

Geography Project On Earthquake For Class 9th
Table of Contents
Acknowledgment
Embarking on this seismic journey into the world of earthquakes has been a collaborative effort, and I extend my heartfelt gratitude to those whose contributions have made this project possible.
First and foremost, I express my appreciation to the educators who have imparted knowledge and provided guidance throughout the exploration of earthquake causes, effects, and mitigation strategies. Your expertise has been an invaluable compass, steering this project towards a deeper understanding of these natural phenomena.
I extend my thanks to the scientific community whose research forms the bedrock of this endeavor. The tireless pursuit of knowledge and dedication to unraveling the complexities of earthquakes have laid the groundwork for a more informed exploration.
To my peers and fellow students, thank you for engaging in discussions, sharing insights, and contributing to the collective learning experience. Your enthusiasm and collaboration have enriched the project, making it a collaborative endeavor that transcends individual efforts.
Furthermore, I am grateful for the support from friends and family who provided encouragement and understanding during the project’s development. Your unwavering support has been a source of inspiration.
Lastly, to the broader community, thank you for fostering an environment that encourages curiosity and exploration. This project is a testament to the collective pursuit of knowledge and the shared commitment to understanding the forces that shape our world.
Together, these acknowledgments reflect the collaborative spirit that fuels the pursuit of knowledge, and I am sincerely grateful for the diverse contributions that have shaped this exploration into the realm of earthquakes.
With gratitude,
Introduction
In the ever-evolving tapestry of our world, natural phenomena hold a mysterious allure, captivating both the curious minds of students and the seasoned wisdom of educators. This project serves as a gateway into the intriguing realm of earthquakes – a force that has fascinated scientists and posed profound challenges to societies across the ages. As we embark on this journey, we will delve into the seismic tapestry of our planet, unraveling the causes, effects, and mitigation strategies associated with earthquakes. This exploration seeks not only to deepen our understanding of these geological events but also to cultivate a sense of preparedness and resilience among 9th-grade students. Join us as we navigate the intricate pathways of tectonic plates, measure the intensity of ground-shaking, and explore the real-world implications of seismic activity. Through this project, we aim to foster a holistic appreciation for the dynamic forces that shape our world and equip students with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of potential seismic events in the future. Welcome to a journey where science meets the profound mysteries beneath our feet – welcome to the seismic exploration of earthquakes.
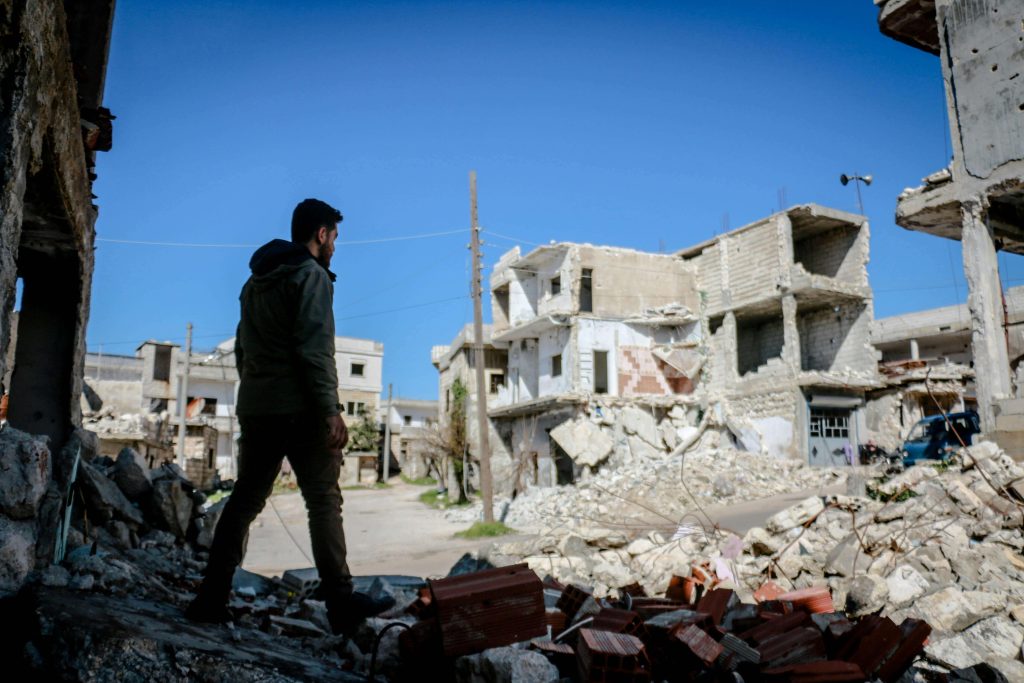

The Roots of Earthquakes
At the heart of earthquake genesis lies the intricate ballet of tectonic plates. These mammoth sections of the Earth’s crust engage in a complex dance at various boundaries, including subduction zones, transform boundaries, and divergent boundaries, giving rise to seismic activities. Furthermore, human activities such as mining, reservoir-induced seismicity linked to dams, and the controversial hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, can induce earthquakes, albeit on a more modest scale.
Quantifying and Observing Earthquakes
In the quest to measure earthquake intensity, scientists employ scales like the Richter Scale and the Moment Magnitude Scale. Seismographs, those silent sentinels, play a pivotal role in recording and dissecting ground movements. The advent of Earthquake Early Warning Systems has further fortified our ability to provide advance notice, offering communities a crucial buffer against the impending impact.
Navigating the Aftermath: Effects of Earthquakes
The repercussions of earthquakes are multifaceted, encompassing ground shaking, surface rupture, and secondary calamities such as tsunamis and landslides. A profound comprehension of these effects becomes imperative in devising and executing effective mitigation strategies and emergency response plans.
Echoes Through Time: Notable Earthquakes in History
History bears witness to seismic events that have left an indelible mark. From the annihilation of Pompeii in 62 AD to the cataclysmic San Francisco earthquake of 1906, the seismic upheaval of the Great Kanto quake in 1923, the formidable Alaska earthquake of 1964, and the catastrophic Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami in 2004, these events have profoundly shaped our understanding of the relentless force wielded by these natural disasters.
Mitigation and Preparedness
Shielding communities from the formidable impact of earthquakes involves a proactive approach, embracing advancements in building design and construction that prioritize seismic resilience. The very foundation of this endeavor rests on emergency preparedness plans, meticulously crafted at both individual and community levels, serving as a crucial line of defense against potential casualties and structural damages. Public education and awareness campaigns stand as pillars in fostering a resilient society, especially in regions prone to seismic activities.

Case Study: Earthquake in [Your Chosen Location]
Now, let’s delve into a practical illustration – a case study focusing on a specific earthquake in a carefully chosen location. This real-world example will serve as a lens through which students can apply the acquired knowledge, gaining insight into the tangible implications of seismic activity and the pivotal role played by effective mitigation measures.
As we draw the curtains on this seismic exploration, we reflect on the profound journey into the world of earthquakes that has unfolded. This project has been more than a mere academic pursuit; it has been a venture into the very essence of our planet’s dynamic nature. Through the exploration of causes, effects, and mitigation strategies associated with earthquakes, we have sought to illuminate the intricate mechanisms that shape our geologic landscape.
Our journey has taken us from the colossal movements of tectonic plates to the delicate dance of seismic waves recorded by vigilant seismographs. We’ve examined the devastating effects of earthquakes, from ground-shaking to the far-reaching consequences of tsunamis and landslides. The strategies to mitigate these impacts have unfolded before us, revealing the importance of resilient structures, meticulous emergency preparedness, and public awareness campaigns.
In crafting this project, our aim was not only to disseminate knowledge but to instill a sense of preparedness and resilience among 9th-grade students. Earthquakes, though formidable, need not be feared. Instead, armed with understanding and awareness, we can navigate their complexities and work towards building communities that stand strong in the face of seismic challenges.
The case study provided a tangible example of the real-world implications of seismic activity, illustrating the crucial role of effective mitigation measures. Through this, we hope students have gained insight into the transformative potential of the knowledge acquired throughout this exploration.
As we close this chapter, let the understanding cultivated here serve as a foundation for future inquiry and a source of empowerment. May the knowledge gained on this seismic journey resonate as a call to action, inspiring a generation equipped to grapple with the forces that shape our dynamic world.
In the spirit of exploration and understanding,
Bibliography
- United States Geological Survey (USGS). “Earthquake Hazards Program.”
- Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology (IRIS). “Teaching Seismology.”
- Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). “Earthquake Safety at Home.”
- Richter, Charles F. “Elementary Seismology.”
- National Geographic. “Earthquakes.”
- The Seismic Monitor. “Real-time Earthquake Map.”
Certificate of Completion
This is to certify that I, [Student’s Name], a [Class/Grade Level] student, have successfully completed the “Geography Project On Earthquake For Class 9th.” The project explores the fundamental principles and key aspects of the chosen topic, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance and implications.
In this project, I delved into in-depth research and analysis, investigating various facets and relevant theories related to the chosen topic. I demonstrated dedication, diligence, and a high level of sincerity throughout the project’s completion.
Key Achievements:
Thoroughly researched and analyzed Geography Project On Earthquake For Class 9th Examined the historical background and evolution of the subject matter. Explored the contributions of notable figures in the field. Investigated the key theories and principles associated with the topic. Discussed practical applications and real-world implications. Considered critical viewpoints and alternative theories, fostering a well-rounded understanding. This project has significantly enhanced my knowledge and critical thinking skills in the chosen field of study. It reflects my commitment to academic excellence and the pursuit of knowledge.
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Subscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Geography Project On Earthquake For Class 9th PDF
Related articles.

EVS Project On Electricity Consumption for Class 11th And 12th

Geography Project On Agriculture In India For Class 10 ICSE

English Project on The Portrait of a Lady For Class 11th CBSE

Geography Project On Meteorological Instruments and Their Uses For Class 9th
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Please Enable JavaScript in your Browser to Visit this Site.
- 0 Shopping Cart £ 0.00 -->

Nepal Earthquake 2015
A case study of an earthquake in a low income country (LIC).
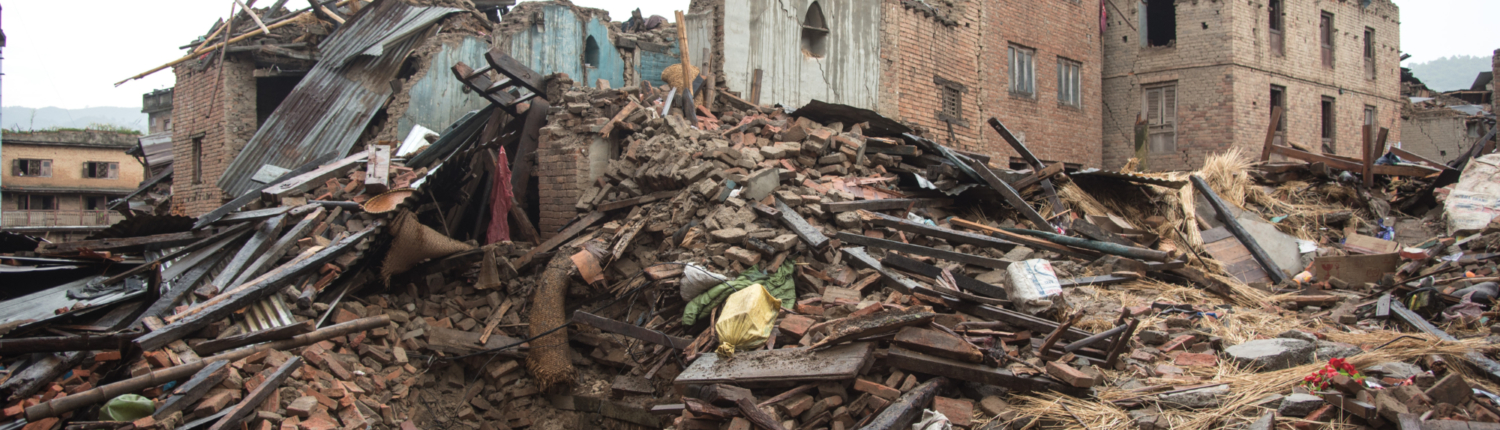

Nepal, one of the poorest countries in the world, is a low-income country. Nepal is located between China and India in Asia along the Himalayan Mountains.
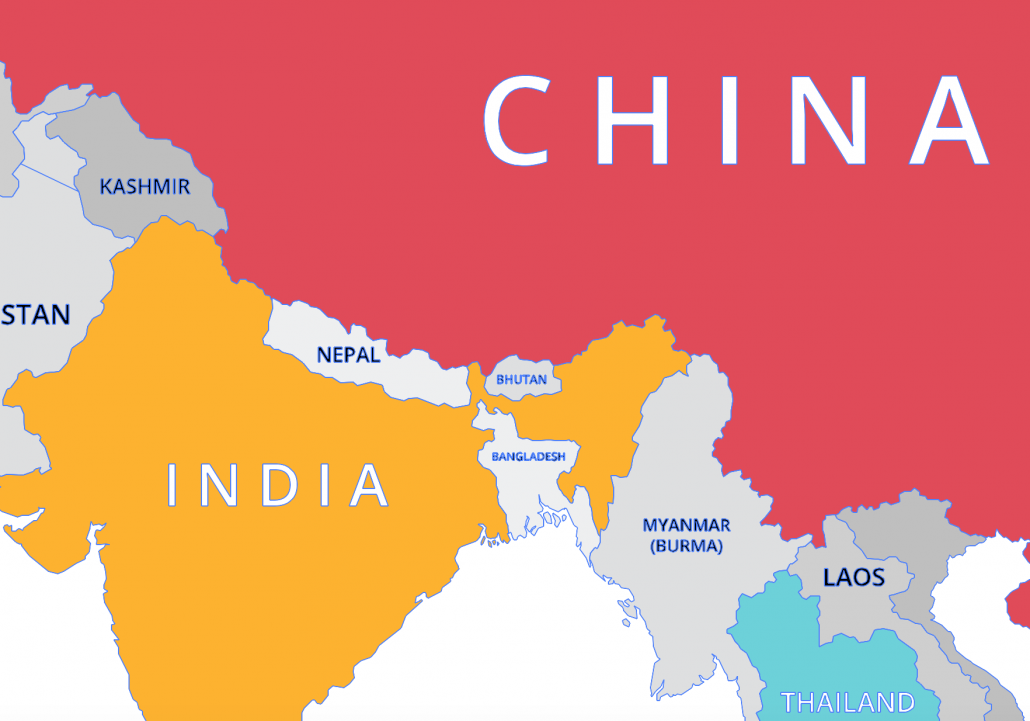
A map to show the location of Nepal in Asia
What caused the Nepal Earthquake?
The earthquake occurred on a collision plate boundary between the Indian and Eurasian plates.
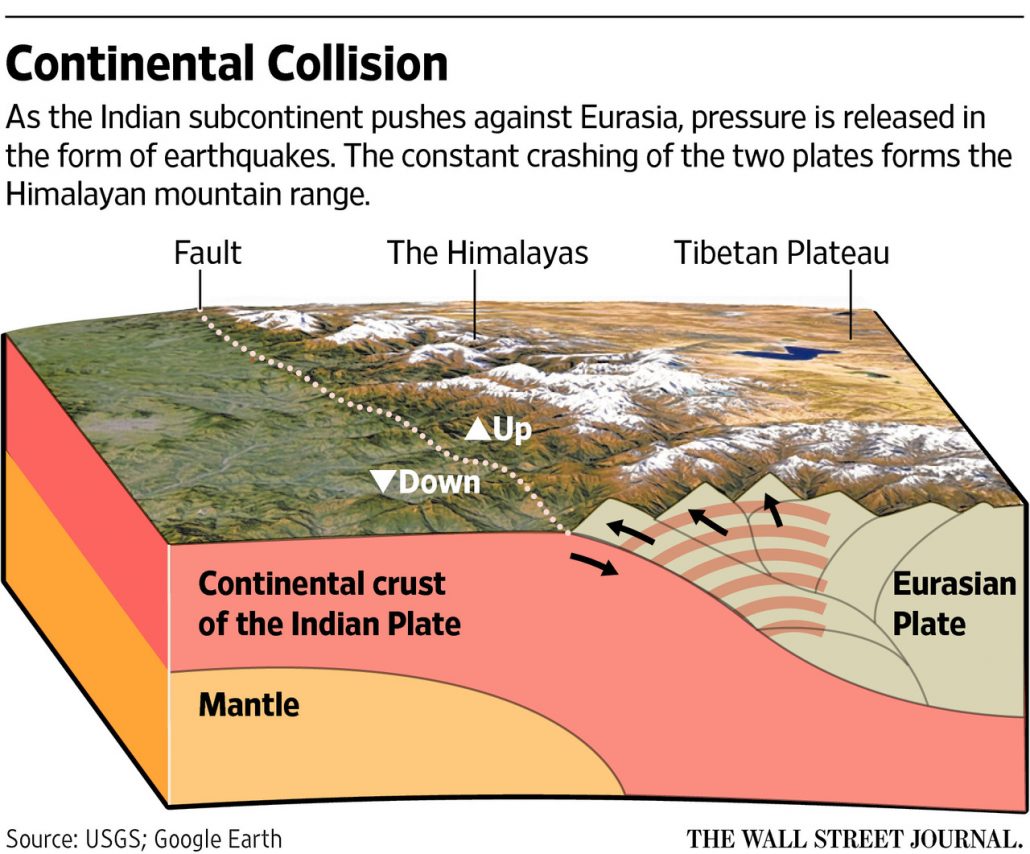
What were the impacts of the Nepal earthquake?
Infrastructure.
- Centuries-old buildings were destroyed at UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the Kathmandu Valley, including some at the Changu Narayan Temple and the Dharahara Tower.
- Thousands of houses were destroyed across many districts of the country.
Social and economic
- Eight thousand six hundred thirty-two dead and 19,009 injured.
- It was the worst earthquake in Nepal in more than 80 years.
- People chose to sleep outside in cold temperatures due to the risk of aftershocks causing damaged buildings to collapse.
- Hundreds of thousands of people were made homeless, with entire villages flattened.
- Harvests were reduced or lost that season.
- Economic losses were estimated to be between nine per cent to 50 per cent of GDP by The United States Geological Survey (USGS).
- Tourism is a significant source of revenue in Nepal, and the earthquake led to a sharp drop in the number of visitors.
- An avalanche killed at least 17 people at the Mount Everest Base Camp.
- Many landslides occurred along steep valleys. For example, 250 people were killed when the village of Ghodatabela was covered in material.
What were the primary effects of the 2015 earthquake in Nepal?
The primary effects of the 2015 earthquake in Nepal include:
- Nine thousand people died, and 19,000 people were injured – over 8 million people were affected.
- Three million people were made homeless.
- Electricity and water supplies, along with communications, were affected.
- 1.4 million people needed support with access to water, food and shelter in the days and weeks after the earthquake
- Seven thousand schools were destroyed.
- Hospitals were overwhelmed.
- As aid arrived, the international airport became congested.
- 50% of shops were destroyed, affecting supplies of food and people’s livelihoods.
- The cost of the earthquake was estimated to be US$5 billion.
What were the secondary effects of the 2015 earthquake in Nepal?
The secondary effects of the 2015 earthquake in Nepal include:
- Avalanches and landslides were triggered by the quake, blocking rocks and hampering the relief effort.
- At least nineteen people lost their lives on Mount Everest due to avalanches.
- Two hundred fifty people were missing in the Langtang region due to an avalanche.
- The Kali Gandaki River was blocked by a landslide leading many people to be evacuated due to the increased risk of flooding.
- Tourism employment and income declined.
- Rice seed ruined, causing food shortage and income loss.
What were the immediate responses to the Nepal earthquake?
- India and China provided over $1 billion of international aid .
- Over 100 search and rescue responders, medics and disaster and rescue experts were provided by The UK, along with three Chinook helicopters for use by the Nepali government.
- The GIS tool “Crisis mapping” was used to coordinate the response.
- Aid workers from charities such as the Red Cross came to help.
- Temporary housing was provided, including a ‘Tent city’ in Kathmandu.
- Search and rescue teams, and water and medical support arrived quickly from China, the UK and India.
- Half a million tents were provided to shelter the homeless.
- Helicopters rescued people caught in avalanches on Mount Everest and delivered aid to villages cut off by landslides.
- Field hospitals were set up to take pressure off hospitals.
- Three hundred thousand people migrated from Kathmandu to seek shelter and support from friends and family.
- Facebook launched a safety feature for users to indicate they were safe.
What were the long-term responses to the Nepal earthquake?
- A $3 million grant was provided by The Asian Development Bank (ADB) for immediate relief efforts and up to $200 million for the first phase of rehabilitation.
- Many countries donated aid. £73 million was donated by the UK (£23 million by the government and £50 million by the public). In addition to this, the UK provided 30 tonnes of humanitarian aid and eight tonnes of equipment.
- Landslides were cleared, and roads were repaired.
- Lakes that formed behind rivers damned by landslides were drained to avoid flooding.
- Stricter building codes were introduced.
- Thousands of homeless people were rehoused, and damaged homes were repaired.
- Over 7000 schools were rebuilt.
- Repairs were made to Everest base camp and trekking routes – by August 2015, new routes were established, and the government reopened the mountain to tourists.
- A blockade at the Indian border was cleared in late 2015, allowing better movement of fuels, medicines and construction materials.

Premium Resources
Please support internet geography.
If you've found the resources on this page useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Related Topics
Use the images below to explore related GeoTopics.
Previous Topic Page
Topic home, amatrice earthquake case study, share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Latest Blog Entries
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- Competency Based Questions
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- JEE Toppers Notes
- JEE Formula
- JEE Important Question
- JEE Mind Map
- JEE Integer-Numerical Type Question
- JEE Study Planner
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- LPU Mock Test
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- NEET Toppers Notes
- NEET Formula
- NEET Important Question
- NEET Assertion Reason Question
- NEET Study Planner
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes PDF (Quick Revision Notes)
The Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes is one of the most effective study materials to get through as it helps the students to get a deeper understanding of each and every topic and also helps the students to score well in their examinations. Each and every topic in these notes is well-explained which helps in increasing the confidence of all the students. The ICSE Geography Class 9 notes Earthquakes acts as a great revision tool for all the students.
Apart from this, the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes also have various other features which include easy language. These notes are written in an easy language to help all the students understand them. As our highly qualified subject matter experts are aware of the learning potential of each and every student, they have designed these Earthquakes notes accordingly. Another important feature of these notes is that they are written as per the latest curriculum of ICSE which helps the students to stay updated and also ensures that the students are covering each and every topic and are not missing any topic. Due to this, the students do not feel stressed and anxious and stay relaxed during exam days.
How to Download the Class 9 ICSE Geography Earthquakes Notes?
It is very simple to download the ICSE Geography Class 9 notes Earthquakes if you know the right steps to download them. Below are the right steps to download them:
- Visit the official website of selfstudys i.e. selfstudys.com.
- After opening the website, you need to scroll down and find the category of ‘Free Study Materials’. After finding the category, you need to click on the category of ‘CISCE’.
- After clicking on the category of ‘CISCE’, a new sub-category will open and you need to click on the option of ‘Revision Notes Exam’.
- Now, you need to choose the class and the subject for which you want to download the notes.
- And you are done! It was this simple to download the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes.
How to Prepare Well From the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes?
There are many tips a student can follow if they want to prepare well from the Class 9 ICSE Geography Earthquakes notes. They are:
- Regularly go through your notes: It is advisable for all the students to go through their Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes regularly as it helps in recalling all the important topics which you have learned previously. It also helps in boosting various skills of the students. This will help the students to remember the concept for a longer time.
- Listen to music while studying: Most students find music very peaceful and it also helps them to study effectively by increasing their concentration and motivation. It is advisable for all the students to listen to soft music without lyrics while studying ICSE Geography Class 9 notes Earthquakes to improve their overall exam preparation. This will also make them relaxed.
- Remove Distractions: If a student wants to prepare well for the exam and wants to score good marks in it, then they should remove all the distractions while studying the ICSE Geography Class 9 Earthquakes notes. The students should find a peaceful place where they study, there should be no noise. This will help the students to prepare well and score well in their examinations.
- Blurting: Another great tip which all the students should try while studying the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes is the blurting technique. In this technique, a student has to read the ICSE Geography Class 9 notes Earthquakes again and again. After reading repeatedly, the students must test their knowledge by writing everything which they have learned.
- Take Short Breaks: All the students are advised to take short breaks while doing exam preparation from the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes as it will help the students to promote quality learning and also prepare well for the examination.
How to Score 100% Marks in Geography While Studying From the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes?
Every student wants to score 100% marks in exams but they are not aware of the various tricks which will help them to score good marks in their exams. The tips are:
- Find a peaceful place: The first and the most important step to score 100% in exams is to find a peaceful place to study the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 notes as it will help you to focus on your studies as Geography is a subject which requires constant focus and concentration and you will not be able to attain that in a place where there are a lot of noises. So, make sure to find a peaceful place if you want to prepare well and score 100% marks in the exams.
- Read various books: It is a pretty obvious fact that every student only has one Geography coursebook but apart from that, there are various other books of Geography with a modified view on the Earthquakes topic which will help the students to understand in detail. Read the different definitions to find the one which makes the most sense to you.
- Develop a routine: All the students are advised to develop a daily routine as it will not only help the students to learn the ICSE Geography Class 9 notes Earthquakes but will also help the students to divide different topics in the chapter and then give time to each topic.
- Practise Mindfulness: All the students are advised to practise mindfulness because during exam days, the stress and anxiety levels are often higher than the normal days. So, the students should take care of themselves and stay relaxed.
- Write the concepts in your own words after learning them: After learning the concepts from the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes, the students should write it down in their own words as it will help them to stick to the learned information and remember it for a long time.
When Should a Student Study From the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes?
There are various moments when a student should study from the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes. Let’s have a look:
- At the time of Lecture: The Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 notes can be used at the time of class lectures. These notes will help you acknowledge the concept with an in-depth understanding of it. These ICSE Geography Class 9 notes Earthquakes can also help the students to remember the concepts which they have previously studied and also help them to score good marks in their exams.
- During Revision: All the students must use the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes during the time of revision as it acts as a great revision tool because it helps the students to get an idea about the progress of their exam and also the stronger and weaker areas and can work on them to improve their overall exam preparation.
- During the last-minute preparations: All the students can also use the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes at the last moment as these notes also consist of the key points which can be really helpful for all the students to understand the concepts in an easy language. These notes will help them remember all the concepts which they have previously learned and will also make it easier for all the students to learn new concepts.
What are the Features of the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes?
There are various features of the ICSE Geography Class 9 notes Earthquakes which proves that it can be a success mantra for all the students. The most important features are:
- Simple Language: Our subject matter experts who have years of experience in the field of education are aware about the learning potential and grasping power of each and every student. That is why they have created the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes ICSE in an easy language to make it easy for all the students to understand them.
- As per the latest pattern: The Class 9 ICSE Geography Earthquakes notes are created as per the latest pattern of ICSE by our highly qualified subject matter experts who have made sure to create them as per the latest pattern of ICSE to ensure that the student stay updated about the latest curriculum and does not miss any important topic.
- Practise Questions: In the ICSE Geography Class 9 Notes Earthquakes, the practice questions are also provided for all the students which can help them to improve their concepts and also score well in the examinations.
- Each and Every Topic is covered: Each and every topic is covered in the Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes which makes the students stress free as they feel that they have covered each and every topic and will eventually score well in the examinations.
- Access in the PDF Format: The Class 9 ICSE Geography Earthquakes notes can easily be accessed in the PDF Format which can be very beneficial for all the students as they will easily be able to access them on their mobile phones. Also, they can be carried anywhere in mobile, laptop etc.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

Study Material
.avif)
Disaster Management Project Class 9 | Free PDF Download
Home > Class 9 Subject-wise Material
Disaster Management Project Class 9
As part of the CBSE 9th 2024–25 syllabus, students are required to prepare and submit Social Science projects on disaster management. Educart has created a special page filled with inspiring ideas for various parts of this project.
Here, you will find creative cover page designs, well-designed acknowledgment pages, and even complete project files (in video form) showcasing the top projects on disaster management from previous years.

Project Structure
The index, also called the Table of Contents, usually comes after acknowledgment. It contains the main heading of the topics arranged in a sequence. Here is an example for reference purpose.
Start your class 9 project on disaster management by providing a brief introduction and overview of disaster management. Define disaster followed by the definition of disaster management. Use the following reference to understand the meaning of disaster management, and write the intro part of the project.

https://www.undrr.org/terminology/disaster-management
https://nidm.gov.in/PDF/Disaster_about.pdf
https://publichealth.tulane.edu/blog/what-is-disaster-management/
https://www.iwapublishing.com/news/disaster-management
Explain why disaster management is important given India’s diversified climatic conditions. Explain natural catastrophes such as earthquakes, cyclones, floods, droughts, etc.

https://publichealth.tulane.edu/blog/disaster-management-cycle/
Write two different types of natural and man-made disasters, along with examples.
3.1 Natural Disasters
Start with the definition—Natural hazards are environmental events that can affect societies and the human environment. They are different from man-made hazards. For example, a flood caused by changes in river flows is a natural hazard, while a flood caused by a dam failure is a man-made hazard.
Now, describe various natural disasters and their impacts. Quote a few, e.g., of natural disasters like:
- Earthquakes
- Hurricanes/Cyclones
- Volcanic Eruptions
- Avalanche, etc.

https://hazards.fema.gov/nri/natural-hazards
3.2 Man-Made Disasters
Next, write about man-made disasters, how they are caused, etc., along with quoting a few examples, like:
- Industrial Accidents
- Nuclear Disasters
- Environmental degradation

https://sdma-arunachal.in/manmade-disasters/
Mention the vulnerability profile of India, discussing the States and Union Territories that are disaster-prone. Describe all the factors, both natural and man-induced, responsible for the vulnerability of these states.
.avif)
https://iasscore.in/data-story/vulnerability-profile-of-india
https://www.drishtiias.com/to-the-points/paper3/disaster-management-i
Write about the two worst disaster cases in India that impacted the lives of millions of people. Mention the following two:
5.1 Natural Disaster: 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami

5.2 Man-Made Disaster: Bhopal Gas Tragedy

https://recovery.preventionweb.net/collections/recovery-collection-2004-indian-ocean-earthquake-and-tsunami
Define what disaster risk reduction is, write about all phases and also describe the disaster management cycle.
6.1 Phases of Disaster Management
Under this topic, describe the key phases of disaster management i.e., the pre-disaster phase, the disaster phase, and the post-disaster phase, and mention all the key components of this phase.
- Preparedness
- Rehabilitation

https://home.akitabox.com/blog/4-phases-of-disaster-management/
6.2 Disaster Management Cycle

Mention various national and international bodies and their role in disaster management.
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)

Mention the Disaster Management Act of 2005. Highlight the key points and explain how the act is beneficial in disaster management.
As technology develops, so does its application, and it has not left any field unaffected. So, describe how technology helps predict, prepare for, and respond to disasters. Provide examples of technologies used in disaster management, such as early warning systems, GIS mapping, and communication tools.

https://www.drishtiias.com/blog/tech-driven-disaster-management-changing-the-game
Other Measures to Prevent Disasters
Write some of the measures that should be taken to mitigate disasters, for eg:
- Disaster resilient infrastructure
- Climate Change Adaptation
- Environmentally Sustainable Development
- Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Mapping
- Urban Planning and Development
https://www.nextias.com/blog/disaster-management/
Once you have written down all the important points in your disaster management project for class 9, you should summarize the key points discussed in your project and highlight the importance of effective disaster management for community resilience and safety.
The last page of your project should be a bibliography. Here, you have to provide a list of sources you used for your research, whether books, websites, articles, or any other relevant materials.
Below is the list of references used to provide you with all the important information on the disaster management project for class 9. This might be useful for you, so please do check this out.
https://www.iwapublishing.com/news/disaster-management
https://iasscore.in/data-story/vulnerability-profile-of-india https://ebooks.inflibnet.ac.in/geop15/chapter/issues-and-challenges-in-disaster-management/
- Explain the main difference between natural and man-made disasters with examples?
- How many phases are there in Disaster Management cycle?
- What measures can be taken to improve disaster preparedness in communities?
- Describe the role of government agencies in disaster mitigation.
- What are some challenges faced during the response phase of disaster management?
Examples: Cover Images
Here are a few cover page ideas for the disaster management project for class 9.

Examples: Acknowledgement / Index page
Have a look at few creative examples for your project acknowledgement and Index Page.

Videos: Topper Project Files
Here are some video links to inspire your disaster management project.
Project Idea- Video 1
Project Idea- Video 2
Project Idea- Video 3
Project Idea- Video 4
Pdfs: full projects.
Download full project PDF of disaster management file for CBSE class 9

Sample Project 1
Sample Project 2
Sample project 3, sample project 4, sample project 5, sample project 6, other projects.
<red> → <red> SST Social Issues Project for Class 10
<red> → <red> SST Sustainable Development Project for Class 10
<red> → <red> SST Consumer Awareness Project for Class 10
- Mathematics (Standard)
- Mathematics (Basic)
- English L&L
- English Communicative
- Social Science
- Information Technology
- English Core
- Mathematics
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political Science
- Computer Application
- Applied Maths
- English L& L
- History & Civics
- Literature in English
- English Language
- 10 Year Solved Papers
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 PCB Combo
- Class 12 PCM Combo
- Math Standard
- Computer Applications
- Class 10 English
- Class 12 English

Revision Notes for Earthquakes Class 9 Geography ICSE
Icse revision notes for earthquakes class 9 geography.

Earthquakes
An earthquake is a tremor below the surface of the Earth which causes shaking of the Earth’s crust.
Causes of Earthquake
Earthquakes are generally caused by sudden forces because of the following reasons:
- Plate tectonics : Most of the earthquakes occur because of the movement of tectonic plates. They are caused when two plates either slip past each other or collide against each other. Under such circumstances, their edges produce faults along the lines of weakness.
- Isostatic disturbances : Earthquakes may occur when disturbances are produced by the deposition of sediments by rivers and glaciers on the ocean floor. Because the asthenosphere (the upper layer of the Earth’s mantle) is in the semi-molten state, any disturbance in the equilibrium between oceans and continents may result in movements causing earthquakes.
- Man-made causes : Construction of large dams near the fault zones may result in isostatic movements causing earthquakes.
Anatomy of an Earthquake
- An earthquake is caused by the movement of lithospheric plates inside the surface of the Earth. Because these plates move, the surface of the Earth vibrates. The vibrations can travel all round the Earth.
- The place in the Earth’s crust where the movement first starts is called focus .
- The place on the surface above the focus is called epicentre .
- It is from the epicentre that vibrations in the form of waves travel outwards. These are known as seismic waves .
- The greatest damage and destruction to human life and property occur at places which are closest to the epicentre. The strength of the earthquake decreases as it moves away from the epicentre.
- ∙Earthquake waves are classified into three types. These are: 1. P waves : These are known as primary waves. They pass through solids, liquids and gases. These are the first earthquake waves which can be recorded on a seismogram. 2. S waves: These waves travel through the Earth’s interior but cannot be transmitted by liquids. They are recorded on a seismograph after the P waves. 3. L waves: They are long waves and are recorded after the P and S waves. L waves may be further classified into Love waves and Rayleigh waves.
A seismograph is an instrument which measures and records the details of an earthquake such as its duration, force and direction. The seismograph has a pen attached to it. When an earthquake occurs, the pen also vibrates along with the vibrations produced by the earthquake. The pen records the movements of vibrations on a moving strip of paper. Various waves which are formed by the moving pen give us an estimate of the direction and force of an earthquake. It also calculates the difference in the arrival of P and S waves.
The intensity of an earthquake is measured on the Richter scale and the Mercalli scale. The Richter scale is commonly used for measuring an earthquake. While the Richter scale measures the intensity of the earthquake on a scale from 1 to 9, the Mercalli scale measures it on a 12 point scale. Earthquakes measured above the Richter scale of 6 onwards cause damage to life and property.
Effects of an Earthquake
Earthquakes have constructive and destructive effects.
Constructive Effects
- Earthquakes help the Earth in releasing its energy.
- As a result of earthquakes, many landforms are built. It also results in changing the coastline. Earthquakes in the Himalayan region have resulted in the formation of various lakes. Further, the formation of bays, estuaries and gulfs because of earthquakes has resulted in better navigation.
Destructive Effects
- Earthquakes measuring 6 and above on the Richter scale may result in the loss of human lives. About 15,000 people are killed every year because of earthquakes.
- Earthquakes inflict serious damage to buildings, structures, roads, bridges and railways. Submergence: Many coastal areas get submerged in water because of earthquakes. For example, Dwarka in Gujarat now lies submerged in water.
- Powerful earthquakes may change the course of rivers which may render an area infertile.
- After earthquakes, fire may also break out. This may happen when inflammable material is thrown onto broken gas lines. In the earthquake of 1906 in San Francisco, a great fire broke out which proved to be more destructive than the earthquake itself.
- Tsunamis are caused by earthquakes occurring in the sea. These can cause huge destruction in the coastal regions.
Tsunamis
Tsunamis are long, high waves mainly caused by earthquakes. They can also be caused by volcanic eruption or meteorite impact. An earthquake in the Indian Ocean in 2004 triggered a series of tsunamis on 26 December 2004 in which thousands of people were killed in India, Indonesia Thailand, Malaysia, Sri Lanka and Maldives.
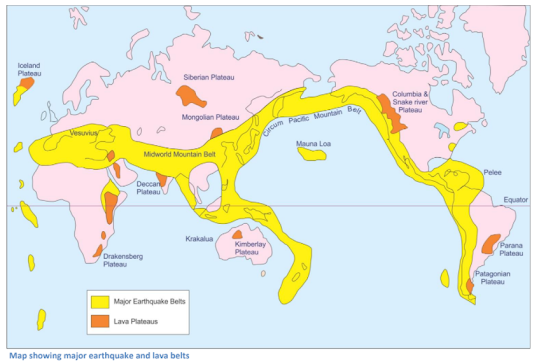
Distribution of Earthquakes
Earthquakes mostly originate from the plate boundaries. There are two main belts where the possibility of the occurrence of an earthquake is the largest.
- The Circum Pacific Mountain Belt: The regions lying in this belt are Japan, the Philippines, Indonesia and California in USA. About 70% of earthquakes originate in this zone.
- The Midway Mountain Belt: This belt extends from Eastern Europe to Asia. It covers the Alpine and Himalayan regions. About 20% of earthquakes originate in this zone.
- The remaining 10% of earthquakes are associated with submarine ridges, ocean floors, rift valleys and other fault zones.
India is located in the Mid-Mountain Belt. The regions in India which are highly prone to earthquakes are Kashmir, the foothills of the Himalayas, the Northeastern region and the Rann of Kachchh. Earthquakes frequently take place in the foothills of the Himalayas and the Ganga Brahmaputra valley as these are the regions where the tectonic plates meet. Maharashtra is also prone to earthquakes.
You might like
Contact form.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The case study provided a tangible example of the real-world implications of seismic activity, illustrating the crucial role of effective mitigation measures. Through this, we hope students have gained insight into the transformative potential of the knowledge acquired throughout this exploration.
The 2011 earthquake occurred off Japan’s Honshu Island, measuring 9.1 on the Moment Magnitude scale, one of the strongest ever recorded. Triggered by a ‘megathrust’ in a destructive plate margin, the Pacific Plate subducted the Eurasian Plate, releasing energy equivalent to 600 million Hiroshima bombs.
Case study: Haiti Earthquake, 2021. On 14th August 2021 a magnitude 7.2 earthquake struck Haiti in the Caribbean. The plate boundaries around Haiti are complex. The North American Plate...
The document summarizes information about the 2001 Bhuj earthquake in Gujarat, India. It provides details about the location, magnitude, damage, response efforts, and reconstruction after the 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck near Bhuj on January 26, 2001.
At 11.26 am on Saturday, 25th of April 2015, a magnitude 7.9 earthquake struck Nepal. The focus was only eight kilometres deep, and the epicentre was just 60 kilometres northwest of Kathmandu, the capital city of Nepal. At the time of the earthquake, Kathmandu had 800,000+ inhabitants.
The Earthquakes ICSE Class 9 Notes is one of the most effective study materials to get through as it helps the students to get a deeper understanding of each and every topic and also helps the students to score well in their examinations.
This document is a student project on disaster management. It begins with an introduction that defines what a disaster is and lists several types of disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, cyclones, epidemics, floods, droughts, landslides, and industrial hazards.
Download the complete Free PDF of Class 9 Disaster Management Project for CBSE Social Science students with detailed analysis, based on CBSE Class 9 syllabus 2025.
The earthquake occurred on a destructive plate margin, where the Nazca plate subducts beneath the South American plate. Smaller aftershocks followed the initial earthquake. As the earthquake occurred in the Pacific Ocean, the plate movement displaced a lot of seawater, triggering a tsunami.
The Richter scale is commonly used for measuring an earthquake. While the Richter scale measures the intensity of the earthquake on a scale from 1 to 9, the Mercalli scale measures it on a 12 point scale. Earthquakes measured above the Richter scale of 6 onwards cause damage to life and property.