

Academic Essay
Essay generator.

When creating an academic essay , it is very important for you to relay a sensible and clear argument to your target readers. Since academic essays are widely used in the field of education and research, you need to ensure that you do both logical, interesting and informative writing . The items that are commonly seen in an academic essay contain insights, actual occurrences, ideas, and facts.
What is Academic Essay?
An academic essay is a structured form of writing that serves the purpose of presenting and supporting a thesis or argument on a specific topic. It is commonly used in educational settings to assess students’ understanding, analytical skills, and ability to research and convey their findings. An academic essay typically follows a clear format, including an introduction with a thesis statement, body paragraphs that provide evidence and analysis to support the thesis, and a conclusion that summarizes the main points and reinforces the essay’s central argument. This type of essay requires critical thinking and a formal tone, with evidence cited from reputable sources to back up claims made within the text.

Download Academic Essay Bundle
A lot of students tend to think that an academic essay, just like any other college essay , is something that is too technical or defined. However, you can always write one depending on how you perceive a specific topic of discussion or how you interpret an instance or any other subjects. The samples that we have for you can be a great help if you would like to start writing your academic essay already.
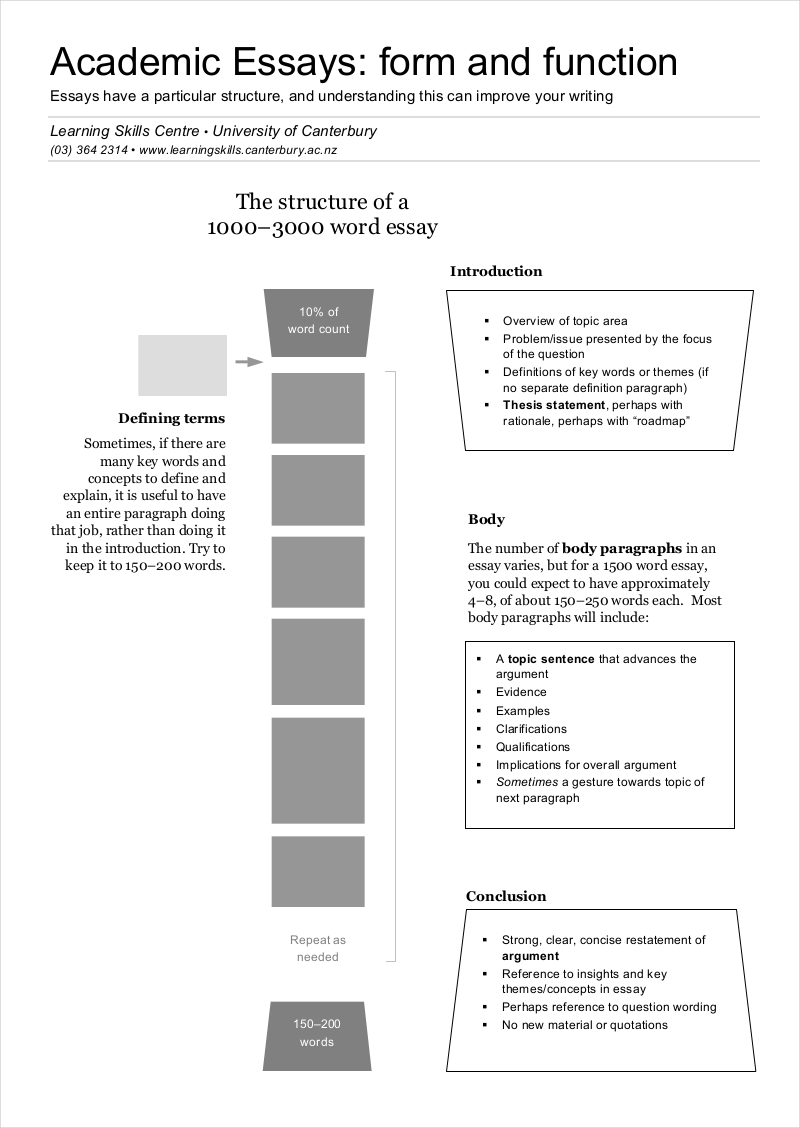
Academic Essay Writing Format/ Outline
1. title page (if required).
Includes the essay’s title, the author’s name, and institutional affiliation.
2. Introduction
Hook : Opens with a statement to grab the reader’s interest. Background Information : Provides context for the topic being discussed. Thesis Statement : Presents the main argument or claim of the essay.
3. Body Paragraphs
Each paragraph should focus on a single idea that supports the thesis, structured as follows:
Topic Sentence : Introduces the main idea of the paragraph. Evidence and Analysis : Includes data, quotes, or examples to support the topic sentence, followed by an explanation of how this evidence supports the thesis. Transition : Connects to the next paragraph or idea.
4. Conclusion
Summary of Main Points : Restates the key arguments or findings presented in the body paragraphs. Restatement of Thesis : Reinforces the essay’s main argument in light of the evidence presented. Closing Thought : Offers a final insight, a call to action, or a suggestion for further research.
Example of Academic Essay Writing
The Impact of Social Media on Communication In the digital age, social media has revolutionized the way we communicate, transcending physical boundaries and transforming social interactions. This essay explores the profound impact of social media on communication, examining both its positive advancements and negative implications. While social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have enhanced our ability to connect with others, they have also led to a decline in face-to-face interactions and a dilution of personal communication skills. Social media has made it easier than ever to stay connected with friends and family, regardless of geographical distance. A study by Smith and Duggan (2016) found that 75% of internet users utilize social media to maintain relationships with distant family and friends. This widespread use of social media for keeping in touch demonstrates its role as a vital communication tool, bridging the gap between people worldwide. However, the reliance on social media for communication has led to a decrease in the quality of interpersonal interactions. Research by Johnson (2018) indicates a 40% decline in face-to-face conversations among young adults, correlating with increased social media usage. The preference for digital communication over personal interaction suggests a shift in social dynamics, potentially harming relational depth and emotional connections. Moreover, social media has affected our communication skills, particularly among younger generations. A survey by Lee (2019) revealed that 60% of teachers believe social media use has adversely affected students’ writing and verbal communication skills. The informal language and abbreviations common in social media posts and messages are infiltrating academic and professional communications, underscoring the need for a balanced approach to digital interactions. Social media has undeniably transformed communication, offering unparalleled connectivity but also presenting significant challenges. While it fosters global connections, its overuse can undermine personal interactions and communication skills. Balancing social media use with face-to-face communication is crucial for maintaining meaningful relationships and effective communication in the 21st century.
What is an example of academic writing?
Title: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
Introduction: Climate change, driven primarily by human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, has emerged as a critical global concern. This essay aims to explore the multifaceted impacts of climate change on biodiversity. The effects of rising temperatures, altered weather patterns, and habitat destruction are increasingly evident, with far-reaching consequences for ecosystems and species worldwide.
Body Paragraph: One of the most noticeable consequences of climate change is the shifting geographical ranges of numerous species. Warmer temperatures prompt species to migrate to higher altitudes or latitudes, as they seek habitats that align with their thermal preferences. This phenomenon is evident in various ecosystems, including mountain regions, where alpine plants and animals have progressively moved uphill. These migrations, while adaptive, can disrupt established predator-prey relationships and competition for resources. Such shifts can also lead to reduced biodiversity in lower-altitude regions as some species fail to adapt or relocate successfully.
- Smith, J., & Johnson, A. (2019). Impacts of Climate Change on Alpine Plant Communities. Environmental Studies Journal , 42(3), 256-270.
- Wilson, P., & Davis, R. (2020). Climate-Induced Shifts in Animal Distributions: Evidence from a Decadal Study. Ecology and Evolution , 10(12), 5963-5972.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, climate change exerts profound effects on biodiversity, manifesting through shifts in species distributions, altered ecological relationships, and habitat loss. As global temperatures continue to rise, addressing these impacts becomes increasingly urgent. Conservation efforts, sustainable practices, and international cooperation are essential in mitigating the repercussions of climate change on the world’s diverse ecosystems and species.
Academic Essay Topics with Samples to Edit & Download
- Pollution due to urbanization
- The environmental causes of smoking
- The outcomes of global warming
- Abortion as a controversy
- Causes of obesity in teenagers
- Childhood memories
- Fathers should get equal paternity leave
- Harmful dogs should be euthanized
- How does divorce affects children?
- How does technology affect productivity?
- Importance of preserving threatened species
- Parenting styles and motives
- Political issues in the U.S.
- Romantic relationships
- Should schools abolish homework?
- Violent video games should be banned
- Ways of protecting the environment
Academic Essay Writing Examples & Templates
1. academic essay example.

Free Download in PDF
2. Academic Essay for College Students

Edit & Download
3. Short Academic Essay

4. Academic Essay Template

5. Academic Writing Essay Template

6. Academic Text Example Essay Template

7. Academic Essay Writing Examples

academic-skills.health.herts.ac.uk
8. Academic Essay for College Students Examples

9. Narrative Academic Essay Examples

learning.hccs.edu
10. Sample Academic Essay Format Example

owll.massey.ac.nz
11. Academic Paper Essay Example

writing.umn.edu
12. Simple Academic Essay Example

cambridgemichigan.org
13. Academic Essay Sample Structure Example
lps.canterbury.ac.nz
14. Short Academic Essay Example in PDF

15. Free Printable Academic Essay Sample

lib.oup.com.au
16. Sample Academic Essay Example

17. Academic Essay Writing Sample Example

18. Free Academic Essay Sample Guide

intranet.ecu.edu.au
19. Sample Academic Essay Outline

lib.uts.edu.au
Are You Ready and Prepared to Create an Academic Essay?
Different types of academic writing require an individual to have a clear thought process within the entirety of idea development. You have to be focused on what you would like to achieve your final written output so you can incorporate successful guides and processes within the activity. Some of the things that you can talk about in an academic essay include the following:
- Human behavior, characteristics, and emotions
- Community relations
- Natural occurrences
- Language and its effective usages
- Culture and the arts
- Academic researchers
- Relevant cultural phenomenon
- Photography and other artistic undertakings
- Human interactions
- Other subjects that are related to education and academics
Knowing the subject of your article is only one of the initial things that can help you prepare during the writing process. Here are some ways on how you can be ready to write your academic essay:
- You need to have an order of writing that can easily showcase the flow of your thoughts. You must ensure that you can easily connect with your readers or audience so they can respond to the content of your article. Your academic essay should evoke an emotion that is necessary to spark other ideas, opinions and other kinds of responses.
- You need to be aware that academic essays differ depending on the educational or academic discipline where they will be used. There are certain ways that are necessary to be followed in various fields for an academic essay to be deemed effective. With this, always be mindful of the directions or instructions were given to you by the entity who requires you to write an academic essay.
- You do not need to pattern your writing to the works of others. You can be ready even by just knowing your subject and researching about it. The style of writing that you have can give the most difference to how you write and how you present your work. Always keep in mind that your academic essay should be playful – it must not bore your audience.
- You must think of your academic essay as an enterprise by using scholastic writing approaches. The conversation that you can create with your readers must be relevant to what is happening nowadays or for the study that specific student groups need. Being able to give focus on the relativity of your written work can make it easier for readers to understand why your academic essay is important within the academic field.
- You should ensure that your thesis statement is precise, concise, and strong. When you are in the process of developing your academic essay’s thesis, you need to make sure that you are not just basing your write-up on unreliable information. Always refer to evidence, facts, and real data as it can help you strengthen your claims. More so, do not forget to reference your essays when necessary.
Things to Remember When Identifying the Purpose of Your Academic Essay
An academic essay always has to be relevant. It needs to be beneficial to a specific group or to the majority of the academic community. The motive of your essay is very important to be considered as it can identify whether you can be of help to the people who need a particular educational reference. Here are a few things that you need to remember when identifying the purpose of your own academic essay:
- Do not create an academic essay just for the sake of passing it. Your academic essay is more than an assignment or a project. There are some last minute essay writing activities that are done in various fields especially if students think that an academic essay is just a part of their requirements. However, what these students do not know is that an academic essay is a representation of themselves. It showcases the thoughts of the students, what they have learned may it be in class or through self-discovery, and how they are impacted by certain issues and subjects of discussion. This is where the value of a Free Essay and an Informative Essay becomes evident, as both types of essays encourage students to express their understanding and insights on a given topic freely and informatively.
- Be precise with the purpose of your writing. An academic letter is not just a document that can showcase your mastery when it comes to a particular academic subject. It can talk about a specific subject or it can also be a general paper that can provide a lot of information about your experiences and/or insights. This is where the importance of a Self-Introduction Essay comes into play, allowing you to present a personal narrative that reflects your academic journey and achievements. Similarly, an Expository Essay helps in laying out facts and an unbiased analysis of a topic, further enriching the academic discourse. If you will have a precise purpose when writing an academic essay, there is no doubt that your essay will not be pointless.
- Always think of the best case that can help you represent your thoughts. Your style of writing, as well as the entire document’s format and content, can help you realize your ideas. This includes the succinctness and clarity often found in a Short Essay , where the challenge is to convey your thoughts within a limited word count effectively. Similarly, a Scholarship Essay requires you to articulate your achievements and aspirations in a way that resonates with scholarship committees, demonstrating your potential and need for financial support. With this, your point of writing can easily be identified by readers. Being able to present your purpose the best way possible can add up to the success of your academic paper.
Developing an Academic Essay
For you to be able to persuade your readers with the content of your academic essay, there is a need for you to present a structure that can easily identify your claims, arguments, observations, and/or factual presentations. Integrating a Student Essay can demonstrate the personal perspective or learning journey of an individual, making your arguments more relatable. Similarly, incorporating a Travel Essay could enrich your essay by providing unique insights and observations from different cultures or environments. Being clear about how you present your idea is essential for people to see the context of your academic essay.
If you have an organized manner of putting together the concepts of your academic essay, then validating your thesis statement can be more evident. To avoid common essay mistakes and other negative factors that can affect your desired output, here is a basic guide on how you can develop your own academic essay:
- Start by creating a strong thesis statement. Identify your stand and make sure to strictly present evidence that can help you claim its authenticity and validity. Reveal evidence after your thesis statement presentation. Your thesis statement serves as your introduction speech . It lets your readers know the topic of your academic essay and what they can expect from the entire article.
- Establish the context of your essay after your thesis statement. The way that you approach your topic can let readers know whether it is the specific approach that they also need for their undertakings. There are different contexts that can be used within the same subject, so you have to make sure that you will be clear when it comes to identifying the part of the topic that you are going to talk about. This clarity can be achieved through a Descriptive Essay , where vivid descriptions and details about the topic can enlighten and engage the reader. Additionally, understanding the Parts of an Essay is crucial in structuring your thoughts and arguments effectively. Limiting your topic discussion can help you give more focus to what is important for your discussion, ensuring that each part contributes meaningfully to the whole.
- Create the next paragraphs based on the data that can support your thesis statement. The body of your academic essay can be based on your observations, reviews, statements and research outputs. You can present these items separately through the usage of various paragraphs. However, there are instances where it will be better if you can combine or compare to evidence to make your statements more effective.
- Conclude. Your conclusion is as important as your introduction. If you believe that you have created a strong introduction, you have to maintain that until the end of your academic essay. Sum up all the information that you have presented so that people can identify whether your conclusion has lived up to the content of what you have written. Your conclusion can also be used to assess whether your thesis statement has been carried within the entirety of your discussion.
Importance of a Well-Defined Thesis Statement in an Academic Essay
A thesis statement is a paragraph or a set of paragraphs that identifies your stand about your subject. There is a need for this statement to be created as it can affect the entirety of your academic paper. Here are some of the reasons why it is important to develop an effective thesis statement before and while writing your academic paper:
- Your thesis statement is a reflection of your actual idea. This helps you present the point that you would like to make and the message that you actually want to disseminate to your readers. Through a thesis statement, you can organize the evidence that are relevant to your claims based on their relevance to the topic and how you view it as a writer.
- Your thesis statement can guide you within the entirety of your writing processes. Just because you have already done an initial thesis statement does not mean that you are going to fully stick with it until the end of your writing. There are instances where thesis statements are developed or even changes during the creation of an academic essay depending on how the research about the topic has evolved.
- Your thesis statement can allow you to establish originality. Since your academic essay can be based on your research findings and observations, your thesis statement can be your platform to specify what you have come up with. Through a well-defined thesis statement, you can set your output apart from other essay examples that have been written by professionals and other entities in the field of academics.
- Your thesis statement is one of the items that the audience will look at when referencing for credibility and validity. Academic essays need to have a strong initial impact on readers. This statement can help them be focused on a particular standpoint which can enlighten them about your views and opinions, and how these are essential to be considered.
- Your thesis statement can help your readers immerse in your academic essay. The material that you will be coming up with can be reviewed by different people. Depending on the field of education where you are currently in, you need to make sure that your readers can see patterns of evidence presented so they can clearly see how you were able to generate and come up with insights. You have to ensure that the thesis statement that you have created contains the most promising thought so you can get the trust or even the acceptance of your readers about your academic essay’s subject.
Guidelines in Writing an Academic Essay
The course materials that you need to talk about within an academic essay can reflect your level of understanding about the subject. Simply put, an academic essay can be an evidence of the depth of your research procedures and all the other activities that you have executed so that you can support the content of your written output. Listed below are some of the guidelines that can be useful to your academic essay writing processes.
- Always analyze your essay prompt or the question that you need to answer or explain. You have to know whether you are tasked to argue, analyze, or discuss the topic. There will be times where you also need to compare the items present in your subject or explain the underlying factors that can affect your topic.
- Make sure that you will research about what you will write about . Your academic essay can only be fully-maximized if you can present facts. Primary research may be a helpful bit a more precise review of your research topic can help you gather more information that can be helpful in the development of your content. Always assess your sources of information so you can ensure that they are credible.
- Create a draft so that you will have a guide when writing your academic essay. If you will be organized when writing your academic essay, you can create an output that is well-curated and comprehensive. With this, your academic essay can provide more impact to your readers. This can also help you gather your thoughts first and identify how you can put them all together in the most cohesive and efficient way possible.
If you still do not feel confident in writing your own academic essay from scratch, then you can refer to templates and samples which you can download online. Doing this will allow you to be more familiar with the common content and basic formats that are usually seen in an academic essay. When using a template as a guide, always make sure that it is applicable to the study that you are practicing or the academic field or discipline where you will use your academic essay.
As a student, there will always be an instance where we will be required to write an academic essay. If you want to create an academic essay that is both outstanding and relevant, always put the items that we have discussed above in mind.
Setting the Stage for Essay Writing Success
- Understand the Assignment: Carefully read and comprehend the essay prompt or assignment to grasp its requirements and objectives.
- Topic Selection: Choose a relevant and interesting topic that aligns with the assignment.
- Research: Gather credible sources and information related to your topic. Take thorough notes and document your sources.
- Thesis Statement: Develop a strong, clear, and concise thesis statement that presents the main argument of your essay.
- Outline: Create an outline that organizes your essay into sections, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each section should have a clear purpose.
- Writing Draft: Begin writing your essay, keeping the introduction engaging, and ensuring each body paragraph addresses a single point or idea supported by evidence.
- Citations: Properly cite sources as you write, following a recognized citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
- Edit and Revise: Review and revise your draft, focusing on grammar, clarity, coherence, and organization.
- Proofread: Carefully proofread your essay for errors in spelling, punctuation, and sentence structure.
- Final Review: Double-check that your essay fulfills the assignment requirements, including formatting, citations, and references.
How do you write an academic essay?
- Understand the Assignment: Read the essay prompt or assignment thoroughly to grasp its requirements and objectives.
- Research: Gather relevant sources and information from books, articles, and credible online sources.
- Plan and Outline: Create an outline with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each section should have a clear purpose.
- Thesis Statement: Develop a strong thesis statement that presents the main argument of your essay.
- Introduction: Start with a compelling hook, provide background information, and present your thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Each paragraph should focus on a single point or idea, supported by evidence or examples. Use topic sentences to introduce the main idea of each paragraph.
- Citations: Cite sources properly using a recognized citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- Analysis and Critical Thinking: Analyze and evaluate the evidence or arguments presented, and make connections between them.
- Transition Sentences: Use transition words and phrases to connect ideas between paragraphs.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main points, restate the thesis, and provide a thoughtful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Academic Essay Characteristics
Academic essays are distinguished by several key characteristics that set them apart from other types of writing. These features ensure that essays meet the rigorous standards of academic discourse and contribute effectively to scholarly conversations. Here are the primary characteristics of academic essays:
- Clear Purpose : An academic essay is written with a clear purpose, often to argue a point, present an analysis, or discuss a research finding. The purpose guides the structure and content of the essay.
- Structured Format : It follows a structured format with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. This organization helps present arguments and evidence in a coherent and logical manner.
- Thesis Statement : A distinctive feature is the thesis statement, a concise summary of the main argument or claim, usually found at the end of the introduction. It sets the direction for the entire essay.
- Critical Analysis : Academic essays involve critical analysis of ideas, texts, or situations. Writers assess evidence, debate viewpoints, and use logic to develop their arguments.
- Evidence-Based Arguments : Claims made in academic essays are supported by evidence from credible sources. This includes data, statistics, research findings, and quotations from experts.
- Formal Tone and Style : The writing adopts a formal tone and style, avoiding colloquial language, personal anecdotes (unless relevant), and slang. It maintains an objective and professional voice.
Types of Academic Writing
Academic writing encompasses a variety of types, each serving a specific purpose and adhering to a particular format. Here are some of the main types of academic writing:
- Descriptive Writing : This type focuses on describing a character, event, or situation in detail. It’s often used in reports or descriptive essays, where the goal is to provide a clear picture of the subject to the reader.
- Analytical Writing : Analytical writing breaks down complex information into smaller components for better understanding. It involves comparing and contrasting, classifying, and analyzing causes and effects. This type is common in research papers and literature reviews.
- Persuasive Writing : Persuasive writing aims to convince the reader of the writer’s viewpoint or argument. It is characterized by a strong thesis statement, clear evidence, and logical reasoning to persuade the reader. Opinion pieces, argumentative essays, and proposals often employ persuasive writing.
- Expository Writing : Expository writing is used to explain or inform the reader about a specific topic in a clear, concise, and logical manner. It focuses on presenting facts, statistics, and examples without the writer’s personal opinions. This type includes most essays, many types of reports, and certain types of research papers.
- Reflective Writing : This type involves the writer reflecting on their personal experiences, thoughts, or feelings regarding a particular subject or experience. Reflective writing is subjective and is often used in journals, blogs, and reflection essays in educational settings.
- Critical Writing : Critical writing evaluates and critiques the work of others, such as books, articles, or artworks. It involves assessing the strengths and weaknesses of arguments, evidence, and methodologies. Literature reviews, critique essays, and certain types of research papers often require critical writing.
- Narrative Writing : Although less common in strict academic settings, narrative writing is used in certain disciplines to tell stories or describe events chronologically. Personal statements and some types of qualitative research may employ narrative writing to convey experiences and observations.
- Report Writing : Reports convey information from a writer to a reader, focusing on facts and evidence. They are structured and include sections like an introduction, methodology, findings, and conclusions. Lab reports, business reports, and technical reports are examples of this type.
Academic Writing Principles
Academic writing is governed by a set of core principles designed to ensure clarity, precision, and rigor in scholarly communication. Understanding and adhering to these principles is essential for effective academic writing. Here are the key principles:
- Clarity : Writing should be clear and understandable, avoiding unnecessary jargon and complexity to ensure that the reader can easily follow the argument or narrative.
- Coherence : The text should be logically organized, with a clear structure that guides the reader through the argument or discussion. Each part of the writing should connect to the others in a meaningful way.
- Conciseness : Academic writing should be concise, conveying ideas in as few words as necessary. This does not mean oversimplifying, but rather avoiding redundancy and verbosity.
- Objectivity : Writers should strive for objectivity, presenting information and arguments based on evidence rather than personal opinions or biases. This includes acknowledging counterarguments and limitations.
- Precision : Precision involves using the exact words to convey your meaning and being specific about your claims, evidence, and references. This also means accurately citing sources and providing specific data when necessary.
- Evidence-Based Argumentation : Arguments should be supported with appropriate evidence, such as data, examples, and citations from authoritative sources. This principle underscores the importance of research and verification in academic writing.
- Formality : The tone of academic writing is formal, which means avoiding colloquial language, contractions, slang, and humor. Formality also involves using the passive voice where appropriate and avoiding personal pronouns when making general arguments.
- Citation and Referencing : Proper citation and referencing of sources are fundamental to academic writing. This practice not only gives credit to original authors but also allows readers to verify sources and understand the basis of the evidence presented.
- Originality and Plagiarism Avoidance : Academic writing must be original and free from plagiarism. This means that writers should produce their own work based on their research and ideas and appropriately cite any sources they use.
- Critical Thinking : Effective academic writing reflects critical thinking, challenging assumptions, evaluating evidence, and synthesizing ideas from various sources to offer new insights or perspectives on a topic.
How do you start an academic essay sample?
Begin an academic essay sample with a captivating hook, provide context on the topic, and conclude the introduction with a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines your main argument.
What is the opening line of an academic essay?
The opening line of an academic essay should engage the reader’s interest, introduce the topic, and provide a sense of the essay’s focus and importance.
What not to write in an academic essay?
In an academic essay, avoid personal opinions, emotional language, unsubstantiated claims, informal language, and plagiarism. Focus on evidence-based arguments and adhere to academic standards and conventions.
How do you write an academic essay quickly?
To write an academic essay quickly, start with a clear thesis, outline main points, research efficiently, focus on key evidence, and minimize editing while maintaining proper citations and structure.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an academic essay on the impact of technology in education
Explain in an academic essay how climate change affects global agriculture
- Study Documents
- Learning Tools
Writing Guides
- Citation Generator
- Flash Card Generator
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Introduction Generator
- Literature Review Generator
- Hypothesis Generator
- Human Editing Service
- Essay Hook Generator
- Essay Paragraph Generator
- Lesson Plan Generator
Writing Guides / Complete Guide to Essay Format: MLA, APA, and Chicago Explained
Complete Guide to Essay Format: MLA, APA, and Chicago Explained

Introduction
Content is king, but mastering the mechanics of academic writing is equally important. That’s why formatting your essay matters. Proper formatting allows you to present your essays and term papers clearly, logically, and academically so that it is easy for readers to follow your argument and for instructors to assess your work. Poor formatting, on the other hand, can lead to point deductions, even if the content of your essay is strong.
What is Proper Essay Format?
The format of an essay refers to its basic structure, layout, and appearance on the page. It includes elements such as margins, font size, line spacing, and citation style, among others. Although it may seem daunting at first, mastering the different essay formats is not as difficult as it might appear. The more essays you write, the more familiar you will become with these formats. (Check out this article for more info on how to write an essay ).
Importance of Following Proper Format
Understanding and applying the correct essay format is essential for several reasons. First, it demonstrates your attention to detail and your ability to follow academic conventions. Proper formatting also improves the readability of your essay, allowing your ideas to be presented in a clear and organized manner. Proper formatting is what lets you meet the academic standards expected in your field of study.
Overview of Main Formats
There are several widely recognized essay formats, each commonly used in different academic disciplines. The Modern Language Association ( MLA ) format is often used in the humanities, particularly in literature and language studies. The American Psychological Association ( APA ) format is typically used in the social sciences, such as psychology and education. The Chicago Manual of Style, or Chicago format , is frequently used in history and some social science fields. Each format has its own set of rules for citations, references, and overall layout.
View 120,000+ High Quality Essay Examples
Learn-by-example to improve your academic writing
Standard College Essay Format
There is no universally “right” college essay format, be we do have some commonly accepted guidelines. Professors may have specific preferences, so understanding the standard structure and formatting rules will help you adapt to any requirements.
Basic Components of Any Essay
- Title Page : This usually includes the title of your essay, your name, the course name, the instructor’s name, and the date of submission. The title should be centered and written in a standard font, without italics or underlining.
- Introduction : The introduction is the opening paragraph of your essay, where you present the topic and your thesis statement . It should contain a hook, a brief overview of the main points that will be discussed in the body of the essay, and your main point.
- Body : The body of the essay is where you develop your arguments or analysis in detail. Each paragraph of the body should focus on a specific point or piece of evidence that supports your thesis.
- Conclusion : The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay, where you summarize the main points and restate your thesis in light of the evidence presented. It should contain no new info, but should leave lasting impression on the reader so as to reinforce the significance of your essay.
- Bibliography : Also known as the Works Cited or References page, the bibliography lists all the sources you cited in your essay. The format of the bibliography varies depending on the citation style (MLA, APA, Chicago, etc.), but it typically includes the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and date.
General Formatting Rules
- Fonts : Standard college essays typically use a uniform font for consistency and readability. Times New Roman is the most widely accepted font, though Arial is sometimes permitted. The font size is usually set to 12 points. Font should be consistent across the entire document.
- Line Spacing : Most college essays require double spacing. Occasionally, you may be asked to use single spacing or 1.5 spacing, depending on the instructor’s preference or the specific assignment guidelines.
- Margins : The standard margin size for college essays is one inch on all sides (top, bottom, left, and right). This margin size is typically the default setting in Word.
- Page Numbers : Including page numbers in your essay is generally expected, especially for longer assignments. Page numbers are usually placed in the upper right corner of each page, sometimes accompanied by your last name or the title of the essay.
- Title Page : Short essays often do not require a title page, but for longer essays or research papers, a title page will probably be mandatory. If required, the title page should follow the specific format outlined by your instructor (APA, MLA, etc.), typically including the title of the essay, your name, course details, and submission date.

MLA Essay Format
Mla structure and layout.
MLA format is known for its simplicity. The following are the basic components of an essay written in MLA format:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman) : Times New Roman in 12-point font is the standard typeface used in MLA format.
- First Line Indent : Each paragraph in an MLA-formatted essay begins with an indentation of the first line, typically set at half an inch from the left margin. This indentation visually separates paragraphs, which makes the essay easy to read.
- Double-Spacing : The entire essay should be double-spaced, including the text, block quotes, and the Works Cited page. Double spacing should be consistent throughout. It is especially helpful as it allows space for instructors to make annotations.
- 1-Inch Margins : MLA format requires uniform 1-inch margins on all sides of the page (top, bottom, left, and right), which keeps the page balanced in appearance.
- Header : Unlike APA format, MLA does not usually require a title page. Instead, your name, your professor’s name, the course name, and the date should be listed in the upper left-hand corner of the first page. Below this information, the title of the essay should be centered and written in standard title case (capitalizing the first and main words of the title). A header with your last name and page number should appear in the upper right corner of each page, beginning with the first page.
MLA In-Text Citations and Works Cited
MLA format has specific guidelines for citing sources both within the text and in the Works Cited page. These citations are crucial for giving credit to the original authors and for allowing readers to trace the sources of your information.
- In-Text Citations : In MLA format, in-text citations are brief and are usually placed at the end of the sentence before the period. They include the author’s last name and the page number where the information was found, all within parentheses. For example: (Smith 123). If the author’s name is mentioned in the sentence, only the page number is required in the citation: (123). Even when paraphrasing or summarizing, the page number must be included, which can be a challenge but is essential to meet MLA standards.
- Works Cited Page : The Works Cited page appears at the end of the essay and lists all the sources referenced in your paper. Each entry should be formatted with a hanging indent, where the first line of the citation is flush with the left margin, and subsequent lines are indented. Entries are listed alphabetically by the author’s last name or by the title if no author is provided. The general format for a book citation in MLA is: Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book . Publisher, Year of Publication.

MLA Common Mistakes to Avoid
While MLA format is straightforward, there are common mistakes that students often make:
- Incorrect In-Text Citations : Failing to include the page number, using the wrong format for the author’s name, or placing the period outside the parentheses are frequent errors. Always double-check your in-text citations for accuracy.
- Improper Works Cited Formatting : Not following the correct order, incorrect use of italics or quotation marks, and missing publication details are common pitfalls. Ensure each entry adheres to MLA guidelines.
- Missing or Incorrect Header : Forgetting to include the header with your last name and page number on each page can lead to a lower grade. Also, ensure that the header is properly aligned with the right margin.
Example of MLA Format
Here’s a simplified example of how the first page of an MLA-formatted essay might look:
First Page of an MLA Paper :

APA Essay Format
Apa structure and layout.
APA format follows a set structure that includes a title page, abstract, body, and references.
- Title Page : The title page in APA format is crucial as it sets the tone for your paper. It includes the title of your essay, your name, and your institutional affiliation, all centered on the page. The title should be concise and informative, reflecting the content of your paper. Below the title, your name appears, followed by your institution (e.g., university name). Some instructors may ask for additional information like the course title, instructor’s name, and the date.
- Abstract : The abstract is a brief summary of your paper, usually between 150-250 words. It gives a summary of your research, including the research question, methods, results, and conclusions. The abstract appears on its own page, right after the title page, and is typically a single paragraph without indentation. Abstracts are used in longer research papers and dissertations to give readers a quick snapshot of the study’s content and findings.
- Body : The body of an APA paper is where you present your argument or findings. It starts on a new page after the abstract and is divided into sections such as the introduction, method, results, discussion, and conclusion, depending on the type of paper you are writing. Each section may include subheadings to improve organization and readability.
- References : The reference page, which comes at the end of your paper, lists all the sources cited in the text. This page follows specific APA formatting rules, including the use of a hanging indent and alphabetical order by the authors’ last names. The reference entries must include detailed information about each source, such as the author’s name, publication year, title of the work, and source.
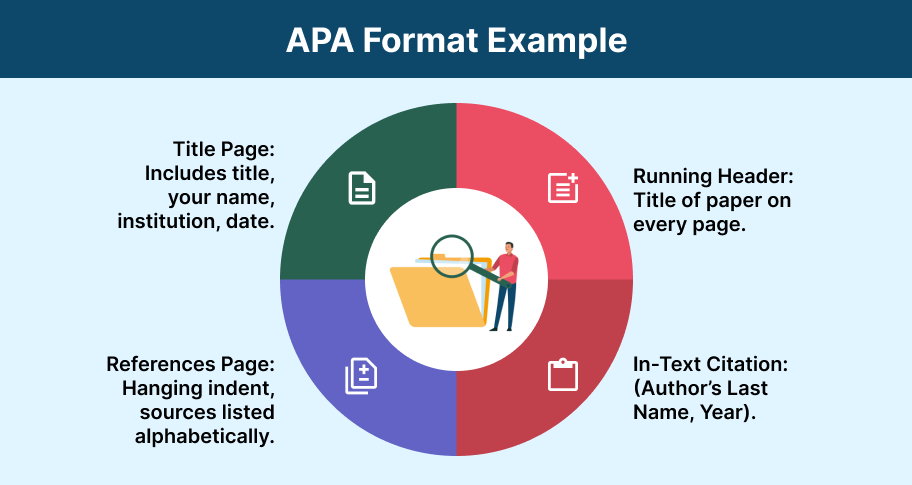
APA In-Text Citations and References
APA style uses the author-date citation method, which includes the author’s last name and the publication year in the text. This method allows readers to locate the full citation in the reference list easily.
- In-Text Citations : In-text citations in APA format are concise. For example, if you’re citing a book by John Doe published in 2020, the citation would appear as (Marve, 2024). If you directly quote a source, you must also include the page number: (Smith & Wesson, 2023, p. 15). These citations are usually placed at the end of a sentence before the period.
- References : Every in-text citation must correspond to an entry in the reference list. The reference list provides full details about the source, formatted in a specific way. For a book, the format is: Author’s Last Name, First Initial(s). (Year). Title of the book . Publisher.
APA Headings and Subheadings
Headings and subheadings are essential in APA format as they help organize the content and guide readers through the paper. APA uses a specific hierarchy of headings:
- Level 1 Heading : Centered, Bold, Title Case (e.g., Introduction)
- Level 2 Heading : Flush Left, Bold, Title Case (e.g., Review of Literature)
- Level 3 Heading : Indented, Bold, Sentence case, ending with a period. (e.g., Methods)
Subheadings break down sections into more detailed parts, making your essay easier to follow.
Example of APA Format

Chicago Essay Format
Overview of chicago style.
Chicago style follows a standard set of formatting guidelines, which include:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman) : Chicago style typically uses Times New Roman in 12-point font, which is considered a classic and highly readable typeface.
- First Line Indent : Each paragraph should begin with a half-inch indent, creating a clear separation between sections of text.
- Double-Spacing : The entire document, including block quotes, notes, and bibliography, should be double-spaced, providing ample room for comments or corrections.
- 1-Inch Margins : Chicago style requires 1-inch margins on all sides of the page, which is standard for most academic papers.
Chicago style is known for its flexibility, especially in the way it handles citations. Unlike MLA or APA formats, which rely on in-text parenthetical citations, Chicago style allows for the use of either footnotes or endnotes, which are a less obtrusive way to cite sources.
Chicago Footnotes vs. Endnotes
- Footnotes : Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page on which the reference is made. They are numbered consecutively throughout the essay. Footnotes are preferred when you want the reader to have immediate access to the source or explanation while reading the text. For example, after quoting a source, a small superscript number is placed at the end of the sentence, corresponding to a footnote at the bottom of the page, where full citation details are provided.
- Endnotes : Endnotes, like footnotes, are numbered consecutively but are placed at the end of the essay, just before the bibliography. Endnotes are often used in longer works where multiple citations might overwhelm the page layout. While they serve the same purpose as footnotes, they require the reader to flip to the end of the document to see the citation, which some writers prefer to keep the main text uncluttered.
Both footnotes and endnotes in Chicago style include detailed citation information, such as the author’s name, title of the work, publication details, and page numbers. The choice between footnotes and endnotes often depends on the nature of the paper and the instructor’s preference.
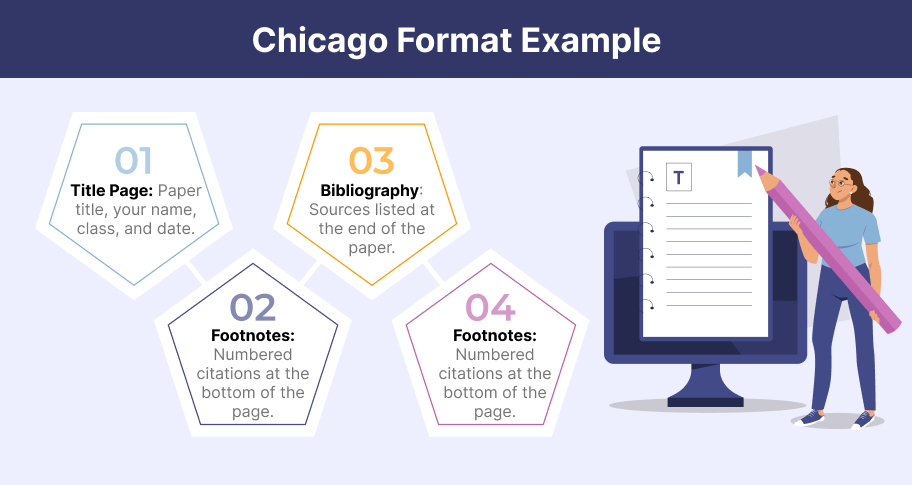
Chicago Bibliography Format
The bibliography in Chicago style lists all sources referenced in the paper. The bibliography page appears at the end of the essay and should follow these guidelines:
- Alphabetical Order : Entries in the bibliography are listed alphabetically by the author’s last name. If no author is provided, the title of the work is used.
- Hanging Indent : Each entry begins flush with the left margin, and subsequent lines are indented by half an inch. This format is known as a hanging indent.
- Detailed Citations : Each entry should include the author’s name, the title of the work (italicized), the place of publication, the publisher, and the year of publication. For example: Smith, John. The History of Modern Europe . New York: Random House, 2020.
Example of Chicago Format
Here’s an example of how a Chicago-style essay might look:
Title Page Example :

Key Differences Between MLA, APA, and Chicago
Citation styles.
- MLA (Modern Language Association) : MLA style is typically used in the humanities, particularly in literature, philosophy, and the arts. Citations are made using brief parenthetical references within the text, including the author’s last name and page number (e.g., Mason 413). The full citation details are provided in a Works Cited page at the end of the document.
- APA (American Psychological Association) : APA format is prevalent in the social sciences, including psychology, sociology, and education. It uses the author-date method for in-text citations, where the author’s last name and the year of publication are included (e.g., Como, 2020). A References page at the end lists all sources in full detail.
- Chicago Style : Chicago style, often used in history, political science, and the arts, offers two citation methods: the Notes and Bibliography system, which uses footnotes or endnotes along with a bibliography, and the Author-Date system, similar to APA but less commonly used. Footnotes or endnotes provide detailed source information at the bottom of the page or at the end of the paper, making this style flexible for detailed commentary.
Paper Structure
The structure of a paper also varies among these formats:
- MLA : MLA format is straightforward, typically consisting of a title page (optional), an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. It does not require a separate title page; instead, the student’s name, instructor’s name, course, and date are placed at the top of the first page.
- APA : APA format is more structured and includes a title page, abstract, main body, and references. The title page presents the title, author’s name, and institutional affiliation, while the abstract provides a brief summary of the paper. APA also often uses headings and subheadings to organize content clearly.
- Chicago : Chicago format is flexible and can vary based on the type of paper. A typical Chicago-style paper includes a title page, the main body of text, and a bibliography. When using the Notes and Bibliography system, Chicago style also incorporates footnotes or endnotes, which can make the structure appear more complex.
Where and When to Use Each Format
Each format is suited to specific academic disciplines:
- MLA : Best used in humanities subjects, especially in writing-intensive courses where the focus is on literary analysis, criticism, or cultural studies.
- APA : Ideal for the social sciences, where research often involves data analysis, experiments, and empirical studies. APA’s structured format helps present research findings clearly.
- Chicago : Often required in history, art history, and some social sciences. It is particularly useful when extensive citation or commentary is needed, thanks to its footnote and endnote options.
Special Essay Formats
When you’re applying for a scholarship, submitting a college application, or crafting a research or persuasive essay, know that each format has unique elements that guide how you should present your work.
Scholarship Essay Format
Scholarship essays are critical for students aiming to secure financial aid for their education. Unlike standard academic essays, a scholarship essay is deeply personal and written in the first person. It focuses on your achievements, goals, and reasons for deserving the scholarship. Here are some key aspects of the scholarship essay format:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman or Arial) : This is the standard for readability.
- First Line Indent : Each paragraph should begin with an indentation, creating a clear structure.
- Double-Spacing : Double-spacing improves readability and allows room for comments.
- 1-Inch Margins : Standard margins provide a clean, professional look.
Unlike academic essays that are typically written in the third person, scholarship essays are personal narratives. The essay should show your determination, goals, and the unique qualities that make you a worthy candidate. Discuss your academic achievements, community involvement, and future aspirations, while avoiding generic statements. Tailor each essay to the specific scholarship, addressing the organization’s values and how they align with your goals.
College Application Essay Format
College application essays are crucial in the admissions process. They offer a glimpse into your personality, values, and potential contributions to the college community. These essays are also written in the first person and vary in length, from short responses to longer personal statements. Key formatting elements include:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman or Arial) : Consistency in font choice helps maintain a formal tone.
- First Line Indent : Indenting paragraphs helps organize your thoughts.
- Double-Spacing : This spacing standard enhances readability and presentation.
- 1-Inch Margins : Uniform margins contribute to a polished appearance.
A strong college application essay often begins with a thoughtful introduction, perhaps a personal anecdote or a significant experience that shaped your character. The body of the essay should go into your interests, goals, and why you are drawn to the specific college or program. Be authentic and reflective. This essay is your chance to stand out among many applicants, so it’s important to convey your own unique story.
Research Essays (Extended Essays, IB Essays)
Research essays, such as those required for International Baccalaureate (IB) programs or extended essays, are more formal and structured than personal essays. These essays require rigorous research and a thorough analysis of the topic. The format for research essays generally includes:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman or Arial) : A professional and readable font choice.
- First Line Indent : Each paragraph should be clearly indented.
- Double-Spacing : Allows for clear presentation and space for feedback.
- 1-Inch Margins : Standard for most academic papers.
- Title Page and Abstract : Depending on the requirements, these elements may be necessary, particularly in extended essays or formal research papers.
Research essays are structured around a thesis statement, with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. The body should be divided into sections, each addressing different aspects of the research question, supported by evidence from credible sources. Use proper citation to avoid plagiarism charges and to give credit to original ideas.
Reflective and Persuasive Essays
Reflective and persuasive essays require different approaches but share some formatting similarities with standard essays.
Reflective Essay : Reflective essays explore personal experiences and the insights gained from them. The format may include:
- 12-Point Font (Times New Roman or Arial) .
- First Line Indent .
- Double-Spacing .
- 1-Inch Margins .
In a reflective essay, you may be asked to consider a personal experience or react to a text, event, or artwork. The essay should include a description of the experience or object of reflection, followed by an analysis of its impact on you. The tone can be informal, but the structure should remain coherent and well-organized.
Persuasive Essay : Persuasive essays aim to convince the reader of a particular point of view. They follow a more traditional academic structure:
Persuasive essays require a strong thesis statement, clear arguments supported by evidence, and a conclusion that reinforces your position. Use rhetorical strategies like ethos, pathos, and logos to strengthen your argument and persuade the reader effectively. Acknowledge opposing views and refute them to build a more compelling case.
Additional Formatting Tips
Creating an outline.
An outline helps you organize your thoughts and structure your essay logically. It serves as a roadmap, guiding you through each section of your paper and ensuring that your arguments flow coherently. An effective outline typically includes:
- Introduction : Start with your thesis statement, followed by a brief overview of the main points you will discuss.
- Body Paragraphs : List the key points or arguments you plan to make, organized into sections. For each section, include supporting evidence or examples.
- Conclusion : Summarize your main points and restate your thesis in a new light, reflecting the arguments made in the body.
Using bullet points or numbering in your outline can help you maintain a clear hierarchy of ideas. While the outline itself is not part of the final essay, creating one can save time during the writing process and improve the overall structure of your paper.
Formatting Headings and Subheadings
Headings and subheadings are essential for breaking up the text and guiding readers through your essay. They provide a clear structure, making it easier for readers to follow your argument. Different formatting styles have specific rules for headings and subheadings:
- MLA : Generally does not require headings, but when used, they should be formatted consistently without a boldface or italics.
- APA : APA uses a five-level heading system. Level 1 is centered and bold, Level 2 is flush left and bold, and so on, down to Level 5, which is indented, bold, and italicized.
- Chicago : Offers flexibility, but generally, headings are bolded or italicized, and subheadings are formatted similarly but in a smaller font size or with less emphasis.
Using clear and consistent formatting for your headings and subheadings helps organize the content and makes your essay more reader-friendly.
Formatting Tables, Charts, and Appendices
Including tables, charts, and appendices in your essay can be an effective way to present data, summarize information, or provide additional context without overcrowding the main text. Proper formatting of these elements is crucial to maintain the professionalism of your document.
- Labeling : Each table and chart should be labeled with a number (e.g., Table 1, Figure 2) and a descriptive title.
- Placement : Tables and charts can be placed within the text close to where they are referenced or included at the end of the document in an appendix.
- Formatting : Ensure that tables are clear, with consistent font and spacing, and that charts are accurately labeled with legends if needed.
- Purpose : Appendices are used to include supplementary material that is relevant but not essential to the main text, such as raw data, questionnaires, or detailed explanations.
- Labeling : Appendices should be labeled (e.g., Appendix A, Appendix B) and referenced in the main text.
- Content : Each appendix should start on a new page, with the title clearly labeled at the top.
Formatting is a big aspect of academic writing that goes beyond mere aesthetics. Proper formatting gives clarity, readability, and professionalism. Whether you’re using MLA, APA, Chicago, or another style, adhering to the specific guidelines of each format will show your attention to detail and your commitment to academic standards.
A well-formatted essay not only makes your work more accessible to readers but it also improves the credibility of your arguments. Be careful about organizing your content with appropriate headings, citations, and supplementary materials like tables or appendices, so that you can turn in a well-structured and persuasive piece of writing.
Final tips: always double-check the specific requirements of your assignment and seek clarification from your instructor if needed. Utilize tools like outlines to plan your essay structure, and pay attention to the nuances of each style, such as citation formats and the use of footnotes or endnotes. Master these elements, and you’ll be able to effectively communicate your ideas and enjoy academic success.
Take the first step to becoming a better academic writer.
Writing tools.
- How to write a research proposal 2021 guide
- Guide to citing in MLA
- Guide to citing in APA format
- Chicago style citation guide
- Harvard referencing and citing guide
- How to complete an informative essay outline

How to Choose the Best Essay Topics

AI Text Detection Services

Unlock Your Writing Potential with Our AI Essay Writing Assistant

The Negative Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Tactile Learning
Essay writing: Formatting
- Introductions
- Conclusions
- Analysing questions
- Planning & drafting
- Revising & editing
- Proofreading
- Essay writing videos
Jump to content on this page:
Essays are formal documents and should look professional Advice from the Skills Team
Whilst there are no hard rules about how you format essays, there are some conventions and common practices that are best to follow. If you use the settings on this page, you will produce an acceptably formatted essay.
Document layout

Margins - between 2 cm and 2.54 cm (1 inch) all around.
Line spacing - either 1.5 or double-line spacing.
Paragraph spacing - either 1 clear line between or at least 8 pt space after each paragraph (more if double-line spaced)
Alignment - left aligned (fully justified with a straight right-edge is not recommended as this reduces readability and accessibility). Some longer essays may require subheadings which should also be left-aligned.
Indents - no indents on first lines of paragraphs are needed.
It is also good practice to put your student number and module number in the header of the document and a page number at the bottom of the page.
Text formatting
Font - the default font that comes with MS Word (currently Calibri) is fine for academic work. You may see persistent advice in handbooks that suggests you should use Times New Roman or Arial. If you prefer these, you can change it - but this is no longer a requirement.
Font size - fonts should be 11 or 12 point.
Font style - headings and subheadings, if they are required (most essays will not use them), are usually formatted in bold and should be at least 2 point sizes larger than the standard text. Underlining should be avoided as this is seen as rather dated. Some text can be formatted in italics - see our page Italics, when to use them , for guidance.
Shorter quotations in the text do not need to be italicised and should have double-quotations marks "like this" to indicate they are direct quotations. Longer quotations (what counts as this differs depending on your referencing style) should be created in their own paragraph, single spaced and indented by 1cm from both left and right margins:
For example:
Graduate attributes for employability are described as:
a set of achievements – skills, understandings and personal attributes – that makes graduates more likely to gain employment and be successful in their chosen occupations, which benefits themselves, the workforce, the community and the economy. (Yorke, 2006)
The main change in this definition compared to the earlier definition of graduate attributes from Bowden (2000) is that that the attributes are no longer ...
UoH Harvard/APA
Your reference list should be in alphabetical order (by author surname) and single line spaced. There should be a clear line space (or at least 6 pt space) between each reference. All references should be left-aligned with no indentation. For information about how to format individual references, see the Harvard Hull Referencing Guide.
UoH Footnotes
Your reference list should be in alphabetical order (by first author surname) and single line spaced. All references should be left-aligned and have a hanging indent (all but the first line are indented by approx. 1cm). For information about how to format individual references, see the Footnotes Hull Referencing Guide.
Other referencing styles
Please see your individual departmental guidance.
We provide here a Microsoft Word template that can be used for your essays. It has the correct layout and formatting, including useful styles.
- Essay template
Download this template to somewhere you can access easily. When you click to open it, it will open a new document based on the template , leaving the original intact.
- << Previous: Conclusions
- Next: Analysing questions >>
- Last Updated: Dec 5, 2024 2:22 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/essays
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem

- Log in Start For Free
Essay Format Made Simple: Academic Style Explained (With Examples)

Introduction
Writing a well-structured essay can be daunting, especially if you’re unsure about formatting requirements. Academic essay formats provide a standardized structure that ensures clarity, readability, and professionalism. From margins and spacing to citations and references, each element plays a role in enhancing the reader’s experience.
In this guide, we’ll simplify essay formatting, covering essential elements such as font size, headings, citations, and references. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to format your essays with ease.

Why Essay Format Matters
Proper essay formatting isn’t just about appearance. Here’s why it matters:
- Readability : Clear structure makes it easier for readers to follow your argument.
- Professionalism : Proper formatting demonstrates attention to detail.
- Compliance : Academic institutions have specific format guidelines that must be followed.
- Grading : Many professors assess formatting as part of the overall grade.
Key Elements of Academic Essay Formatting
1. margins and spacing.
- Margins : Use 1-inch margins on all sides (top, bottom, left, and right).
- Line Spacing : Double-space the entire essay, including the reference page.
- Paragraph Indentation : Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
This is an example paragraph. Notice how the first line is indented, while the following lines are aligned to the left margin. Double-spacing is used throughout the entire document.
External Resource: Learn how to adjust margins and spacing in Microsoft Word’s guide or Google Docs’ formatting instructions .
2. Font and Font Size
- Font : Use clear, legible fonts such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri.
- Font Size : Use 12-point font for body text. Titles and headings can be slightly larger (14 or 16 points).
Example: Your entire essay’s text should be in 12-point Times New Roman, with any subheadings in bold.
External Resource: Explore font best practices on Google Fonts .
3. Title Page
Some essays, especially those in APA format , require a title page. Here’s what to include:
- Title of the Essay : Centered and bolded, about one-third down the page.
- Your Name : Below the title.
- Course Name and Number : Listed under your name.
- Date : Submission date.
Example Title Page (APA Style):
The Impact of Climate Change on Urban Areas [Your Name] Environmental Studies 101 [Date of Submission]
External Resource: Check Purdue OWL’s guide for detailed information on title pages.
4. Headings and Subheadings
Headings and subheadings help organize your essay, making it easier to read and understand.
- APA Style : Uses five levels of headings, with specific formatting for each.
- MLA Style : Usually does not use section headings, but subheadings are allowed in longer essays.
Example (APA Headings):
Level 1 Heading : Bold, Centered (e.g., "Introduction") Level 2 Heading : Bold, Left-aligned (e.g., "Methods") Level 3 Heading : Bold, Indented, Ends with a period (e.g., "Research Design.")
External Resource: Review detailed heading guidelines on APA’s official page .
5. In-text Citations and References
- APA Style : Uses (Author, Year) for in-text citations.
- MLA Style : Uses (Author Page) for in-text citations.
- Chicago Style : Uses footnotes or endnotes for citations.
Example (APA Style In-text Citation):
Research indicates that early childhood education improves cognitive outcomes (Smith, 2020).
- Reference List : List all sources alphabetically on a new page at the end of the essay.
External Resource: Use free tools like EasyBib or Cite This For Me to generate properly formatted citations.
6. Page Numbers and Running Headers
- Page Numbers : Placed in the upper-right corner on every page.
- Running Header : Required for APA format. It’s a short title placed in the upper-left corner of each page.
Example of a Running Header (APA Style):
Running head: CLIMATE CHANGE AND URBAN AREAS
External Resource: Check out Purdue OWL’s APA formatting guide for more on headers.
Common Essay Formatting Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring Margins : Stick to the 1-inch margin rule.
- Inconsistent Font Sizes : Use 12-point font throughout.
- Incorrect Citation Style : Follow the citation style required by your institution.
- Missing Page Numbers : Ensure page numbers are present on every page.
- Lack of Indentation : Always indent the first line of every paragraph.
Introducing PaperGen : Revolutionizing Essay Writing
In the fast-paced world of academia, managing deadlines while producing high-quality papers can feel overwhelming. This is where PaperGen , an innovative AI-powered platform, steps in to transform the paper-writing experience. Designed for learners seeking to balance originality, quality, and efficiency, PaperGen offers features tailored to meet the demands of academic writing.
How PaperGen Enhances Your Essay Writing
AI-Powered Draft Generation
PaperGen creates unique paper drafts tailored to your topic and requirements. Its sophisticated algorithms ensure the content is well-researched, logically structured, and undetectable by AI detection tools, maintaining academic integrity.
Outline and Formatting Assistance
The platform provides a detailed framework to guide your writing process. From opening sections to closing summarys, PaperGen helps you structure your paper for maximum impact.
Integrated Editing Tools
Beyond draft creation, PaperGen features an advanced editing interface that:
- Suggests rephrasing and vocabulary enhancements.
- Improves sentence structure and coherence.
- Ensures your paper meets the highest academic standards.
- Plagiarism-Free Guarantees PaperGen prioritizes originality, providing tools to verify that your paper is free from plagiarism. This feature instills confidence in your work and safeguards your academic reputation.
Why Choose PaperGen ?
- Efficiency: Save time with AI-generated drafts and intelligent editing suggestions.
- Quality: Produce papers that meet or exceed professor expectations.
- Originality: Ensure your work is unique and undetectable by AI tools.
PaperGen bridges the gap between traditional academic composition and modern technology, empowering learners to achieve academic excellence with less stress. By integrating this tool into your workflow, you can focus more on developing ideas and less on the mechanics of writing.
Mastering essay formatting is essential for creating polished, professional work. From margins and spacing to citations and headers , each element contributes to a well-organized, clear essay. Use this guide as a reference whenever you need help with formatting.
By following these guidelines, you’ll create essays that are not only visually appealing but also professional and academically sound. Happy writing!
Spark Your Content Potential with PaperGen AI
Let PaperGen be your ultimate AI paper generator and writing assistant. Effortlessly create human-like, plagiarism-free long-form content for research papers, blog posts, market analysis, and more. PaperGen has everything you need to write with confidence
Discover Related Blog Posts

Free Homework Clipart: Top Resources & Tips

Using Homework Clipart to Enhance Your Academic Presentations and Reports

Where to Find High-Quality Homework Clipart for Your Study Materials
Start composing your initial paper draft today..

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Sep 18, 2020 · There are two main things to keep in mind when working on your essay structure: making sure to include the right information in each part, and deciding how you’ll organize the information within the body. The three parts that make up all essays are described in the table below.
Are you seeking to describe, narrate, argue or explain, these being the four common purposes for writing academic essays. Below is a brief description of each purpose, or ‘mode’, illustrated with examples. • Exposition – You seek to inform your reader about a given subject and explain what it’s all about.
Jul 23, 2024 · An academic essay typically follows a clear format, including an introduction with a thesis statement, body paragraphs that provide evidence and analysis to support the thesis, and a conclusion that summarizes the main points and reinforces the essay’s central argument.
Discover everything you need to know about essay formats in this comprehensive guide. Learn how to format your essays in MLA, APA, and Chicago styles with step-by-step instructions on citations, structure, and page layout to ensure academic success.
Formatting an academic essay is essential for ensuring clarity, professionalism, and readability. From setting margins and choosing the right font to structuring citations and references, a properly formatted essay reflects your attention to detail and adherence to academic guidelines.
See details on what should be included in these parts of an academic essay below and/or within our Basic Essay Structure Infographic. The introduction is the first paragraph of an academic paper. Its purpose is to introduce a reader to the topic and to present the main point or argument.
Dec 5, 2024 · Typical layout for an essay is as shown here: Margins - between 2 cm and 2.54 cm (1 inch) all around. Line spacing - either 1.5 or double-line spacing. Paragraph spacing - either 1 clear line between or at least 8 pt space after each paragraph (more if double-line spaced)
In this guide, we walk you through what to include in the introduction, body, and conclusion of an academic essay, using paragraphs from our interactive essay example. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes.
Why Essay Format Matters. Proper essay formatting isn’t just about appearance. Here’s why it matters: Readability: Clear structure makes it easier for readers to follow your argument.; Professionalism: Proper formatting demonstrates attention to detail.; Compliance: Academic institutions have specific format guidelines that must be followed.; Grading: Many professors assess formatting as ...
Feb 9, 2015 · This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction, focused paragraphs, clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion. Each paragraph addresses a single central point, introduced by a topic sentence, and each point is directly related to the thesis statement.