GI031 - Gerund or Infinitive
Complete the sentence using the GERUND or INFINITIVE (with or without TO)
- My sister reminded me late for the ceremony (NOT BE) .
- Why does he always avoid at me (LOOK) ?
- I promised by tomorrow. (STOP)
- You can go. I don't mind alone. (BE)
- I'm already so tired. I need a short break. (TAKE)
- After we finished our homework we went for a walk. (DO)
- When does he expect for Rome? (LEAVE)
- His secretary advised us until autumn. (NOT WAIT)
- My boss expects me the report by next Friday. (FINISH)
- My dad seems in a very good mood today. (BE)
- Mr Jackson warned the boys the wires. (NOT TOUCH)
- He advised me against that apartment. (RENT)
- Would you please stop so much noise. (MAKE)
- He doesn't let anyone in his new office. (SMOKE)

The Roadrunner's Guide to English: Identifying Dependent and Independent Clauses
- Planning to Read or Write
- Editing and Revising
- Proofreading
- Unstated Main Idea
- Thesis/Topic/Main Idea
- Examples/Supporting Ideas
- Modes of Organization
- Sentence Formation (Type 1 Errors)
- Mechanics (Type 2 Errors)
- Proper Word Usage (Type 3 Errors)
- Vocabulary, Context Clues, and Acquiring a Word
- Practice Games
- Style, Tone, and Inference
- Writing in Class
- English Language Learners
- Comma Splice
- Fact & Opinion
- Fused Sentence
- Identifying Dependent and Independent Clauses
- Interactive Semicolon
- Logical Fallacy
- Parts of Speech
- Pronoun/Antecedent Agreement
- Subject Identification
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Supporting Details
Attribution
The practice exercises on this page were developed by Dr. Mary Nielsen, Dean of the Dalton State College School of Liberal Arts.

Identifying Dependent and Independent Clauses - Practice 1
An independent clause, also known as a simple sentence, includes a subject and verb and expresses a complete thought.
Example: Juliet, a border collie puppy, prefers to chase apples and pears. Subject Verb
A dependent clause has a subject and verb, is introduced by a subordinate conjunction or a relative pronoun, but does not express a complete thought. A dependent clause is not a complete sentence.
Example: Because the heavy rains flooded the entrance to the subdivision. Sub. Conj. Subject Verb
Example: After Laura carefully read the assigned chapter. Sub. Conj. Subject Verb
Determine whether the underlined word groups are dependent clauses, independent clauses, or not a clause.
1. Although it was raining , Maria went for a jog at Civitan Park.
2. Brianna eats chocolate whenever she gets a poor grade in math .
3. After the flood , the family moved into a temporary shelter.
4. While walking at the park, John saw a raccoon eating potato chips.
5. Students enrolled in bachelor's and associate's degree programs must pass the Regents' Test as a graduation requirement.
6. Students who fail to show up for the Regents' test must enroll in the Regents' remediation courses.
7. When you finish your homework , please take the dog for a walk.
8. After Juan completed the assignment, he swam laps at the gym.
9. Christa left home at 4:00 a.m. since she had to drive to Atlanta for a meeting.
10. Before completing the assignment , Evan decided to eat a quick lunch.
- Identifying Dependent and Independent Clauses - Practice 1 Answer Key
Identifying Dependent and Independent Clauses - Practice 2
1. Juan continued playing although he injured his knee . 2. I thought that the offer was too good to be true . 3. While I was scrubbing the floors , Juliet was watching television. 4. Although tired and grumpy, Laura agreed to babysit for her sister-in-law. 5. Inspired and energized, Sean solved the case of the missing energy drink . 6. While driving home from spring break , Maria saw a tornado touch down. 7. People who drink and drive should be arrested. 8. Ever since my daughter purchased a ferret , I have noticed that authors describe their bad guys as ferret-like. 9. Such descriptions are not fair to ferrets . 10. Since I could not go to the Pancake Breakfast , I gave away my tickets.
- Identifying Dependent and Independent Clauses - Practice 2 Answer Key
- << Previous: Fused Sentence
- Next: Interactive Semicolon >>
- Last Updated: Sep 5, 2023 11:00 AM
- URL: https://libguides.daltonstate.edu/ENGL0098
- Parts of speech
- Picture Vocabulary
- Confused Words
- Phrasal Verbs
- Applications
- Essay Writing
- Kindergarten Worksheets
Simple Past Tense (Past Indefinite Tense) is used when an action or event has already happened before a specific point in time and it has no connection to the present. This tense is used to express past and distinct events. Or “Simple Past Tense refers to the time when an action or event happened before a specific point in time”. In the Simple Past Tense, to identify an action, “ed” is used for regular verbs. For irregular verbs, there is a specific pattern that changes the verb into its past form. To learn to make proper and grammatically correct sentences in simple past tense, you need to understand how regular and irregular verbs are formed.
Formation of Regular Verbs
The formation of regular verbs in the Simple Past Tense involves adding “ -ed “ to the base form of the verb. This is the general rule for most regular verbs in English.
Formation of Irregular Verbs
Irregular verbs do not follow the standard “-ed” pattern for forming the past tense. Instead, they have unique forms for their past tense. Each of them has its own unique past tense form. As you can see, these verbs have irregular forms that need to be memorized.
Usages of the Simple Past Tense
To Describe Completed Actions
“To Describe Completed Actions” refers to using a specific tense in language, in this case, the Simple Past Tense (also known as the simple past tense), to talk about events or actions that have already happened and are now finished.
- I visited the museum yesterday.
- She finished her homework before dinner.
- She painted a beautiful landscape.
- They visited the historic castle.
- He did not finish reading the novel.
- We did not clean the entire house.
- I did not bake a delicious cake for the party.
- The team did not win the championship last year.
- Did he fix the broken window?
- Did she complete her assignment on time?
- Did they watch a thrilling movie?
- Did you attend the conference last month?
To Talk About Past Habits or Routines
“To Talk About Past Habits or Routines” refers to using the Simple Past Tense to describe actions or behaviors that were regularly performed in the past. These actions were habits or routines that happened repeatedly.
- Every morning, she took a long walk in the park. (Habit)
- They played tennis every Sunday afternoon. (Habit)
- He visited his grandparents every summer vacation. (Habit)
- She read a book before bedtime every night. (Habit)
- We did not have family dinners together every Friday. (Routines)
- He did not attend Spanish classes every weekday after work. (Routines)
- They did not watch their favorite TV show every evening. (Routines)
- Did I swim at the beach every summer? (Habit)
- Did she volunteer at the local shelter every weekend? (Routines)
- Did we practice the piano every afternoon? (Routines)
For Statements of Fact in the Past
“For Statements of Fact in the Past” refers to using the Simple Past Tense to state historical or factual information about events, discoveries, or general truths that occurred in the past.
- The Titanic sank in 1912.
- Shakespeare wrote many famous plays.
- Thomas Edison invented the light bulb.
- World War II did not end in 1945.
- The first manned moon landing did not occur in 1969.
- Albert Einstein did not formulate the theory of relativity.
- Was the Great Wall of China built over several centuries?
- Was the Declaration of Independence signed in 1776?
- Did Leonardo da Vinci paint the Mona Lisa?
- Was the first computer invented in the 1940s?
To Narrate a Story or Describe Past Events in Literature
“To Narrate a Story or Describe Past Events in Literature” refers to the use of the Simple Past Tense to recount events or tell a story in a narrative form. This tense is commonly used in literature to create a sense of immediacy and vividness in storytelling.
- Once upon a time, there lived a wise old wizard in a distant forest.
- The brave knight rescued the princess from the tower.
- Little Red Riding Hood met a cunning wolf in the woods.
- The spaceship did not land on an unknown planet full of strange creatures.
- Tom and Jerry did not chase each other around the house all day.
- The magical lamp did not grant three wishes to the kind-hearted boy.
- Cinderella did not lose her glass slipper at the royal ball.
- Did the friendly dragon help the villagers rebuild their homes?
- Was the mysterious treasure buried deep underground for centuries?
- Did the mischievous elves play pranks on the woodland creatures?
For Reported Speech when Reporting Past Statements
“For Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) when Reporting Past Statements” refers to the use of the Simple Past Tense to convey something that was said or stated by someone else in the past. It involves reporting or paraphrasing what was previously said.
- She said that she liked the movie.
- He told me that he had a great time at the party.
- They mentioned that they were going on vacation.
- The teacher did not explain that the test was postponed.
- Sarah did not inform us that she had finished her project.
- He did not mention that he would come to the meeting.
- Did my mom say that dinner was ready?
- Did they tell us that they had seen a shooting star?
- Did she inform me that the store was closed?
- Did he explain that the concert had been canceled?
To Express Future in the Past (2nd Conditional)
- She said that if it rained tomorrow, she would stay indoors.
- He hoped that if he had more time, he would travel around the world.
- They thought that if they won the lottery, they would buy a new house.
- The teacher did not tell us that if we studied harder, we would get better grades.
- She did not believe that if she practiced more, she would become a better pianist.
- He did not wish that if he had known, he would have helped.
- Did they wonder if they found a genie, they would ask for three wishes?
- Did she imagine that if she had a time machine, she would visit the past?
- Did he speculate that if he learned a new language, he would travel more?
- Did they think that if they had wings, they would fly ?
- If I had more time, would I have visited the museum?
- Do I wish I knew how to swim when we were at the beach?
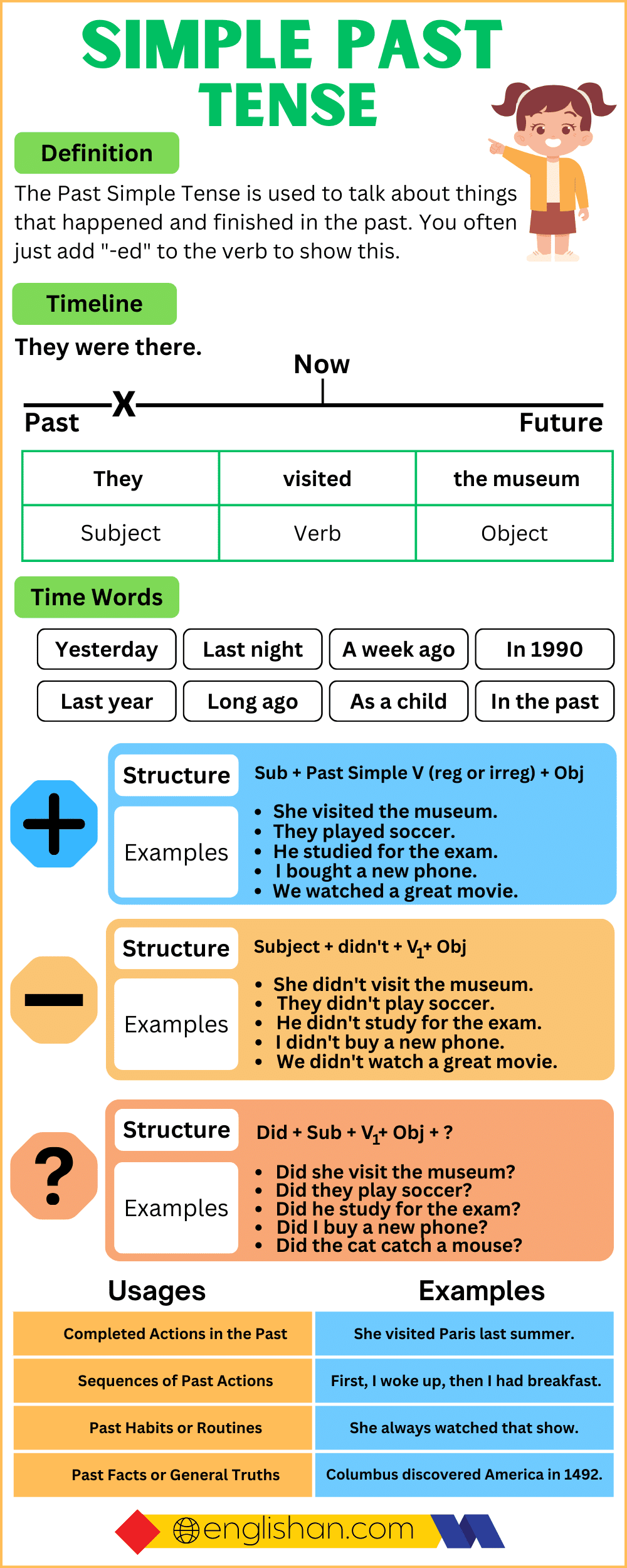
Forming the Simple Past Tense
Affirmative sentences.
To form the Simple Past Tense (past indefinite tense) in an affirmative sentence, you typically add “-ed” to regular verbs. For irregular verbs, you use the specific past tense form.
Subject + verb (2nd form) + object
- I walked to the park yesterday.
- She read a book last night.
- He played with his friends after school.
- We visited Grandma on Sunday.
- They watched a movie on Friday evening.
- The cat slept all day.
- My parents cooked dinner for us.
- She danced at the party.
- He helped his mom in the kitchen.
- We cleaned our rooms on Saturday.
- The sun shone brightly.
- I finished my homework early.
- She baked cookies for the school bake sale.
- He rode his bike in the park.
- They planted flowers in the garden.
- The teacher praised our hard work.
- I found my lost keys.
- She received a gift from her friend.
- He painted a beautiful picture.
- We played board games in the evening.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
Negative Sentences
Negative sentences in the simple past tense express actions or states that did not happen in the past.
Subject + did not + verb(1st form) + object.
- He did not take a bath.
- It did not rain yesterday.
- They did not help us.
- You did not keep your promise.
- He did not act upon my advice.
- I did not walk to school yesterday.
- She did not eat a sandwich for lunch.
- He did not play with his dog in the park.
- We did not visit the zoo last summer.
- They did not watch a cartoon on TV.
- She did not read the newspaper yesterday.
- They did not play soccer after school.
- I did not meet my friend at the cafe.
- He did not buy a new car last month.
- We did not watch the movie at the cinema.
- The cat did not catch the mouse in the kitchen.
- My parents did not prepare dinner for us.
- You did not complete the assignment on time.
- She did not dance at the party last night.
- He did not fix the broken window in the morning.
Interrogative Sentences
- Use “Did”: Begin the sentence with “Did.” This is the past tense auxiliary verb that helps in forming questions.
- Base Form of the Verb: Use the base form (1st form) of the verb without “to.” This forms the question.
Did + Subject + verb(1st form) + object + ?
- Did I go to the park yesterday?
- Did she eat cake for dessert?
- Did he watch TV in the morning?
- Did we visit the zoo last week?
- Did they play outside after school?
- Did the cat like the new toy?
- Did my mom bake cookies on Sunday?
- Did she draw a picture?
- Did he read a book before bed?
- Did we see a movie on Friday?
- Did you visit the park yesterday?
- Did she eat pizza for lunch?
- Did he watch a movie last night?
- Did they play soccer after school?
- Did the cat sleep on the couch?
- Did your mom cook dinner on Friday?
- Did he draw a picture for his friend?
- Did she read a story before bed?
- Did we go to the beach last summer?
- Did the dog chase its tail?
The Spelling Rules
- Simple Past Tense Example Sentences
Positive Sentences:
- We went to the zoo yesterday.
- I boarded the train.
- You bought a new pen.
- She boiled the eggs.
- They waited for us.
- The students told the lesson.
- The peon locked the door.
- They played hide and seek in the yard.
- I helped my little brother with his homework.
- She received a nice gift from her friend.
- He visited his grandparents last weekend.
- We watched a movie on Friday night.
- She read a story before bedtime.
- They cleaned their rooms yesterday.
- He played with his dog in the park.
- We had a family dinner together on Friday.
- She attended the art class after school.
- They practiced singing in the evening.
Negative Sentences:
- I did not visit the museum last weekend.
- They did not plant flowers in the garden.
- He did not attend the meeting.
- She did not cook dinner yesterday.
- We did not watch TV in the morning.
- They did not play football after school.
- The cat did not catch the mouse.
- My parents did not go for a walk.
- She did not read a book before bedtime.
- He did not clean his room on Saturday.
- They did not have ice cream for dessert.
- I did not forget your birthday.
- We did not go to the beach last summer.
- The dog did not bark all night.
- She did not receive a letter from her friend.
- He did not play the guitar at the party.
- They did not visit their grandparents last holiday.
- The bird did not sing in the morning.
- I did not invite my friends to the party.
- We did not swim in the river last weekend.
- She did not take a nap in the afternoon.
- He did not draw a picture for his sister.

Interrogative Sentences:
- Did Ali win a prize?
- Did he go there?
- Did he post the letter?
- Whom did you consult?
- How did the break into the house?
- Did the hare run fast?
- Did he keep his promise?
- Did your friend live here?
- Where did you go?
- Did he clean his room on Saturday?
- Did they have ice cream for dessert?
- Did you forget my birthday?
- Did the dog bark all night?
- Did she receive a letter from her friend?
- Did he play the guitar at the party?
- Did they visit their grandparents last holiday?
- Did the bird sing in the morning?
- Did you invite your friends to the party?
- Did we swim in the river last weekend?
- Did she take a nap in the afternoon?
- Did he draw a picture for his sister?
- a) She is reading a book.
- b) They played soccer yesterday.
- c) He will eat lunch later.
- a) They have visited the museum.
- b) She danced at the party.
- c) We will go to the park.
- a) I am writing a letter.
- b) He visited his grandparents last summer.
- c) She will bake a cake.
- a) They are playing in the garden.
- b) We studied for the exam.
- c) She will sing a song.
- a) He has a new car.
- b) They watched a movie last night.
- c) She is cooking dinner.
- a) We will visit the zoo tomorrow.
- b) He played with his dog in the park.
- c) She is reading a novel.
- a) They are going to the party tonight.
- b) I visited my friend yesterday.
- c) He will study for the test.
- a) She will bake cookies for the party.
- b) They played hide and seek in the yard.
- c) We are singing a song.
- a) I am going to the market.
- b) He visited the museum last weekend.
- c) They will have a picnic.
- c) sleeping
- a) She has a beautiful garden.
- b) We went for a walk in the park.
- c) He is playing chess.
- The Simple Past Tense, also known as the Simple Past Tense, is a grammatical tense used to describe actions or events that occurred in the past and are now completed.
- For regular verbs, the past tense is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb (e.g., walk -> walked, play -> played).
- a) She visited the museum yesterday.
- b) They played soccer in the park.
- c) He finished his homework before dinner.
- Irregular verbs have unique past tense forms that do not follow a regular pattern. For example, the past tense of “go” is “went” and the past tense of “eat” is “ate”.
- No, the Simple Past Tense is used to describe completed actions in the past, not actions that were ongoing or continuous.
- Yesterday, last week, two days ago, in 1995, when I was a child, etc.
- Yes, the negative form is formed by adding “did not” (or the contraction “didn’t”) before the base form of the verb.
- No, the Simple Past Tense is specifically for describing completed actions in the past. To talk about future events, a different tense like the Future Indefinite Tense should
You May Also Like
- Simple Present Tense With Examples
- Simple Past Tense Worksheets
- Past Tenses Rules, Sentences
- Participle Clauses in English
- Irregular Verbs in English with Examples
- Verbs Starting with D
- 500 Regular Verbs List PDF
- Participle Adjectives in English
- Worksheet Tenses
- Present Simple
- Present Simple Tense
- Simple Past Tense Definition
- Simple Past Tense Exercise
- simple past tense formula
- Simple Past Tense In English
- Simple Past Tense In Grammar
- Simple Past Tense Rules
- simple past tense structure
Recently Published

Words That Start with B

Words That Start with A for Vocabulary Building

Gender Nouns Worksheet with Answers
Verbal Nouns
Regular Verbs Worksheets with Answers
Related articles.
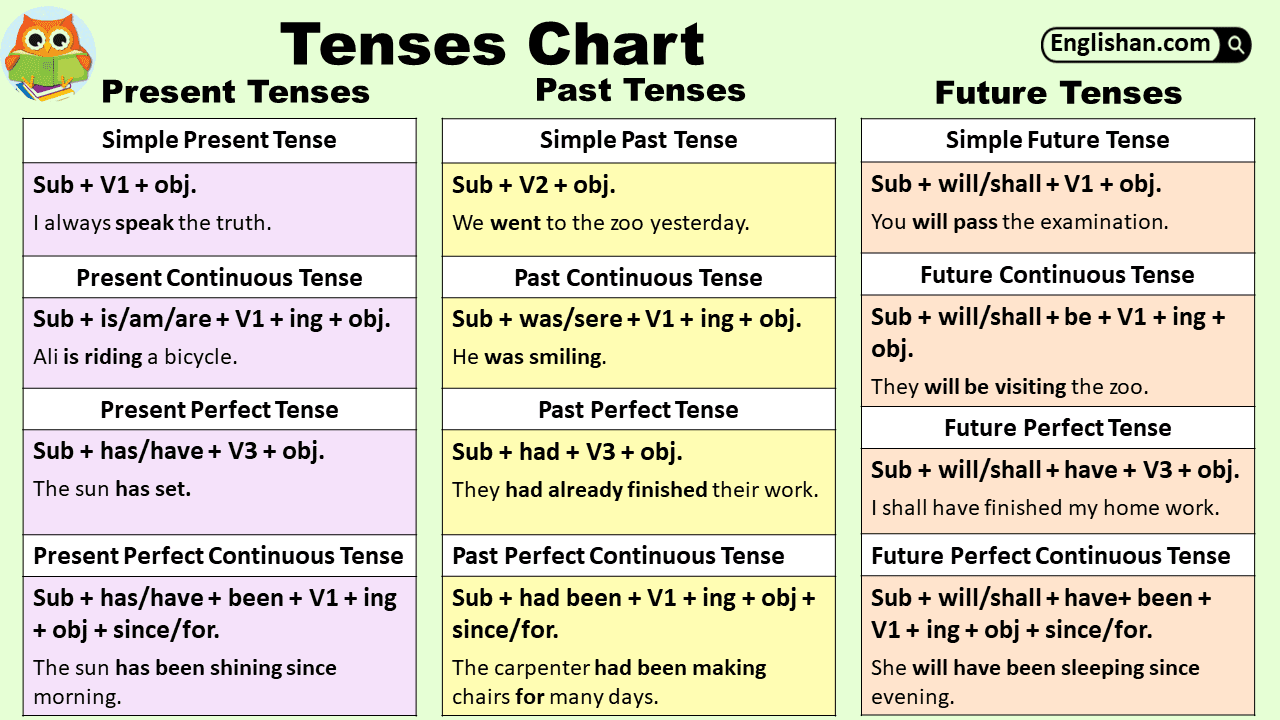
Tenses Chart With Examples, Rules, Usage
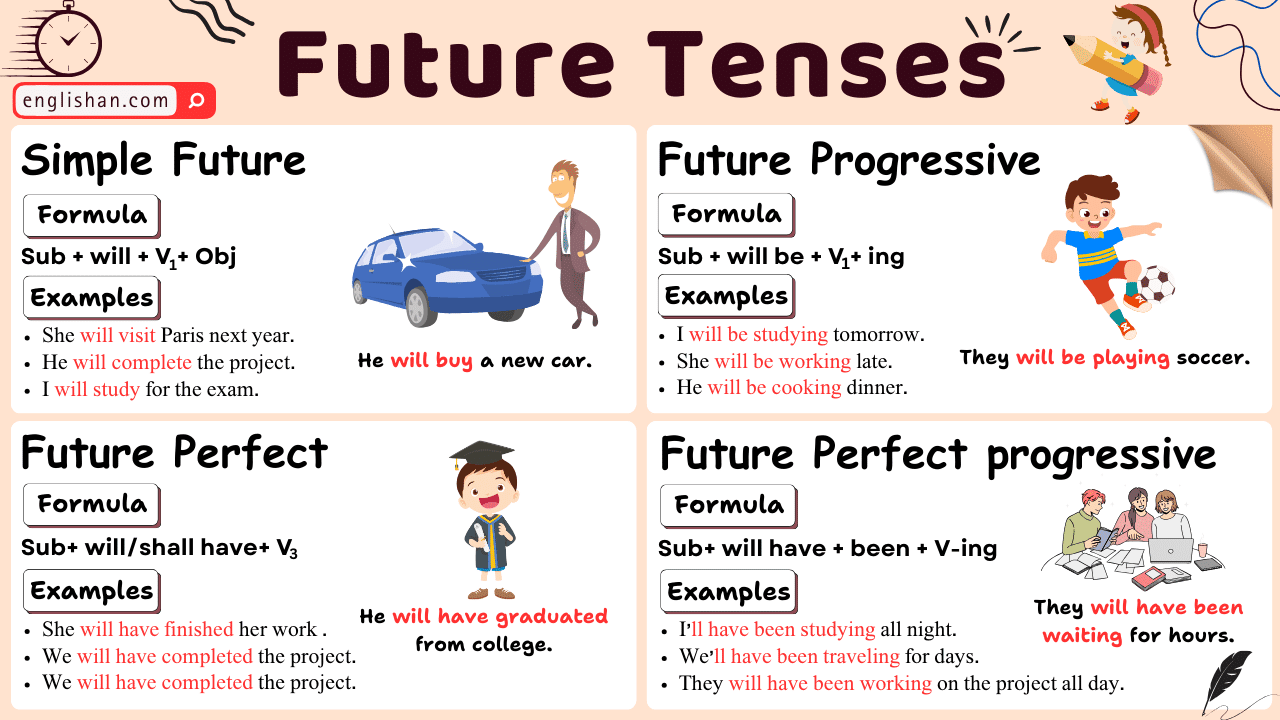
Future Tenses With Examples, Rules, Usage
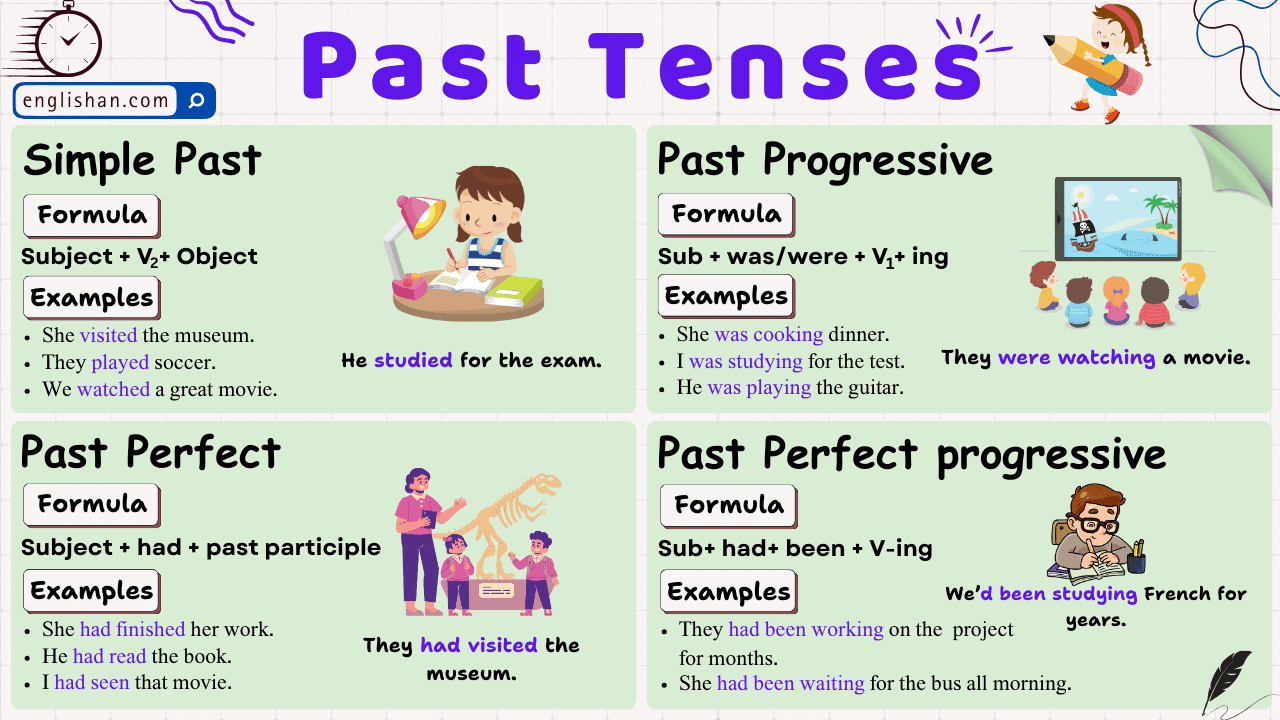
Past Tenses With Examples, Rules, Usage

IMAGES
VIDEO