Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise
Turn the following sentences into indirect speech.
1. John said, ‘I am very busy now.’ 2. He said, ‘The horse has been fed.’ 3. ‘I know her name and address,’ said John. 4. ‘German is easy to learn,’ she said. 5. He said, ‘I am writing letters.’ 6. ‘It is too late to go out,’ Alice said. 7. He said to me, ‘I don’t believe you.’ 8. He says, ‘I am glad to be here this evening.’ 9. He said to me, ‘What are you doing?’ 10. ‘Where is the post office?’ asked the stranger. 11. He said, ‘Will you listen to me?’ 12. John said to Peter, ‘Go away.’ 13. She said to me, ‘Please wait here till I return.’ 14. ‘Call the witness,’ said the judge. 15. The speaker said, ‘Be quiet and listen to my words.’
1. John said that he was very busy then. 2. He said that the horse had been fed. 3. John said that he knew/knows her name and address. (Note that the tenses may not change if the statement is still relevant or if it is a universal truth.) 4. She said that German is/was easy to learn. 5. He said that he was writing letters. 6. Alice said that it was too late to go out. 7. He told me that he didn’t believe me. OR He said he didn’t believe me. 8. He says that he is glad to be here this evening. (When the reporting verb is in the present tense, adverbs of time and place do not normally change in indirect speech.) 9. He asked me what I was doing. 10. The stranger asked where the post office is/was. 11. He asked me if I would listen to him. 12. John ordered Peter to go away. 13. She asked me to wait there till she returned. 14. The judge commanded them to call the first witness. 15. He urged them to be quiet and listen to them.


Search Articles
Recent articles.
- Prepositions Quiz
- General Grammar Exercise
- Pronouns Exercise
- Proper Nouns Exercise
- General Vocabulary Exercise
- Identify the Adverbs Exercise
- Grammar Exercise (Intermediate Level)
- Intermediate Level Grammar Exercise
- General Grammar Worksheet
- Vocabulary Exercise
- Gap Filling Tenses Exercise
- Gap Filling Grammar Exercise
- More resources
EnglishPractice.com © 2024 - All rights Reserved.

Direct and Indirect Speech Worksheets

Sentence Swap
Speech Selector

Indirect Shift

Quote Conversion

Speech Facts

Punctuation Check

Quote Mastery

Dialogue Rewrite

Cartoon Quotes
Statement Shifts

Direct Conversion
Quote Formatter
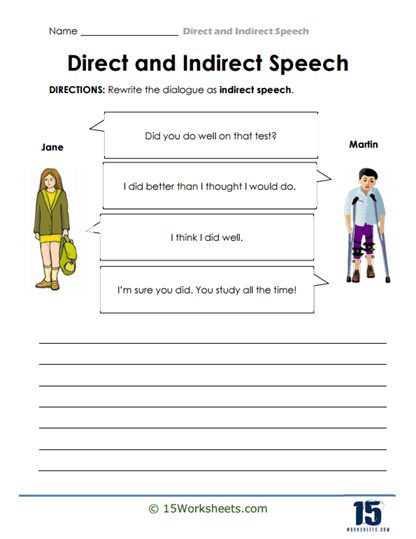
Speech Shift

Winter Words

Dialogue Craft
About these 15 worksheets.
This series of worksheets is an invaluable resource for teachers and homeschooling parents looking to enhance their students’ understanding of reported speech. These worksheets are thoughtfully designed to be both engaging and educational, providing students with a comprehensive approach to mastering the differences between direct and indirect speech. The collection, available in easy-to-access PDF format, offers a variety of activities that cater to different learning styles, making it an excellent tool for reinforcing this essential grammar concept in a fun and interactive way.
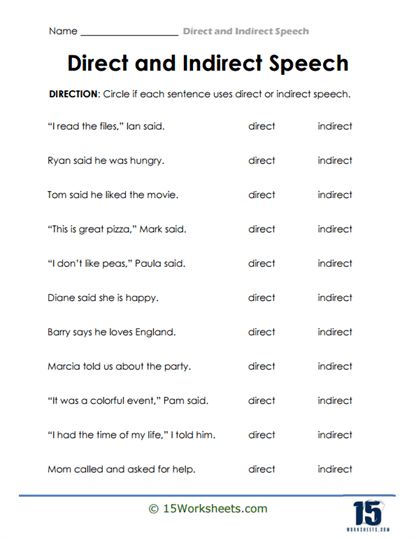
One of the standout features of this collection is its clear and simple explanations that guide students through the nuances of direct and indirect speech. For example, one worksheet starts by introducing the basics of direct speech, where the exact words of a speaker are quoted, and indirect speech, where those words are paraphrased without quotation marks. This foundational knowledge is then applied through exercises that ask students to identify whether a sentence uses direct or indirect speech, providing immediate practice that solidifies their understanding.
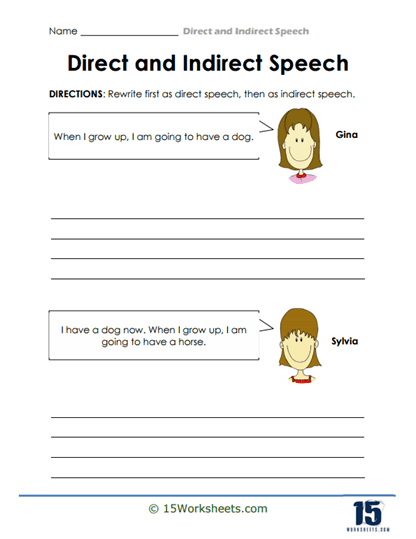
The collection also includes worksheets that focus on the practical application of these concepts. In one activity, students are asked to convert direct speech into indirect speech. For instance, a sentence like “Let’s go swimming,” George suggested, would be rewritten as “George suggested that they go swimming.” This exercise not only reinforces the rules of changing pronouns, verb tenses, and time expressions but also encourages students to think critically about how to convey the same meaning without using the speaker’s exact words.
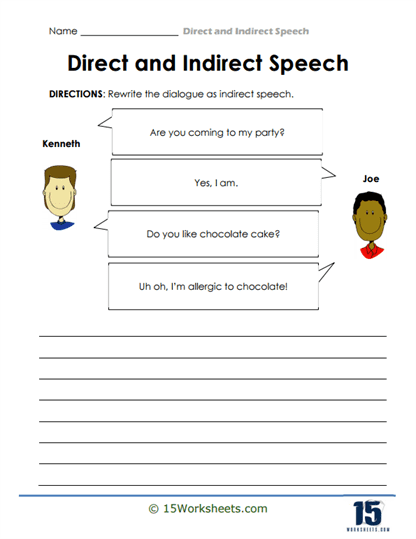
Another engaging activity in this collection involves dialogue rewriting. Students are presented with a short conversation and are tasked with transforming it from direct speech into indirect speech. This type of exercise helps students understand the flow of dialogue and how to maintain the original message while adapting it into a different grammatical structure. It also fosters creativity as students must carefully consider how to rephrase each line while preserving its intent.
The worksheets also include true or false questions that challenge students to test their knowledge of the rules governing direct and indirect speech. These questions cover essential points, such as whether direct speech requires quotation marks and whether indirect speech can change the tense of the original statement. This activity is particularly effective for reinforcing the theoretical aspects of the topic, ensuring that students grasp the underlying rules before moving on to more complex tasks.
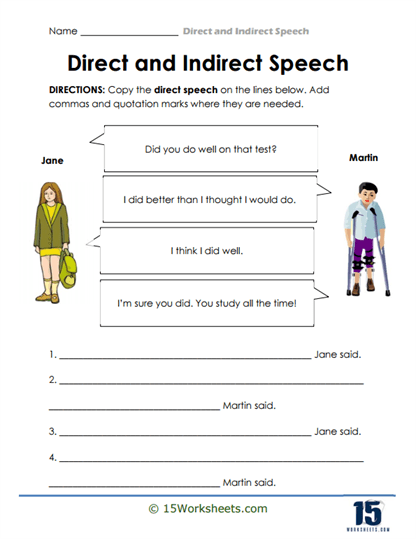
In addition to these activities, the collection features worksheets that focus on punctuation, an often overlooked but crucial aspect of direct speech. Students are given sentences and asked to determine whether they are punctuated correctly. This exercise sharpens their attention to detail and reinforces the importance of proper punctuation in conveying clear and accurate speech. By mastering these skills, students gain confidence in their writing and communication abilities.
The visual appeal of these worksheets also deserves mention. Each worksheet is accompanied by engaging illustrations that make the learning process more enjoyable for younger students. For instance, a worksheet might feature a cartoon character speaking a line of dialogue, which students must then convert into indirect speech. These visuals not only make the exercises more fun but also help visual learners better understand and remember the concepts being taught.
The worksheets include exercises that encourage students to think about the context in which direct and indirect speech is used. For example, students might be asked to rewrite a statement from a formal speech into indirect speech, considering the tone and formality required. This helps students understand how the context can influence the choice between direct and indirect speech, making them more versatile communicators.
This worksheet collection provides students with a thorough understanding of reported speech. By combining clear explanations with practical exercises, the worksheets help students grasp the rules of direct and indirect speech, apply them in various contexts, and develop strong communication skills. The variety of activities ensures that students remain engaged and challenged, making the learning process both effective and enjoyable. Whether used in the classroom or at home, these worksheets are an excellent resource for any teacher or parent looking to enhance their students’ grammar skills.
What Is Direct and Indirect Speech?
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of conveying what someone has said, with distinct differences and some similarities. Direct speech involves quoting the exact words of the speaker, typically enclosed in quotation marks, and it maintains the original tense, pronouns, and punctuation used by the speaker. For example, “I am going to the store,” she said. In contrast, indirect speech involves paraphrasing the speaker’s words without using quotation marks, often resulting in changes to pronouns, verb tenses, and time expressions to fit the context of the report. For instance, the previous example in indirect speech would be, “She said that she was going to the store.” Both forms of speech aim to convey the original message, but while direct speech preserves the speaker’s exact words, indirect speech focuses on the meaning and adjusts the language to fit the narrative context. Despite these differences, both forms are used to communicate what someone has said, making them essential tools for reporting speech in various contexts.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reported speech : worksheets pdf, printable exercises, handouts. Direct and indirect speech for esl.
Direct speech is mainly used to write dialogue or quoted speech. Read how to punctuate direct speech below.
Practise the difference between the direct and indirect speech in questions, commands and requests. Online exercises with answers: Direct - indirect speech exercise 1 Rewrite sentences …
Improve your knowledge with over 200 exercises and answers focused on Direct and Indirect Speech. By practicing changing quotes into reported speech, you’ll learn the rules and improve your ability to tell the …
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise. Turn the following sentences into indirect speech. 1. John said, ‘I am very busy now.’. 2. He said, ‘The horse has been fed.’. 3. ‘I know her name and …
Multiple-choice tests designed to strengthen learners' comprehension of grammar rules on questions, namely question words, indirect questions, subject and object qu... 243 uses. A …
By combining clear explanations with practical exercises, the worksheets help students grasp the rules of direct and indirect speech, apply them in various contexts, and develop strong …
Indirect Speech. Exercise to practice indirect speech. The students are supposed to change the direct sentences to indirect ones, paying attention on the verb tense, subject and pronouns. …
Direct and Indirect Questions. Marcela Torquato Maciel. Member for. 4 years 5 months. Age: 15+. Level: A2. Language: English (en) ID: 7592133. 01/03/2024. Country code: …