the range of the bin, and the height should correspond to the frequency. To make your histogram understandable, label the X and Y axes.
In this case, the X-axis should represent the bins (e.g., test score ranges), and the Y-axis represents the frequency.

The histogram of the class grades reveals insightful patterns in the distribution. Most students, with seven students, fall within the 80-89 score range. The histogram provides a clear visualization of the class’s performance. It showcases a concentration of grades in the upper-middle range with few outliers at both ends. This analysis helps in understanding the overall academic standing of the class. It also identifies the areas for potential improvement or recognition.
Thus, histograms provide a clear visual representation of data distribution. They are easy to interpret, even for those without a statistical background. They apply to various types of data, including continuous and discrete variables. One weak point is that histograms do not capture detailed patterns in students’ data, with seven compared to other visualization methods.
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables. It consists of individual data points on a two-dimensional plane. This plane plots one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point represents a unique observation. It visualizes patterns, trends, or correlations between the two variables.
Scatter plots are also effective in revealing the strength and direction of relationships. They identify outliers and assess the overall distribution of data points. The points’ dispersion and clustering reflect the relationship’s nature, whether it is positive, negative, or lacks a discernible pattern. In business, scatter plots assess relationships between variables such as marketing cost and sales revenue. They help present data correlations and decision-making.
Real-Life Application of Scatter Plot
A group of scientists is conducting a study on the relationship between daily hours of screen time and sleep quality. After reviewing the data, they managed to create this table to help them build a scatter plot graph:
In the provided example, the x-axis represents Daily Hours of Screen Time, and the y-axis represents the Sleep Quality Rating.

The scientists observe a negative correlation between the amount of screen time and the quality of sleep. This is consistent with their hypothesis that blue light, especially before bedtime, has a significant impact on sleep quality and metabolic processes.
There are a few things to remember when using a scatter plot. Even when a scatter diagram indicates a relationship, it doesn’t mean one variable affects the other. A third factor can influence both variables. The more the plot resembles a straight line, the stronger the relationship is perceived [11] . If it suggests no ties, the observed pattern might be due to random fluctuations in data. When the scatter diagram depicts no correlation, whether the data might be stratified is worth considering.
Choosing the appropriate data presentation type is crucial when making a presentation . Understanding the nature of your data and the message you intend to convey will guide this selection process. For instance, when showcasing quantitative relationships, scatter plots become instrumental in revealing correlations between variables. If the focus is on emphasizing parts of a whole, pie charts offer a concise display of proportions. Histograms, on the other hand, prove valuable for illustrating distributions and frequency patterns.
Bar charts provide a clear visual comparison of different categories. Likewise, line charts excel in showcasing trends over time, while tables are ideal for detailed data examination. Starting a presentation on data presentation types involves evaluating the specific information you want to communicate and selecting the format that aligns with your message. This ensures clarity and resonance with your audience from the beginning of your presentation.
1. Fact Sheet Dashboard for Data Presentation

Convey all the data you need to present in this one-pager format, an ideal solution tailored for users looking for presentation aids. Global maps, donut chats, column graphs, and text neatly arranged in a clean layout presented in light and dark themes.
Use This Template
2. 3D Column Chart Infographic PPT Template

Represent column charts in a highly visual 3D format with this PPT template. A creative way to present data, this template is entirely editable, and we can craft either a one-page infographic or a series of slides explaining what we intend to disclose point by point.
3. Data Circles Infographic PowerPoint Template

An alternative to the pie chart and donut chart diagrams, this template features a series of curved shapes with bubble callouts as ways of presenting data. Expand the information for each arch in the text placeholder areas.
4. Colorful Metrics Dashboard for Data Presentation

This versatile dashboard template helps us in the presentation of the data by offering several graphs and methods to convert numbers into graphics. Implement it for e-commerce projects, financial projections, project development, and more.
5. Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides

A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
6. Statistics Waffle Charts PPT Template for Data Presentations

This PPT template helps us how to present data beyond the typical pie chart representation. It is widely used for demographics, so it’s a great fit for marketing teams, data science professionals, HR personnel, and more.
7. Data Presentation Dashboard Template for Google Slides

A compendium of tools in dashboard format featuring line graphs, bar charts, column charts, and neatly arranged placeholder text areas.
8. Weather Dashboard for Data Presentation

Share weather data for agricultural presentation topics, environmental studies, or any kind of presentation that requires a highly visual layout for weather forecasting on a single day. Two color themes are available.
9. Social Media Marketing Dashboard Data Presentation Template

Intended for marketing professionals, this dashboard template for data presentation is a tool for presenting data analytics from social media channels. Two slide layouts featuring line graphs and column charts.
10. Project Management Summary Dashboard Template

A tool crafted for project managers to deliver highly visual reports on a project’s completion, the profits it delivered for the company, and expenses/time required to execute it. 4 different color layouts are available.
11. Profit & Loss Dashboard for PowerPoint and Google Slides

A must-have for finance professionals. This typical profit & loss dashboard includes progress bars, donut charts, column charts, line graphs, and everything that’s required to deliver a comprehensive report about a company’s financial situation.
Overwhelming visuals
One of the mistakes related to using data-presenting methods is including too much data or using overly complex visualizations. They can confuse the audience and dilute the key message.
Inappropriate chart types
Choosing the wrong type of chart for the data at hand can lead to misinterpretation. For example, using a pie chart for data that doesn’t represent parts of a whole is not right.
Lack of context
Failing to provide context or sufficient labeling can make it challenging for the audience to understand the significance of the presented data.
Inconsistency in design
Using inconsistent design elements and color schemes across different visualizations can create confusion and visual disarray.
Failure to provide details
Simply presenting raw data without offering clear insights or takeaways can leave the audience without a meaningful conclusion.
Lack of focus
Not having a clear focus on the key message or main takeaway can result in a presentation that lacks a central theme.
Visual accessibility issues
Overlooking the visual accessibility of charts and graphs can exclude certain audience members who may have difficulty interpreting visual information.
In order to avoid these mistakes in data presentation, presenters can benefit from using presentation templates . These templates provide a structured framework. They ensure consistency, clarity, and an aesthetically pleasing design, enhancing data communication’s overall impact.
Understanding and choosing data presentation types are pivotal in effective communication. Each method serves a unique purpose, so selecting the appropriate one depends on the nature of the data and the message to be conveyed. The diverse array of presentation types offers versatility in visually representing information, from bar charts showing values to pie charts illustrating proportions.
Using the proper method enhances clarity, engages the audience, and ensures that data sets are not just presented but comprehensively understood. By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding.
If you need a quick method to create a data presentation, check out our AI presentation maker . A tool in which you add the topic, curate the outline, select a design, and let AI do the work for you.
[1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart , 5.2 Bar chart . https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/bargraph-diagrammeabarres/5214818-eng.htm
[2] Kosslyn, S.M., 1989. Understanding charts and graphs. Applied cognitive psychology, 3(3), pp.185-225. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA183409.pdf
[3] Creating a Dashboard . https://it.tufts.edu/book/export/html/1870
[4] https://www.goldenwestcollege.edu/research/data-and-more/data-dashboards/index.html
[5] https://www.mit.edu/course/21/21.guide/grf-line.htm
[6] Jadeja, M. and Shah, K., 2015, January. Tree-Map: A Visualization Tool for Large Data. In GSB@ SIGIR (pp. 9-13). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1393/gsb15proceedings.pdf#page=15
[7] Heat Maps and Quilt Plots. https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/research/population-health-methods/heat-maps-and-quilt-plots
[8] EIU QGIS WORKSHOP. https://www.eiu.edu/qgisworkshop/heatmaps.php
[9] About Pie Charts. https://www.mit.edu/~mbarker/formula1/f1help/11-ch-c8.htm
[10] Histograms. https://sites.utexas.edu/sos/guided/descriptive/numericaldd/descriptiven2/histogram/ [11] https://asq.org/quality-resources/scatter-diagram
Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Business • October 8th, 2024
Data-Driven Decision Making: Presenting the Process Behind Informed Choices
Discover how to harness data for informed decision-making and create impactful presentations. A detailed guide + templates on DDDM presentation slides.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • June 3rd, 2024
How To Make a Graph on Google Slides
Creating quality graphics is an essential aspect of designing data presentations. Learn how to make a graph in Google Slides with this guide.

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!
Leave a Reply
Call Us Today! +91 99907 48956 | [email protected]

It is the simplest form of data Presentation often used in schools or universities to provide a clearer picture to students, who are better able to capture the concepts effectively through a pictorial Presentation of simple data.
2. Column chart

It is a simplified version of the pictorial Presentation which involves the management of a larger amount of data being shared during the presentations and providing suitable clarity to the insights of the data.
3. Pie Charts

Pie charts provide a very descriptive & a 2D depiction of the data pertaining to comparisons or resemblance of data in two separate fields.
4. Bar charts

A bar chart that shows the accumulation of data with cuboid bars with different dimensions & lengths which are directly proportionate to the values they represent. The bars can be placed either vertically or horizontally depending on the data being represented.
5. Histograms
It is a perfect Presentation of the spread of numerical data. The main differentiation that separates data graphs and histograms are the gaps in the data graphs.
6. Box plots

Box plot or Box-plot is a way of representing groups of numerical data through quartiles. Data Presentation is easier with this style of graph dealing with the extraction of data to the minutes of difference.

Map Data graphs help you with data Presentation over an area to display the areas of concern. Map graphs are useful to make an exact depiction of data over a vast case scenario.
All these visual presentations share a common goal of creating meaningful insights and a platform to understand and manage the data in relation to the growth and expansion of one’s in-depth understanding of data & details to plan or execute future decisions or actions.
Importance of Data Presentation
Data Presentation could be both can be a deal maker or deal breaker based on the delivery of the content in the context of visual depiction.
Data Presentation tools are powerful communication tools that can simplify the data by making it easily understandable & readable at the same time while attracting & keeping the interest of its readers and effectively showcase large amounts of complex data in a simplified manner.
If the user can create an insightful presentation of the data in hand with the same sets of facts and figures, then the results promise to be impressive.
There have been situations where the user has had a great amount of data and vision for expansion but the presentation drowned his/her vision.
To impress the higher management and top brass of a firm, effective presentation of data is needed.
Data Presentation helps the clients or the audience to not spend time grasping the concept and the future alternatives of the business and to convince them to invest in the company & turn it profitable both for the investors & the company.
Although data presentation has a lot to offer, the following are some of the major reason behind the essence of an effective presentation:-
- Many consumers or higher authorities are interested in the interpretation of data, not the raw data itself. Therefore, after the analysis of the data, users should represent the data with a visual aspect for better understanding and knowledge.
- The user should not overwhelm the audience with a number of slides of the presentation and inject an ample amount of texts as pictures that will speak for themselves.
- Data presentation often happens in a nutshell with each department showcasing their achievements towards company growth through a graph or a histogram.
- Providing a brief description would help the user to attain attention in a small amount of time while informing the audience about the context of the presentation
- The inclusion of pictures, charts, graphs and tables in the presentation help for better understanding the potential outcomes.
- An effective presentation would allow the organization to determine the difference with the fellow organization and acknowledge its flaws. Comparison of data would assist them in decision making.
Recommended Courses

Data Visualization
Using powerbi &tableau.

Tableau for Data Analysis

MySQL Certification Program

The PowerBI Masterclass
Need help call our support team 7:00 am to 10:00 pm (ist) at (+91 999-074-8956 | 9650-308-956), keep in touch, email: [email protected].
WhatsApp us
Data presentation: A comprehensive guide
Learn how to create data presentation effectively and communicate your insights in a way that is clear, concise, and engaging.
Raja Bothra
Building presentations


Table of contents
Hey there, fellow data enthusiast!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on data presentation.
Whether you're an experienced presenter or just starting, this guide will help you present your data like a pro. We'll dive deep into what data presentation is, why it's crucial, and how to master it. So, let's embark on this data-driven journey together.
What is data presentation?
Data presentation is the art of transforming raw data into a visual format that's easy to understand and interpret. It's like turning numbers and statistics into a captivating story that your audience can quickly grasp. When done right, data presentation can be a game-changer, enabling you to convey complex information effectively.
Why are data presentations important?
Imagine drowning in a sea of numbers and figures. That's how your audience might feel without proper data presentation. Here's why it's essential:
- Clarity : Data presentations make complex information clear and concise.
- Engagement : Visuals, such as charts and graphs, grab your audience's attention.
- Comprehension : Visual data is easier to understand than long, numerical reports.
- Decision-making : Well-presented data aids informed decision-making.
- Impact : It leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Types of data presentation:
Now, let's delve into the diverse array of data presentation methods, each with its own unique strengths and applications. We have three primary types of data presentation, and within these categories, numerous specific visualization techniques can be employed to effectively convey your data.
1. Textual presentation
Textual presentation harnesses the power of words and sentences to elucidate and contextualize your data. This method is commonly used to provide a narrative framework for the data, offering explanations, insights, and the broader implications of your findings. It serves as a foundation for a deeper understanding of the data's significance.
2. Tabular presentation
Tabular presentation employs tables to arrange and structure your data systematically. These tables are invaluable for comparing various data groups or illustrating how data evolves over time. They present information in a neat and organized format, facilitating straightforward comparisons and reference points.
3. Graphical presentation
Graphical presentation harnesses the visual impact of charts and graphs to breathe life into your data. Charts and graphs are powerful tools for spotlighting trends, patterns, and relationships hidden within the data. Let's explore some common graphical presentation methods:
- Bar charts: They are ideal for comparing different categories of data. In this method, each category is represented by a distinct bar, and the height of the bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar charts provide a clear and intuitive way to discern differences between categories.
- Pie charts: It excel at illustrating the relative proportions of different data categories. Each category is depicted as a slice of the pie, with the size of each slice corresponding to the percentage of the total value it represents. Pie charts are particularly effective for showcasing the distribution of data.
- Line graphs: They are the go-to choice when showcasing how data evolves over time. Each point on the line represents a specific value at a particular time period. This method enables viewers to track trends and fluctuations effortlessly, making it perfect for visualizing data with temporal dimensions.
- Scatter plots: They are the tool of choice when exploring the relationship between two variables. In this method, each point on the plot represents a pair of values for the two variables in question. Scatter plots help identify correlations, outliers, and patterns within data pairs.
The selection of the most suitable data presentation method hinges on the specific dataset and the presentation's objectives. For instance, when comparing sales figures of different products, a bar chart shines in its simplicity and clarity. On the other hand, if your aim is to display how a product's sales have changed over time, a line graph provides the ideal visual narrative.
Additionally, it's crucial to factor in your audience's level of familiarity with data presentations. For a technical audience, more intricate visualization methods may be appropriate. However, when presenting to a general audience, opting for straightforward and easily understandable visuals is often the wisest choice.
In the world of data presentation, choosing the right method is akin to selecting the perfect brush for a masterpiece. Each tool has its place, and understanding when and how to use them is key to crafting compelling and insightful presentations. So, consider your data carefully, align your purpose, and paint a vivid picture that resonates with your audience.
What to include in data presentation?
When creating your data presentation, remember these key components:
- Data points : Clearly state the data points you're presenting.
- Comparison : Highlight comparisons and trends in your data.
- Graphical methods : Choose the right chart or graph for your data.
- Infographics : Use visuals like infographics to make information more digestible.
- Numerical values : Include numerical values to support your visuals.
- Qualitative information : Explain the significance of the data.
- Source citation : Always cite your data sources.
How to structure an effective data presentation?
Creating a well-structured data presentation is not just important; it's the backbone of a successful presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a compelling and organized presentation that captivates your audience:
1. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is paramount. Consider their needs, interests, and existing knowledge about your topic. Tailor your presentation to their level of understanding, ensuring that it resonates with them on a personal level. Relevance is the key.
2. Have a clear message
Every effective data presentation should convey a clear and concise message. Determine what you want your audience to learn or take away from your presentation, and make sure your message is the guiding light throughout your presentation. Ensure that all your data points align with and support this central message.
3. Tell a compelling story
Human beings are naturally wired to remember stories. Incorporate storytelling techniques into your presentation to make your data more relatable and memorable. Your data can be the backbone of a captivating narrative, whether it's about a trend, a problem, or a solution. Take your audience on a journey through your data.
4. Leverage visuals
Visuals are a powerful tool in data presentation. They make complex information accessible and engaging. Utilize charts, graphs, and images to illustrate your points and enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Visuals should not just be an accessory; they should be an integral part of your storytelling.
5. Be clear and concise
Avoid jargon or technical language that your audience may not comprehend. Use plain language and explain your data points clearly. Remember, clarity is king. Each piece of information should be easy for your audience to digest.
6. Practice your delivery
Practice makes perfect. Rehearse your presentation multiple times before the actual delivery. This will help you deliver it smoothly and confidently, reducing the chances of stumbling over your words or losing track of your message.
A basic structure for an effective data presentation
Armed with a comprehensive comprehension of how to construct a compelling data presentation, you can now utilize this fundamental template for guidance:
In the introduction, initiate your presentation by introducing both yourself and the topic at hand. Clearly articulate your main message or the fundamental concept you intend to communicate.
Moving on to the body of your presentation, organize your data in a coherent and easily understandable sequence. Employ visuals generously to elucidate your points and weave a narrative that enhances the overall story. Ensure that the arrangement of your data aligns with and reinforces your central message.
As you approach the conclusion, succinctly recapitulate your key points and emphasize your core message once more. Conclude by leaving your audience with a distinct and memorable takeaway, ensuring that your presentation has a lasting impact.
Additional tips for enhancing your data presentation
To take your data presentation to the next level, consider these additional tips:
- Consistent design : Maintain a uniform design throughout your presentation. This not only enhances visual appeal but also aids in seamless comprehension.
- High-quality visuals : Ensure that your visuals are of high quality, easy to read, and directly relevant to your topic.
- Concise text : Avoid overwhelming your slides with excessive text. Focus on the most critical points, using visuals to support and elaborate.
- Anticipate questions : Think ahead about the questions your audience might pose. Be prepared with well-thought-out answers to foster productive discussions.
By following these guidelines, you can structure an effective data presentation that not only informs but also engages and inspires your audience. Remember, a well-structured presentation is the bridge that connects your data to your audience's understanding and appreciation.
Do’s and don'ts on a data presentation
- Use visuals : Incorporate charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
- Keep it simple : Avoid clutter and complexity.
- Highlight key points : Emphasize crucial data.
- Engage the audience : Encourage questions and discussions.
- Practice : Rehearse your presentation.
Don'ts:
- Overload with data : Less is often more; don't overwhelm your audience.
- Fit Unrelated data : Stay on topic; don't include irrelevant information.
- Neglect the audience : Ensure your presentation suits your audience's level of expertise.
- Read word-for-word : Avoid reading directly from slides.
- Lose focus : Stick to your presentation's purpose.
Summarizing key takeaways
- Definition : Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding.
- Importance : Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact.
- Types : Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
- Choosing methods : Select the right method based on data, audience, and purpose.
- Components : Include data points, comparisons, visuals, infographics, numerical values, and source citations.
- Structure : Know your audience, have a clear message, tell a compelling story, use visuals, be concise, and practice.
- Do's and don'ts : Do use visuals, keep it simple, highlight key points, engage the audience, and practice. Don't overload with data, include unrelated information, neglect the audience's expertise, read word-for-word, or lose focus.
FAQ's on a data presentation
1. what is data presentation, and why is it important in 2024.
Data presentation is the process of visually representing data sets to convey information effectively to an audience. In an era where the amount of data generated is vast, visually presenting data using methods such as diagrams, graphs, and charts has become crucial. By simplifying complex data sets, presentation of the data may helps your audience quickly grasp much information without drowning in a sea of chart's, analytics, facts and figures.
2. What are some common methods of data presentation?
There are various methods of data presentation, including graphs and charts, histograms, and cumulative frequency polygons. Each method has its strengths and is often used depending on the type of data you're using and the message you want to convey. For instance, if you want to show data over time, try using a line graph. If you're presenting geographical data, consider to use a heat map.
3. How can I ensure that my data presentation is clear and readable?
To ensure that your data presentation is clear and readable, pay attention to the design and labeling of your charts. Don't forget to label the axes appropriately, as they are critical for understanding the values they represent. Don't fit all the information in one slide or in a single paragraph. Presentation software like Prezent and PowerPoint can help you simplify your vertical axis, charts and tables, making them much easier to understand.
4. What are some common mistakes presenters make when presenting data?
One common mistake is trying to fit too much data into a single chart, which can distort the information and confuse the audience. Another mistake is not considering the needs of the audience. Remember that your audience won't have the same level of familiarity with the data as you do, so it's essential to present the data effectively and respond to questions during a Q&A session.
5. How can I use data visualization to present important data effectively on platforms like LinkedIn?
When presenting data on platforms like LinkedIn, consider using eye-catching visuals like bar graphs or charts. Use concise captions and e.g., examples to highlight the single most important information in your data report. Visuals, such as graphs and tables, can help you stand out in the sea of textual content, making your data presentation more engaging and shareable among your LinkedIn connections.
Create your data presentation with prezent
Prezent can be a valuable tool for creating data presentations. Here's how Prezent can help you in this regard:
- Time savings : Prezent saves up to 70% of presentation creation time, allowing you to focus on data analysis and insights.
- On-brand consistency : Ensure 100% brand alignment with Prezent's brand-approved designs for professional-looking data presentations.
- Effortless collaboration : Real-time sharing and collaboration features make it easy for teams to work together on data presentations.
- Data storytelling : Choose from 50+ storylines to effectively communicate data insights and engage your audience.
- Personalization : Create tailored data presentations that resonate with your audience's preferences, enhancing the impact of your data.
In summary, Prezent streamlines the process of creating data presentations by offering time-saving features, ensuring brand consistency, promoting collaboration, and providing tools for effective data storytelling. Whether you need to present data to clients, stakeholders, or within your organization, Prezent can significantly enhance your presentation-making process.
So, go ahead, present your data with confidence, and watch your audience be wowed by your expertise.
Thank you for joining us on this data-driven journey. Stay tuned for more insights, and remember, data presentation is your ticket to making numbers come alive! Sign up for our free trial or book a demo !
More zenpedia articles

How to create a compelling brand positioning presentation

How to write a persuasive speech: Outline and tips for success

How to make a presentation longer without losing your audience?
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Present Your Data Like a Pro
- Joel Schwartzberg

Demystify the numbers. Your audience will thank you.
While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn’t guarantee a good presentation. It’s all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by sharing too many details at once. The only data points you should share are those that significantly support your point — and ideally, one point per chart. To avoid the debacle of sheepishly translating hard-to-see numbers and labels, rehearse your presentation with colleagues sitting as far away as the actual audience would. While you’ve been working with the same chart for weeks or months, your audience will be exposed to it for mere seconds. Give them the best chance of comprehending your data by using simple, clear, and complete language to identify X and Y axes, pie pieces, bars, and other diagrammatic elements. Try to avoid abbreviations that aren’t obvious, and don’t assume labeled components on one slide will be remembered on subsequent slides. Every valuable chart or pie graph has an “Aha!” zone — a number or range of data that reveals something crucial to your point. Make sure you visually highlight the “Aha!” zone, reinforcing the moment by explaining it to your audience.
With so many ways to spin and distort information these days, a presentation needs to do more than simply share great ideas — it needs to support those ideas with credible data. That’s true whether you’re an executive pitching new business clients, a vendor selling her services, or a CEO making a case for change.
- JS Joel Schwartzberg oversees executive communications for a major national nonprofit, is a professional presentation coach, and is the author of Get to the Point! Sharpen Your Message and Make Your Words Matter and The Language of Leadership: How to Engage and Inspire Your Team . You can find him on LinkedIn and X. TheJoelTruth
Partner Center
Data Presentation
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2024
- pp 1589–1599
- Cite this reference work entry

- Filomena Maggino 2 &
- Marco Trapani 3
Many international institutions, like World Bank and UNESCO (Patel et al. 2003 ) and Eurostat ( 2000a , b ), have identified different attributes to be considered in evaluating quality of statistics, such as methodological soundness, integrity, serviceability, and accessibility.
At the same time, less attention is paid to presentation and communication of statistics, which represent important aspects of the statistical activities and should be considered an integral part of data production and dissemination.
The need to deal with this issue is significantly increasing especially in the perspective of the role the statistics have in ICT societies. Presentation and communication of quality of life data are not easy tasks to be carried on since they cannot be accomplished through improvising and approximating methods and instruments. They require a combined and joint knowledge and expertise of statistical methodology, cognitive science, and communication.
Description
Characteristics....
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Aristotele. (1996). Retorica (trad.it. a cura di Dorati M.). Milano: Oscar Mondadori.
Google Scholar
Ellero, M. P. (1997). Introduzione alla retorica . Milano: Sansoni Editore.
Eurostat. (2000a, April 4–5). Definition of quality in Statistics Eurostat Working Group on Assessment of Quality in Statistics , Eurostat/A4/Quality/00/General/Definition, Luxembourg.
Eurostat. (2000b). Standard Quality Report, Eurostat Working Group on Assessment of Quality in Statistics , Eurostat/A4/Quality/00/General/Standard Report, Luxembourg, April 4–5.
Giovannini, E. (2008, May 26–27). The role of communication in transforming statistics into knowledge, OECD . Paper to be presented at conference innovative approaches to turning statistics into knowledge, Stockholm.
Kosslyn, S. M. (2006). Graph design for the eye and mind . New York: Oxford University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Kosslyn, S. M. (2007). Clear and to the point . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Lakoff, G., & Johnson, M. (1980). Metaphors we live by . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Patel, S., Hiraga, M., Wang, L. (World Bank), Drew, D., & Lynd, D. (UNESCO). (2003). A framework for assessing the quality of education statistics . World Bank – Development Data Group and UNESCO – Institute for Statistics.
Perelman, C. (2005). Teoria e pratica dell’argomentazione (a cura di G. Fornari Luvarà) . Soveria Mannelli: Rubettino.
Statistics Canada. (2003). Statistics Canada quality guidelines (4th ed.). Statistics Canada, Ottawa, Catalogue No 12-539-XIE.
Vale, S. (2008, July 7–8). Accessibility and clarity: The most neglected dimensions of quality? Paper presented at Conference on Data Quality for International Organizations, Rome, Italy, nella Session 3: Dissemination platforms to make data more accessible and interpretable. UNECE.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Dipartimento di Statistica, Informatica, Applicazioni “G. Parenti” (DiSIA), Università degli Studi di Firenze, Florence, Italy
Filomena Maggino
University of Florence, Florence, Italy
Marco Trapani
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Filomena Maggino .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Dipartimento di Scienze Statistiche, Sapienza Università di Roma, Roma, Roma, Italy
Section Editor information
Department of Political Science, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy
Mara Tognetti
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Maggino, F., Trapani, M. (2023). Data Presentation. In: Maggino, F. (eds) Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17299-1_666
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17299-1_666
Published : 11 February 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-17298-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-17299-1
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
How To Present Research Data?
Tong seng fah, aznida firzah abdul aziz.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Dr. Tong Seng Fah, Department of Family Medicine, Medical Faculty, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Jalan Yaacob Latif, Cheras, 56000 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Tel: 603-91733333 Ext 2831, Fax: 603-91738153, Email: [email protected]
Corresponding author.
Collection date 2006.
INTRODUCTION
The result section of an original research paper provides answer to this question “What was found?” The amount of findings generated in a typical research project is often much more than what medical journal can accommodate in one article. So, the first thing the author needs to do is to make a selection of what is worth presenting. Having decided that, he/she will need to convey the message effectively using a mixture of text, tables and graphics. The level of details required depends a great deal on the target audience of the paper. Hence it is important to check the requirement of journal we intend to send the paper to (e.g. the Uniform Requirements for Manuscripts Submitted to Medical Journals 1 ). This article condenses some common general rules on the presentation of research data that we find useful.
SOME GENERAL RULES
Keep it simple. This golden rule seems obvious but authors who have immersed in their data sometime fail to realise that readers are lost in the mass of data they are a little too keen to present. Present too much information tends to cloud the most pertinent facts that we wish to convey.
First general, then specific. Start with response rate and description of research participants (these information give the readers an idea of the representativeness of the research data), then the key findings and relevant statistical analyses.
Data should answer the research questions identified earlier.
Leave the process of data collection to the methods section. Do not include any discussion. These errors are surprising quite common.
Always use past tense in describing results.
Text, tables or graphics? These complement each other in providing clear reporting of research findings. Do not repeat the same information in more than one format. Select the best method to convey the message.
Consider these two lines:
Mean baseline HbA 1c of 73 diabetic patients before intervention was 8.9% and mean HbA 1c after intervention was 7.8%.
Mean HbA 1c of 73 of diabetic patients decreased from 8.9% to 7.8% after an intervention.
In line 1, the author presents only the data (i.e. what exactly was found in a study) but the reader is forced to analyse and draw their own conclusion (“mean HbA 1c decreased”) thus making the result more difficult to read. In line 2, the preferred way of writing, the data was presented together with its interpretation.
Data, which often are numbers and figures, are better presented in tables and graphics, while the interpretation are better stated in text. By doing so, we do not need to repeat the values of HbA 1c in the text (which will be illustrated in tables or graphics), and we can interpret the data for the readers. However, if there are too few variables, the data can be easily described in a simple sentence including its interpretation. For example, the majority of diabetic patients enrolled in the study were male (80%) compare to female (20%).
Using qualitative words to attract the readers’ attention is not helpful. Such words like “remarkably” decreased, “extremely” different and “obviously” higher are redundant. The exact values in the data will show just how remarkable, how extreme and how obvious the findings are.
“It is clearly evident from Figure 1B that there was significant different (p=0.001) in HbA 1c level at 6, 12 and 18 months after diabetic self-management program between 96 patients in intervention group and 101 patients in control group, but no difference seen from 24 months onwards.” [Too wordy]
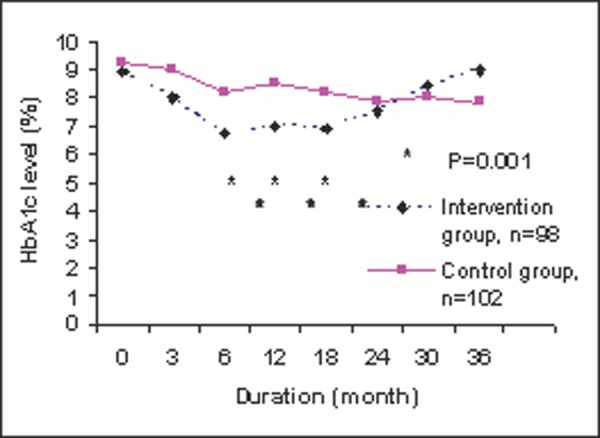
Changes of HbA 1c level after diabetic self-management program.
The above can be rewritten as:
“Statistical significant difference was only observed at 6, 12 and 18 months after diabetic self-management program between intervention and control group (Fig 1B)”. [The p values and numbers of patients are already presented in Figure 1B and need not be repeated.]
Avoid redundant words and information. Do not repeat the result within the text, tables and figures. Well-constructed tables and graphics should be self-explanatory, thus detailed explanation in the text is not required. Only important points and results need to be highlighted in the text.
Tables are useful to highlight precise numerical values; proportions or trends are better illustrated with charts or graphics. Tables summarise large amounts of related data clearly and allow comparison to be made among groups of variables. Generally, well-constructed tables should be self explanatory with four main parts: title, columns, rows and footnotes.
Title. Keep it brief and relate clearly the content of the table. Words in the title should represent and summarise variables used in the columns and rows rather than repeating the columns and rows’ titles. For example, “Comparing full blood count results among different races” is clearer and simpler than “Comparing haemoglobin, platelet count, and total white cell count among Malays, Chinese and Indians”.
Columns and rows. Columns are vertically listed data, and rows are horizontally listed data. Similar data ought to be presented in columns. Often these are dependant variables and allow clearer comparison among groups. Compare Table 1A and 1B , the dependant variables in Table 1B are waist circumference, HbA 1c , SBP and etc. Table 1B shows a better comparison of dependant variables among ethnicity than Table 1A . The first column to the left is usually a list of its independent variables i.e. Malay, Chinese, Indian and others, as the example of Table 1B . A table with too many dependent variables would become too wide for a page. There are two alternatives to this problem. We can list the dependant variables in the first left column and independent variables across the top. However, doing so should not compromise clarity of the message we want to get across. The second alternative is to cut down unnecessary columns, which, can be replaced by footnotes explaining their definition. For example, we can eliminate the columns on p, student-t test and chi-square values (see Table 2 ). Significant test result can be marked using * or # with a footnote. Presenting exact values of statistical data with no significant difference is rarely useful.
Table 1A: Baseline waist circumference, HbA 1c , Blood pressure and LDL-cholesterol level among Malay, Chinese, Indian and others races.
Table 1b: mean (sd) baseline diabetic metabolic control among different races..
*WC, waist circumference (in cm)
†SBP, systolic blood pressure (in mmHg)
‡DBP, diastolic blood pressure (in mmHg)
£LDL-cholesterol (in mmol/L)
Table 2: Comparison of the presenting symptoms among patients with and without thrombocytopaenia.
*Odds ratio (95% confidence interval)
Footnotes. These add clarity to the data presented. They are listed at the bottom of tables. Their use is to define unconventional abbreviation, symbols, statistical analysis and acknowledgement (if the table is adapted from a published table). Generally the font size is smaller in the footnotes and follows a sequence of foot note signs (*, †, ‡, §, ‖, ¶, **, ††, # ). 1 These symbols and abbreviation should be standardised in all tables to avoid confusion and unnecessary long list of footnotes. Proper use of footnotes will reduce the need for multiple columns (e.g. replacing a list of p values) and the width of columns (abbreviating waist circumference to WC as in table 1B )
Body of the table. We can improve the clarity of data presented in body of the tables by the following:
Consistent use of units and its decimal places. The data on systolic blood pressure in Table 1B is neater than the similar data in Table 1A .
Arrange date and timing from left to the right.
Round off the numbers to fewest decimal places possible to convey meaningful precision. Mean systolic blood pressure of 165.1mmHg (as in Table 1B ) does not add much precision compared to 165mmHg. Furthermore, 0.1mmHg does not add any clinical importance. Hence blood pressure is best to round off to nearest 1mmHg.
Avoid listing numerous zeros, which made comparison incomprehensible. For example total white cell count is best represented with 11.3 ×10 6 /L rather than 11,300,000/L. This way, we only need to write 11.3 in the cell of the table.
Avoid too many lines in a table. Often it is sufficient to just have three horizontal lines in a table; one below the title; one dividing the column titles and data; one dividing the data and footnotes. Vertical lines are not necessary. It will only make a table more difficult to read (compare Tables 1A and 1B ).
Standard deviation can be added to show precision of the data in our table. Placement of standard deviation can be difficult to decide. If we place the standard deviation at the side of our data, it allows clear comparison when we read down ( Table 1B ). On the other hand, if we place the standard deviation below our data, it makes comparison across columns easier. Hence, we should decide what we want the readers to compare.
It is neater and space-saving if we highlight statistically significant finding with an asterisk (*) or other symbols instead of listing down all the p values ( Table 2 ). It is not necessary to add an extra column to report the detail of student-t test or chi-square values.
Graphics are particularly good for demonstrating a trend in the data that would not be apparent in tables. It provides visual emphasis and avoids lengthy text description. However, presenting numerical data in the form of graphs will lose details of its precise values which tables are able to provide. The authors have to decide the best format of getting the intended message across. Is it for data precision or emphasis on a particular trend and pattern? Likewise, if the data is easily described in text, than text will be the preferred method, as it is more costly to print graphics than text. For example, having a nicely drawn age histogram is take up lots of space but carries little extra information. It is better to summarise it as mean ±SD or median depends on whether the age is normally distributed or skewed. Since graphics should be self-explanatory, all information provided has to be clear. Briefly, a well-constructed graphic should have a title, figure legend and footnotes along with the figure. As with the tables, titles should contain words that describe the data succinctly. Define symbols and lines used in legends clearly.
Some general guides to graphic presentation are:
Bar charts, either horizontal or column bars, are used to display categorical data. Strictly speaking, bar charts with continuous data should be drawn as histograms or line graphs. Usually, data presented in bar charts are better illustrated in tables unless there are important pattern or trends need to be emphasised.
Avoid 3-D graphs and charts. Three dimensional graphics are impressive in slide show and easily capture the attention of the audience. In medical writing, they are not effective because it is difficult to read the exact value on the Y axis (the height of the bars) accurately ( Figure 1A ).
Line graphs are most appropriate in tracking changing values between variables over a period of time or when the changing values are continuous data. Independent variables (e.g. time) are usually on the X-axis and dependant variables (for example, HbA 1c ) are usually on the Y-axis. The trend of HbA 1c changes is much more apparent with Figure 1B than Figure 1A , and HbA 1c level at any time after intervention can be accurately read in Figure 1B .
Pie charts should not be used often as any data in a pie chart is better represented in bar charts (if there are specific data trend to be emphasised) or simple text description (if there are only a few variables). A common error is presenting sex distribution of study subjects in a pie chart. It is simpler by just stating % of male or female in text form.
Patients’ identity in all illustrations, for example pictures of the patients, x-ray films, and investigation results should remain confidential. Use patient’s initials instead of their real names. Cover or blackout the eyes whenever possible. Obtain consent if pictures are used. Highlight and label areas in the illustration, which need emphasis. Do not let the readers search for details in the illustration, which may result in misinterpretation. Remember, we write to avoid misunderstanding whilst maintaining clarity of data.
Papers are often rejected because wrong statistical tests are used or interpreted incorrectly. A simple approach is to consult the statistician early. Bearing in mind that most readers are not statisticians, the reporting of any statistical tests should aim to be understandable by the average audience but sufficiently rigorous to withstand the critique of experts.
Simple statistic such as mean and standard deviation, median, normality testing is better reported in text. For example, age of group A subjects was normally distributed with mean of 45.4 years old kg (SD=5.6). More complicated statistical tests involving many variables are better illustrated in tables or graphs with their interpretation by text. (See section on Tables).
We should quote and interpret p value correctly. It is preferable to quote the exact p value, since it is now easily obtained from standard statistical software. This is more so if the p value is statistically not significant, rather just quoting p>0.05 or p=ns. It is not necessary to report the exact p value that is smaller than 0.001 (quoting p<0.001 is sufficient); it is incorrect to report p=0.0000 (as some software apt to report for very small p value).
We should refrain from reporting such statement: “mean systolic blood pressure for group A (135mmHg, SD=12.5) was higher than group B (130mmHg, SD= 9.8) but did not reach statistical significance (t=4.5, p=0.56).” When p did not show statistical significance (it might be >0.01 or >0.05, depending on which level you would take), it simply means no difference among groups.
Confidence intervals. It is now preferable to report the 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) together with p value, especially if a hypothesis testing has been performed.
The main core of the result section consists of text, tables and graphics. As a general rule, text provides narration and interpretation of the data presented. Simple data with few categories is better presented in text form. Tables are useful in summarising large amounts of data systemically and graphics should be used to highlight evidence and trends in the data presented. The content of the data presented must match the research questions and objectives of the study in order to give meaning to the data presented. Keep the data and its statistical analyses as simple as possible to give the readers maximal clarity.
Contributor Information
Tong Seng Fah, MMed (FamMed UKM), Department of Family Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia.
Aznida Firzah Abdul Aziz, MMed (FamMed UKM), Department of Family Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia.
- 1. International Committee for Medical Journal Editors. Uniform requirements for manuscripts submitted to biomedical journals: Writing and Editing for Biomedical Publication.
FURTHER READINGS
- 1. Hall GM, editor. 3rd Edition. London: BMJ Publishing Group; 2003. How to write a paper. [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Grange RI. Saving time, effort and tears: a guide to presenting results. Br J Urol. 1998;81((2)):335–9. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.1998.00612.x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Huth EJ. 3rd Edition. Maryland: Williams & Wilkins; 1999. Writing and publishing in Medicine. [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Lang Lang, Secic M. Philadelphia: American College of Physicians; 1997. How to report statistics in medicine: Annotated guidelines for authors, editors and reviewers. [ Google Scholar ]
- PDF (200.4 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
Data Presentation
Josée Dupuis, PhD, Professor of Biostatistics, Boston University School of Public Health
Wayne LaMorte, MD, PhD, MPH, Professor of Epidemiology, Boston University School of Public Health
Introduction
While graphical summaries of data can certainly be powerful ways of communicating results clearly and unambiguously in a way that facilitates our ability to think about the information, poorly designed graphical displays can be ambiguous, confusing, and downright misleading. The keys to excellence in graphical design and communication are much like the keys to good writing. Adhere to fundamental principles of style and communicate as logically, accurately, and clearly as possible. Excellence in writing is generally achieved by avoiding unnecessary words and paragraphs; it is efficient. In a similar fashion, excellence in graphical presentation is generally achieved by efficient designs that avoid unnecessary ink.
Excellence in graphical presentation depends on:
- Choosing the best medium for presenting the information
- Designing the components of the graph in a way that communicates the information as clearly and accurately as possible.
Table or Graph?
- Tables are generally best if you want to be able to look up specific information or if the values must be reported precisely.
- Graphics are best for illustrating trends and making comparisons
The side by side illustrations below show the same information, first in table form and then in graphical form. While the information in the table is precise, the real goal is to compare a series of clinical outcomes in subjects taking either a drug or a placebo. The graphical presentation on the right makes it possible to quickly see that for each of the outcomes evaluated, the drug produced relief in a great proportion of subjects. Moreover, the viewer gets a clear sense of the magnitude of improvement, and the error bars provided a sense of the uncertainty in the data.
Principles for Table Display
- Sort table rows in a meaningful way
- Avoid alphabetical listing!
- Use rates, proportions or ratios in addition (or instead of) totals
- Show more than two time points if available
- Multiple time points may be better presented in a Figure
- Similar data should go down columns
- Highlight important comparisons
- Show the source of the data
Consider the data in the table below from http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/commoncancers
Our ability to quickly understand the relative frequency of these cancers is hampered by presenting them in alphabetical order. It is much easier for the reader to grasp the relative frequency by listing them from most frequent to least frequent as in the next table.
However, the same information might be presented more effectively with a dot plot, as shown below.

Data from http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/commoncancers
Principles of Graphical Excellence from E.R. Tufte
Pattern perception.
Pattern perception is done by
- Detection: recognition of geometry encoding physical values
- Assembly: grouping of detected symbol elements; discerning overall patterns in data
- Estimation: assessment of relative magnitudes of two physical values
Geographic Variation in Cancer
As an example, Tufte offers a series of maps that summarize the age-adjusted mortality rates for various types of cancer in the 3,056 counties in the United States. The maps showing the geographic variation in stomach cancer are shown below.
These maps summarize an enormous amount of information and present it efficiently, coherently, and effectively.in a way that invites the viewer to make comparisons and to think about the substance of the findings. Consider, for example, that the region to the west of the Great Lakes was settled largely by immigrants from Germany and Scand anavia, where traditional methods of preserving food included pickling and curing of fish by smoking. Could these methods be associated with an increased risk of stomach cancer?
John Snow's Spot Map of Cholera Cases
Consider also the spot map that John Snow presented after the cholera outbreak in the Broad Street section of London in September 1854. Snow ascertained the place of residence or work of the victims and represented them on a map of the area using a small black disk to represent each victim and stacking them when more than one occurred at a particular location. Snow reasoned that cholera was probably caused by something that was ingested, because of the intense diarrhea and vomiting of the victims, and he noted that the vast majority of cholera deaths occurred in people who lived or worked in the immediate vicinity of the broad street pump (shown with a red dot that we added for clarity). He further ascertained that most of the victims drank water from the Broad Street pump, and it was this evidence that persuaded the authorities to remove the handle from the pump in order to prevent more deaths.

Humans can readily perceive differences like this when presented effectively as in the two previous examples. However, humans are not good at estimating differences without directly seeing them (especially for steep curves), and we are particularly bad at perceiving relative angles (the principal perception task used in a pie chart).
The use of pie charts is generally discouraged. Consider the pie chart on the left below. It is difficult to accurately assess the relative size of the components in the pie chart, because the human eye has difficulty judging angles. The dot plot on the right shows the same data, but it is much easier to quickly assess the relative size of the components and how they changed from Fiscal Year 2000 to Fiscal Year 2007.
Consider the information in the two pie charts below (showing the same information).The 3-dimensional pie chart on the left distorts the relative proportions. In contrast the 2-dimensional pie chart on the right makes it much easier to compare the relative size of the varies components..
More Principles of Graphical Excellence
Exclude unneeded dimensions.
These 3-dimensional techniques distort the data and actually interfere with our ability to make accurate comparisons. The distortion caused by 3-dimensional elements can be particularly severe when the graphic is slanted at an angle or when the viewer tends to compare ends up unwittingly comparing the areas of the ink rather than the heights of the bars.
It is much easier to make comparisons with a chart like the one below.

Source: Huang, C, Guo C, Nichols C, Chen S, Martorell R. Elevated levels of protein in urine in adulthood after exposure to
the Chinese famine of 1959–61 during gestation and the early postnatal period. Int. J. Epidemiol. (2014) 43 (6): 1806-1814 .
Omit "Chart Junk"
Consider these two examples.
Here is a simple enumeration of the number of pets in a neighborhood. There is absolutely no reason to connect these counts with lines. This is, in fact, confusing and inappropriate and nothing more than "chart junk."

Source: http://www.go-education.com/free-graph-maker.html
Moiré Vibration
Moiré effects are sometimes used in modern art to produce the appearance of vibration and movement. However, when these effects are applied to statistical presentations, they are distracting and add clutter because the visual noise interferes with the interpretation of the data.
Tufte presents the example shown below from Instituto de Expansao Commercial, Brasil, Graphicos Estatisticas (Rio de Janeiro, 1929, p. 15).
While the intention is to present quantitative information about the textile industry, the moiré effects do not add anything, and they are distracting, if not visually annoying.
Present Data to Facilitate Comparisons
Here is an attempt to compare catches of cod fish and crab across regions and to relate the variation to changes in water temperature. The problem here is that the Y-axes are vastly different, making it hard to sort out what's really going on. Even the Y-axes for temperature are vastly different.

http://seananderson.ca/courses/11-multipanel/multipanel.pdf1
The ability to make comparisons is greatly facilitated by using the same scales for axes, as illustrated below.

Data source: Dawber TR, Meadors GF, Moore FE Jr. Epidemiological approaches to heart disease:
the Framingham Study. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1951;41(3):279-81. PMID: 14819398
It is also important to avoid distorting the X-axis. Note in the example below that the space between 0.05 to 0.1 is the same as space between 0.1 and 0.2.

Source: Park JH, Gail MH, Weinberg CR, et al. Distribution of allele frequencies and effect sizes and
their interrelationships for common genetic susceptibility variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:18026-31.
Consider the range of the Y-axis. In the examples below there is no relevant information below $40,000, so it is not necessary to begin the Y-axis at 0. The graph on the right makes more sense.
Also, consider using a log scale. this can be particularly useful when presenting ratios as in the example below.

Source: Broman KW, Murray JC, Sheffield VC, White RL, Weber JL (1998) Comprehensive human genetic maps:
Individual and sex-specific variation in recombination. American Journal of Human Genetics 63:861-869, Figure 1
We noted earlier that pie charts make it difficult to see differences within a single pie chart, but this is particularly difficult when data is presented with multiple pie charts, as in the example below.

Source: Bell ML, et al. (2007) Spatial and temporal variation in PM2.5 chemical composition in the United States
for health effects studies. Environmental Health Perspectives 115:989-995, Figure 3
When multiple comparisons are being made, it is essential to use colors and symbols in a consistent way, as in this example.

Source: Manning AK, LaValley M, Liu CT, et al. Meta-Analysis of Gene-Environment Interaction:
Joint Estimation of SNP and SNP x Environment Regression Coefficients. Genet Epidemiol 2011, 35(1):11-8.
Avoid putting too many lines on the same chart. In the example below, the only thing that is readily apparent is that 1980 was a very hot summer.

Data from National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office at
http://www.srh.noaa.gov/tsa/?n=climo_tulyeartemp
Make Efficient Use of Space
Reduce the ratio of ink to information.
This isn't efficient, because this graphic is totally uninformative.

Source: Mykland P, Tierney L, Yu B (1995) Regeneration in Markov chain samplers. Journal of the American Statistical Association 90:233-241, Figure 1
Bar graphs add ink without conveying any additional information, and they are distracting. The graph below on the left inappropriately uses bars which clutter the graph without adding anything. The graph on the right displays the same data, by does so more clearly and with less clutter.
Multiple Types of Information on the Same Figure
Choosing the best graph type, bar charts, error bars and dot plots.
As noted previously, bar charts can be problematic. Here is another one presenting means and error bars, but the error bars are misleading because they only extend in one direction. A better alternative would have been to to use full error bars with a scatter plot, as illustrated previously (right).
Consider the four graphs below presenting the incidence of cancer by type. The upper left graph unnecessary uses bars, which take up a lot of ink. This layout also ends up making the fonts for the types of cancer too small. Small font is also a problem for the dot plot at the upper right, and this one also has unnecessary grid lines across the entire width.
The graph at the lower left has more readable labels and uses a simple dot plot, but the rank order is difficult to figure out.
The graph at the lower right is clearly the best, since the labels are readable, the magnitude of incidence is shown clearly by the dot plots, and the cancers are sorted by frequency.
Single Continuous Numeric Variable
In this situation a cumulative distribution function conveys the most information and requires no grouping of the variable. A box plot will show selected quantiles effectively, and box plots are especially useful when stratifying by multiple categories of another variable.
Histograms are also possible. Consider the examples below.
Two Variables
The two graphs below summarize BMI (Body Mass Index) measurements in four categories, i.e., younger and older men and women. The graph on the left shows the means and 95% confidence interval for the mean in each of the four groups. This is easy to interpret, but the viewer cannot see that the data is actually quite skewed. The graph on the right shows the same information presented as a box plot. With this presentation method one gets a better understanding of the skewed distribution and how the groups compare.
The next example is a scatter plot with a superimposed smoothed line of prediction. The shaded region embracing the blue line is a representation of the 95% confidence limits for the estimated prediction. This was created using "ggplot" in the R programming language.

Source: Frank E. Harrell Jr. on graphics: http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/twiki/pub/Main/StatGraphCourse/graphscourse.pdf (page 121)
Multivariate Data
The example below shows the use of multiple panels.

Source: Cleveland S. The Elements of Graphing Data. Hobart Press, Summit, NJ, 1994.
Displaying Uncertainty
- Error bars showing confidence limits
- Confidence bands drawn using two lines
- Shaded confidence bands
- Bayesian credible intervals
- Bayesian posterior densities
Confidence Limits
Shaded Confidence Bands

Source: Frank E. Harrell Jr. on graphics: http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/twiki/pub/Main/StatGraphCourse/graphscourse.pdf

Source: Tweedie RL and Mengersen KL. (1992) Br. J. Cancer 66: 700-705
Forest Plot
This is a Forest plot summarizing 26 studies of cigarette smoke exposure on risk of lung cancer. The sizes of the black boxes indicating the estimated odds ratio are proportional to the sample size in each study.

Data from Tweedie RL and Mengersen KL. (1992) Br. J. Cancer 66: 700-705
Summary Recommendations
- In general, avoid bar plots
- Avoid chart junk and the use of too much ink relative to the information you are displaying. Keep it simple and clear.
- Avoid pie charts, because humans have difficulty perceiving relative angles.
- Pay attention to scale, and make scales consistent.
- Explore several ways to display the data!
12 Tips on How to Display Data Badly
Adapted from Wainer H. How to Display Data Badly. The American Statistician 1984; 38: 137-147.
- Show as few data as possible
- Hide what data you do show; minimize the data-ink ratio
- Ignore the visual metaphor altogether
- Only order matters
- Graph data out of context
- Change scales in mid-axis
- Emphasize the trivial; ignore the important
- Jiggle the baseline
- Alphabetize everything.
- Make your labels illegible, incomplete, incorrect, and ambiguous.
- More is murkier: use a lot of decimal places and make your graphs three dimensional whenever possible.
- If it has been done well in the past, think of another way to do it
Additional Resources
- Stephen Few: Designing Effective Tables and Graphs. http://www.perceptualedge.com/images/Effective_Chart_Design.pdf
- Gary Klaas: Presenting Data: Tabular and graphic display of social indicators. Illinois State University, 2002. http://lilt.ilstu.edu/gmklass/pos138/datadisplay/sections/goodcharts.htm (Note: The web site will be discontinued to be replaced by the Just Plain Data Analysis site).

COMMENTS
What is a Data Presentation? A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable.
Data Presentation - Types & Its Importance in Data Analytics. What is Data Presentation? Data Analysis and Data Presentation have a practical implementation in every possible field. It can range from academic studies, commercial, industrial and marketing activities to professional practices.
Data presentation is a process of comparing two or more data sets with visual aids, such as graphs. Using a graph, you can represent how the information relates to other data. This process follows data analysis and helps organise information by visualising and putting it into a more readable format.
Definition: Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding. Importance: Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact. Types: Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
Give them the best chance of comprehending your data by using simple, clear, and complete language to identify X and Y axes, pie pieces, bars, and other diagrammatic elements.
The data presentation process involves three fundamental aspects (or pillars), related to (i) content, (ii) appeal, and (iii) persuasion. They reflect the own base of classic rhetoric, according to the principles of teaching (“docere”), entertaining (“delectare”), and moving (“movere”).
Overall, data presentation is the story of our work and our contribution to the ever-growing pool of knowledge in scientific and surgical research. Previous chapter in book. Next chapter in book. Keywords. Data presentation. Data visualization. Effective communication. Figures. Preattentive attributes. Qualitative data. Quantitative data. Tables.
Start with response rate and description of research participants (these information give the readers an idea of the representativeness of the research data), then the key findings and relevant statistical analyses.
Encourage the eye to compare different pieces of data; Reveal the data at several levels of detail, from a broad overview to the fine structure; Serve a clear purpose: description, exploration, tabulation, or decoration; Be closely integrated with the statistical and verbal descriptions of the data set; From E. R. Tufte.
1. Understand Your Data & Make It Seen. Data slides aren’t really about data; they’re about the meaning of that data. As data professionals, everyone approaches data differently.