
- > Machine Learning
- > Statistics

What is Hypothesis Testing? Types and Methods
- Soumyaa Rawat
- Jul 23, 2021

Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is the act of testing a hypothesis or a supposition in relation to a statistical parameter. Analysts implement hypothesis testing in order to test if a hypothesis is plausible or not.
In data science and statistics , hypothesis testing is an important step as it involves the verification of an assumption that could help develop a statistical parameter. For instance, a researcher establishes a hypothesis assuming that the average of all odd numbers is an even number.
In order to find the plausibility of this hypothesis, the researcher will have to test the hypothesis using hypothesis testing methods. Unlike a hypothesis that is ‘supposed’ to stand true on the basis of little or no evidence, hypothesis testing is required to have plausible evidence in order to establish that a statistical hypothesis is true.
Perhaps this is where statistics play an important role. A number of components are involved in this process. But before understanding the process involved in hypothesis testing in research methodology, we shall first understand the types of hypotheses that are involved in the process. Let us get started!
Types of Hypotheses
In data sampling, different types of hypothesis are involved in finding whether the tested samples test positive for a hypothesis or not. In this segment, we shall discover the different types of hypotheses and understand the role they play in hypothesis testing.
Alternative Hypothesis
Alternative Hypothesis (H1) or the research hypothesis states that there is a relationship between two variables (where one variable affects the other). The alternative hypothesis is the main driving force for hypothesis testing.
It implies that the two variables are related to each other and the relationship that exists between them is not due to chance or coincidence.
When the process of hypothesis testing is carried out, the alternative hypothesis is the main subject of the testing process. The analyst intends to test the alternative hypothesis and verifies its plausibility.
Null Hypothesis
The Null Hypothesis (H0) aims to nullify the alternative hypothesis by implying that there exists no relation between two variables in statistics. It states that the effect of one variable on the other is solely due to chance and no empirical cause lies behind it.
The null hypothesis is established alongside the alternative hypothesis and is recognized as important as the latter. In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis has a major role to play as it influences the testing against the alternative hypothesis.
(Must read: What is ANOVA test? )
Non-Directional Hypothesis
The Non-directional hypothesis states that the relation between two variables has no direction.
Simply put, it asserts that there exists a relation between two variables, but does not recognize the direction of effect, whether variable A affects variable B or vice versa.
Directional Hypothesis
The Directional hypothesis, on the other hand, asserts the direction of effect of the relationship that exists between two variables.
Herein, the hypothesis clearly states that variable A affects variable B, or vice versa.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a hypothesis that can be verified to be plausible on the basis of statistics.
By using data sampling and statistical knowledge, one can determine the plausibility of a statistical hypothesis and find out if it stands true or not.
(Related blog: z-test vs t-test )
Performing Hypothesis Testing
Now that we have understood the types of hypotheses and the role they play in hypothesis testing, let us now move on to understand the process in a better manner.
In hypothesis testing, a researcher is first required to establish two hypotheses - alternative hypothesis and null hypothesis in order to begin with the procedure.
To establish these two hypotheses, one is required to study data samples, find a plausible pattern among the samples, and pen down a statistical hypothesis that they wish to test.
A random population of samples can be drawn, to begin with hypothesis testing. Among the two hypotheses, alternative and null, only one can be verified to be true. Perhaps the presence of both hypotheses is required to make the process successful.
At the end of the hypothesis testing procedure, either of the hypotheses will be rejected and the other one will be supported. Even though one of the two hypotheses turns out to be true, no hypothesis can ever be verified 100%.
(Read also: Types of data sampling techniques )
Therefore, a hypothesis can only be supported based on the statistical samples and verified data. Here is a step-by-step guide for hypothesis testing.
Establish the hypotheses
First things first, one is required to establish two hypotheses - alternative and null, that will set the foundation for hypothesis testing.
These hypotheses initiate the testing process that involves the researcher working on data samples in order to either support the alternative hypothesis or the null hypothesis.
Generate a testing plan
Once the hypotheses have been formulated, it is now time to generate a testing plan. A testing plan or an analysis plan involves the accumulation of data samples, determining which statistic is to be considered and laying out the sample size.
All these factors are very important while one is working on hypothesis testing.
Analyze data samples
As soon as a testing plan is ready, it is time to move on to the analysis part. Analysis of data samples involves configuring statistical values of samples, drawing them together, and deriving a pattern out of these samples.
While analyzing the data samples, a researcher needs to determine a set of things -
Significance Level - The level of significance in hypothesis testing indicates if a statistical result could have significance if the null hypothesis stands to be true.
Testing Method - The testing method involves a type of sampling-distribution and a test statistic that leads to hypothesis testing. There are a number of testing methods that can assist in the analysis of data samples.
Test statistic - Test statistic is a numerical summary of a data set that can be used to perform hypothesis testing.
P-value - The P-value interpretation is the probability of finding a sample statistic to be as extreme as the test statistic, indicating the plausibility of the null hypothesis.
Infer the results
The analysis of data samples leads to the inference of results that establishes whether the alternative hypothesis stands true or not. When the P-value is less than the significance level, the null hypothesis is rejected and the alternative hypothesis turns out to be plausible.
Methods of Hypothesis Testing
As we have already looked into different aspects of hypothesis testing, we shall now look into the different methods of hypothesis testing. All in all, there are 2 most common types of hypothesis testing methods. They are as follows -
Frequentist Hypothesis Testing
The frequentist hypothesis or the traditional approach to hypothesis testing is a hypothesis testing method that aims on making assumptions by considering current data.
The supposed truths and assumptions are based on the current data and a set of 2 hypotheses are formulated. A very popular subtype of the frequentist approach is the Null Hypothesis Significance Testing (NHST).
The NHST approach (involving the null and alternative hypothesis) has been one of the most sought-after methods of hypothesis testing in the field of statistics ever since its inception in the mid-1950s.
Bayesian Hypothesis Testing
A much unconventional and modern method of hypothesis testing, the Bayesian Hypothesis Testing claims to test a particular hypothesis in accordance with the past data samples, known as prior probability, and current data that lead to the plausibility of a hypothesis.
The result obtained indicates the posterior probability of the hypothesis. In this method, the researcher relies on ‘prior probability and posterior probability’ to conduct hypothesis testing on hand.
On the basis of this prior probability, the Bayesian approach tests a hypothesis to be true or false. The Bayes factor, a major component of this method, indicates the likelihood ratio among the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
The Bayes factor is the indicator of the plausibility of either of the two hypotheses that are established for hypothesis testing.
(Also read - Introduction to Bayesian Statistics )
To conclude, hypothesis testing, a way to verify the plausibility of a supposed assumption can be done through different methods - the Bayesian approach or the Frequentist approach.
Although the Bayesian approach relies on the prior probability of data samples, the frequentist approach assumes without a probability. A number of elements involved in hypothesis testing are - significance level, p-level, test statistic, and method of hypothesis testing.
(Also read: Introduction to probability distributions )
A significant way to determine whether a hypothesis stands true or not is to verify the data samples and identify the plausible hypothesis among the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis.
Share Blog :
Be a part of our Instagram community
Trending blogs
5 Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Elasticity of Demand and its Types
An Overview of Descriptive Analysis
What is PESTLE Analysis? Everything you need to know about it
What is Managerial Economics? Definition, Types, Nature, Principles, and Scope
5 Factors Affecting the Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
6 Major Branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Scope of Managerial Economics
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: The Shortest Path Algorithm
Different Types of Research Methods
Latest Comments
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a tool for making statistical inferences about the population data. It is an analysis tool that tests assumptions and determines how likely something is within a given standard of accuracy. Hypothesis testing provides a way to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid.
A null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis are set up before performing the hypothesis testing. This helps to arrive at a conclusion regarding the sample obtained from the population. In this article, we will learn more about hypothesis testing, its types, steps to perform the testing, and associated examples.
What is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
Hypothesis testing uses sample data from the population to draw useful conclusions regarding the population probability distribution . It tests an assumption made about the data using different types of hypothesis testing methodologies. The hypothesis testing results in either rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Testing Definition
Hypothesis testing can be defined as a statistical tool that is used to identify if the results of an experiment are meaningful or not. It involves setting up a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis. These two hypotheses will always be mutually exclusive. This means that if the null hypothesis is true then the alternative hypothesis is false and vice versa. An example of hypothesis testing is setting up a test to check if a new medicine works on a disease in a more efficient manner.

Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a concise mathematical statement that is used to indicate that there is no difference between two possibilities. In other words, there is no difference between certain characteristics of data. This hypothesis assumes that the outcomes of an experiment are based on chance alone. It is denoted as \(H_{0}\). Hypothesis testing is used to conclude if the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. Suppose an experiment is conducted to check if girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5. The null hypothesis will say that they are the same height.
Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is an alternative to the null hypothesis. It is used to show that the observations of an experiment are due to some real effect. It indicates that there is a statistical significance between two possible outcomes and can be denoted as \(H_{1}\) or \(H_{a}\). For the above-mentioned example, the alternative hypothesis would be that girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5.
Hypothesis Testing P Value
In hypothesis testing, the p value is used to indicate whether the results obtained after conducting a test are statistically significant or not. It also indicates the probability of making an error in rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.This value is always a number between 0 and 1. The p value is compared to an alpha level, \(\alpha\) or significance level. The alpha level can be defined as the acceptable risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis. The alpha level is usually chosen between 1% to 5%.
Hypothesis Testing Critical region
All sets of values that lead to rejecting the null hypothesis lie in the critical region. Furthermore, the value that separates the critical region from the non-critical region is known as the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Formula
Depending upon the type of data available and the size, different types of hypothesis testing are used to determine whether the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. The hypothesis testing formula for some important test statistics are given below:
- z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\). \(\overline{x}\) is the sample mean, \(\mu\) is the population mean, \(\sigma\) is the population standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
- t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\). s is the sample standard deviation.
- \(\chi ^{2} = \sum \frac{(O_{i}-E_{i})^{2}}{E_{i}}\). \(O_{i}\) is the observed value and \(E_{i}\) is the expected value.
We will learn more about these test statistics in the upcoming section.
Types of Hypothesis Testing
Selecting the correct test for performing hypothesis testing can be confusing. These tests are used to determine a test statistic on the basis of which the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected. Some of the important tests used for hypothesis testing are given below.
Hypothesis Testing Z Test
A z test is a way of hypothesis testing that is used for a large sample size (n ≥ 30). It is used to determine whether there is a difference between the population mean and the sample mean when the population standard deviation is known. It can also be used to compare the mean of two samples. It is used to compute the z test statistic. The formulas are given as follows:
- One sample: z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing t Test
The t test is another method of hypothesis testing that is used for a small sample size (n < 30). It is also used to compare the sample mean and population mean. However, the population standard deviation is not known. Instead, the sample standard deviation is known. The mean of two samples can also be compared using the t test.
- One sample: t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: t = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{s_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{s_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing Chi Square
The Chi square test is a hypothesis testing method that is used to check whether the variables in a population are independent or not. It is used when the test statistic is chi-squared distributed.
One Tailed Hypothesis Testing
One tailed hypothesis testing is done when the rejection region is only in one direction. It can also be known as directional hypothesis testing because the effects can be tested in one direction only. This type of testing is further classified into the right tailed test and left tailed test.
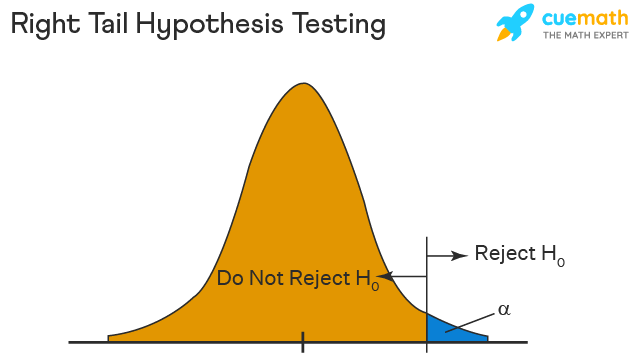
Right Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The right tail test is also known as the upper tail test. This test is used to check whether the population parameter is greater than some value. The null and alternative hypotheses for this test are given as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≤ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is > some value.
If the test statistic has a greater value than the critical value then the null hypothesis is rejected
Left Tailed Hypothesis Testing
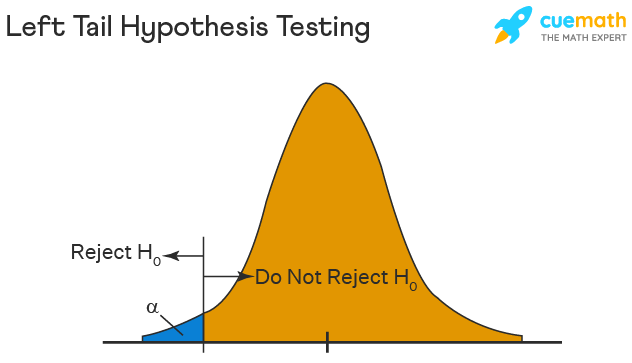
The left tail test is also known as the lower tail test. It is used to check whether the population parameter is less than some value. The hypotheses for this hypothesis testing can be written as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≥ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is < some value.
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value lesser than the critical value.
Two Tailed Hypothesis Testing
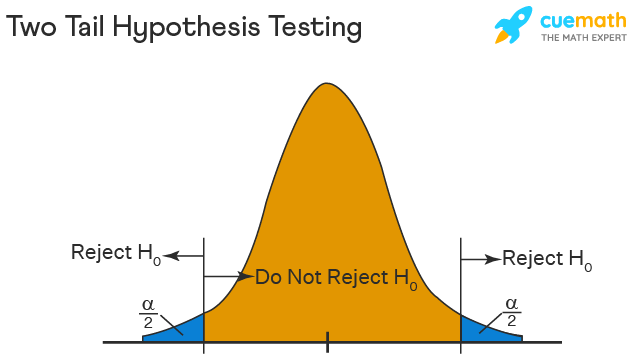
In this hypothesis testing method, the critical region lies on both sides of the sampling distribution. It is also known as a non - directional hypothesis testing method. The two-tailed test is used when it needs to be determined if the population parameter is assumed to be different than some value. The hypotheses can be set up as follows:
\(H_{0}\): the population parameter = some value
\(H_{1}\): the population parameter ≠ some value
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value that is not equal to the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Steps
Hypothesis testing can be easily performed in five simple steps. The most important step is to correctly set up the hypotheses and identify the right method for hypothesis testing. The basic steps to perform hypothesis testing are as follows:
- Step 1: Set up the null hypothesis by correctly identifying whether it is the left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed hypothesis testing.
- Step 2: Set up the alternative hypothesis.
- Step 3: Choose the correct significance level, \(\alpha\), and find the critical value.
- Step 4: Calculate the correct test statistic (z, t or \(\chi\)) and p-value.
- Step 5: Compare the test statistic with the critical value or compare the p-value with \(\alpha\) to arrive at a conclusion. In other words, decide if the null hypothesis is to be rejected or not.
Hypothesis Testing Example
The best way to solve a problem on hypothesis testing is by applying the 5 steps mentioned in the previous section. Suppose a researcher claims that the mean average weight of men is greater than 100kgs with a standard deviation of 15kgs. 30 men are chosen with an average weight of 112.5 Kgs. Using hypothesis testing, check if there is enough evidence to support the researcher's claim. The confidence interval is given as 95%.
Step 1: This is an example of a right-tailed test. Set up the null hypothesis as \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 100.
Step 2: The alternative hypothesis is given by \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 100.
Step 3: As this is a one-tailed test, \(\alpha\) = 100% - 95% = 5%. This can be used to determine the critical value.
1 - \(\alpha\) = 1 - 0.05 = 0.95
0.95 gives the required area under the curve. Now using a normal distribution table, the area 0.95 is at z = 1.645. A similar process can be followed for a t-test. The only additional requirement is to calculate the degrees of freedom given by n - 1.
Step 4: Calculate the z test statistic. This is because the sample size is 30. Furthermore, the sample and population means are known along with the standard deviation.
z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
\(\mu\) = 100, \(\overline{x}\) = 112.5, n = 30, \(\sigma\) = 15
z = \(\frac{112.5-100}{\frac{15}{\sqrt{30}}}\) = 4.56
Step 5: Conclusion. As 4.56 > 1.645 thus, the null hypothesis can be rejected.
Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals form an important part of hypothesis testing. This is because the alpha level can be determined from a given confidence interval. Suppose a confidence interval is given as 95%. Subtract the confidence interval from 100%. This gives 100 - 95 = 5% or 0.05. This is the alpha value of a one-tailed hypothesis testing. To obtain the alpha value for a two-tailed hypothesis testing, divide this value by 2. This gives 0.05 / 2 = 0.025.
Related Articles:
- Probability and Statistics
- Data Handling
Important Notes on Hypothesis Testing
- Hypothesis testing is a technique that is used to verify whether the results of an experiment are statistically significant.
- It involves the setting up of a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis.
- There are three types of tests that can be conducted under hypothesis testing - z test, t test, and chi square test.
- Hypothesis testing can be classified as right tail, left tail, and two tail tests.
Examples on Hypothesis Testing
- Example 1: The average weight of a dumbbell in a gym is 90lbs. However, a physical trainer believes that the average weight might be higher. A random sample of 5 dumbbells with an average weight of 110lbs and a standard deviation of 18lbs. Using hypothesis testing check if the physical trainer's claim can be supported for a 95% confidence level. Solution: As the sample size is lesser than 30, the t-test is used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 5, s = 18. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 Using the t-distribution table, the critical value is 2.132 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = 2.484 As 2.484 > 2.132, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: The average weight of the dumbbells may be greater than 90lbs
- Example 2: The average score on a test is 80 with a standard deviation of 10. With a new teaching curriculum introduced it is believed that this score will change. On random testing, the score of 38 students, the mean was found to be 88. With a 0.05 significance level, is there any evidence to support this claim? Solution: This is an example of two-tail hypothesis testing. The z test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 80, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) ≠ 80 \(\overline{x}\) = 88, \(\mu\) = 80, n = 36, \(\sigma\) = 10. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 / 2 = 0.025 The critical value using the normal distribution table is 1.96 z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) z = \(\frac{88-80}{\frac{10}{\sqrt{36}}}\) = 4.8 As 4.8 > 1.96, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: There is a difference in the scores after the new curriculum was introduced.
- Example 3: The average score of a class is 90. However, a teacher believes that the average score might be lower. The scores of 6 students were randomly measured. The mean was 82 with a standard deviation of 18. With a 0.05 significance level use hypothesis testing to check if this claim is true. Solution: The t test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) < 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 6, s = 18 The critical value from the t table is -2.015 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = \(\frac{82-90}{\frac{18}{\sqrt{6}}}\) t = -1.088 As -1.088 > -2.015, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Answer: There is not enough evidence to support the claim.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
FAQs on Hypothesis Testing
What is hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis testing in statistics is a tool that is used to make inferences about the population data. It is also used to check if the results of an experiment are valid.
What is the z Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The z test in hypothesis testing is used to find the z test statistic for normally distributed data . The z test is used when the standard deviation of the population is known and the sample size is greater than or equal to 30.
What is the t Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The t test in hypothesis testing is used when the data follows a student t distribution . It is used when the sample size is less than 30 and standard deviation of the population is not known.
What is the formula for z test in Hypothesis Testing?
The formula for a one sample z test in hypothesis testing is z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) and for two samples is z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
What is the p Value in Hypothesis Testing?
The p value helps to determine if the test results are statistically significant or not. In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected based on the comparison between the p value and the alpha level.
What is One Tail Hypothesis Testing?
When the rejection region is only on one side of the distribution curve then it is known as one tail hypothesis testing. The right tail test and the left tail test are two types of directional hypothesis testing.
What is the Alpha Level in Two Tail Hypothesis Testing?
To get the alpha level in a two tail hypothesis testing divide \(\alpha\) by 2. This is done as there are two rejection regions in the curve.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Hypothesis testing, sometimes called significance testing, is an act in statistics whereby an analystan assumption regarding a population parameter…
Hypothesis testing is a mathematical tool for confirming a financial or business claim or idea. Hypothesis testing is useful for investors trying to decide what to …
Statistical significance is used in null hypothesis testing, where researchers attempt to support their theories by rejecting other explanations. Although the method is sometimes...
What is Hypothesis Testing? Hypothesis Testing is a method of statistical inference. It is used to test if a statement regarding a population parameter is statistically significant. Hypothesis testing is a powerful tool for testing the …
Hypothesis Testing is a statistical concept to verify the plausibility of a hypothesis that is based on data samples derived from a given population, using two competing hypotheses.
A hypothesis test consists of five steps: 1. State the hypotheses. State the null and alternative hypotheses. These two hypotheses need to be mutually exclusive, so if one is true …
Hypothesis testing is used to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid or not by using the null and alternate hypotheses. Understand hypothesis testing using solved examples.