- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips

How to Write a Thesis Chapter Outline
4-minute read
- 30th April 2023
Are you writing a thesis ? That’s amazing! Give yourself a pat on the back, because reaching that point in your academic career takes a lot of hard work.
When you begin to write, you may feel overwhelmed and unsure of where to start. That’s where outlines come in handy. In this article, we’ll break down an effective outline for a thesis chapter – one that you can follow for each section of your paper.
What Is a Thesis Chapter?
Your thesis will be broken up into several sections . Usually, there’s an introduction, some background information, the methodology, the results and discussion, and a conclusion – or something along those lines.
Your institution will have more specific guidelines on the chapters you need to include and in what order, so make sure you familiarize yourself with those requirements first. To help you organize the content of each chapter, an outline breaks it down into smaller chunks.
The Outline
While the content and length of each chapter will vary, you can follow a similar pattern to organize your information. Each chapter should include:
1. An Introduction
At the start of your chapter, spend some time introducing what you’re about to discuss. This will give readers the chance to quickly get an idea of what you’ll be covering and decide if they want to keep reading.
You could begin with a link to the previous chapter, which will help keep your audience from getting lost if they’re not reading it from start to finish in one sitting. You should then explain the purpose of the chapter and briefly describe how you will achieve it.
Every chapter should have an intro like this, even the introduction ! Of course, the length of this part will vary depending on the length of the chapter itself.
2. The Main Body
After introducing the chapter, you can dive into the meat of it. As with the introduction, the content can be as brief or as lengthy as it needs to be.
While piecing together your outline, jot down which points are most important to include and then decide how much space you can devote to fleshing out each one. Let’s consider what this might look like, depending on the chapter .
If your thesis is broken up into an introduction, a background/literature review section, a methodology chapter, a discussion of the results, and a conclusion, here’s what the main body could include for each:
● Introduction : A brief summary of the problem or topic and its background, the purpose of the thesis, the research questions that will be addressed, the terminology you’ll be using, and any limitations or unique circumstances.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
● Background/literature review : A more thorough explanation of the problem, relevant studies and literature, and current knowledge and gaps in knowledge.
● Methodology : A detailed explanation of the research design, participants and how they were chosen, and how the data was collected and analyzed.
● Results/discussion : A thorough description of the results of the study and a discussion of what they could mean.
● Conclusion : A summary of everything that’s been covered, an explanation of the answers that were (or weren’t) found to the research questions, and suggestions for future research.
This is a rough plan of what the main body of each chapter might look like. Your thesis will likely have more chapters, and some of these topics may be broken down into multiple paragraphs, but this offers an idea of where to start.
3. A Conclusion
Once you’ve detailed everything the chapter needs to include, you should summarize what’s been covered and tie it all together. Explain what the chapter accomplished, and once again, you can link back to the previous chapter to point out what questions have been answered at this point in the thesis.
If you’re just getting started on writing your thesis, putting together an outline will help you to get your thoughts organized and give you a place to start. Each chapter should have its own introduction, main body, and conclusion.
And once you have your draft written, be sure to send it our way! Our editors will be happy to check it for grammar, punctuation, spelling, references, formatting, and more. Try out our service for free today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you outline a thesis chapter.
Each chapter of your thesis should have its own introduction, the main content or body of the chapter, and a conclusion summarizing what was covered and linking it to the rest of the thesis.
How do you write a thesis statement?
A thesis statement should briefly summarize the topic you’re looking into and state your assumption about it.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Published on 8 June 2022 by Tegan George .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process . It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation, such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
In the final product, you can also provide a chapter outline for your readers. This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organisational structure of your thesis or dissertation . This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline.
Table of contents
How to outline your thesis or dissertation, dissertation and thesis outline templates, chapter outline example, sample sentences for your chapter outline, sample verbs for variation in your chapter outline, frequently asked questions about outlines.
While there are some inter-institutional differences, many outlines proceed in a fairly similar fashion.
- Working Title
- ‘Elevator pitch’ of your work (often written last).
- Introduce your area of study, sharing details about your research question, problem statement , and hypotheses . Situate your research within an existing paradigm or conceptual or theoretical framework .
- Subdivide as you see fit into main topics and sub-topics.
- Describe your research methods (e.g., your scope, population , and data collection ).
- Present your research findings and share about your data analysis methods.
- Answer the research question in a concise way.
- Interpret your findings, discuss potential limitations of your own research and speculate about future implications or related opportunities.
To help you get started, we’ve created a full thesis or dissertation template in Word or Google Docs format. It’s easy adapt it to your own requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template

It can be easy to fall into a pattern of overusing the same words or sentence constructions, which can make your work monotonous and repetitive for your readers. Consider utilising some of the alternative constructions presented below.
Example 1: Passive construction
The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise.
Example 2: IS-AV construction
You can also present your information using the ‘IS-AV’ (inanimate subject with an active verb) construction.
A chapter is an inanimate object, so it is not capable of taking an action itself (e.g., presenting or discussing). However, the meaning of the sentence is still easily understandable, so the IS-AV construction can be a good way to add variety to your text.
Example 3: The I construction
Another option is to use the ‘I’ construction, which is often recommended by style manuals (e.g., APA Style and Chicago style ). However, depending on your field of study, this construction is not always considered professional or academic. Ask your supervisor if you’re not sure.
Example 4: Mix-and-match
To truly make the most of these options, consider mixing and matching the passive voice , IS-AV construction , and ‘I’ construction .This can help the flow of your argument and improve the readability of your text.
As you draft the chapter outline, you may also find yourself frequently repeating the same words, such as ‘discuss’, ‘present’, ‘prove’, or ‘show’. Consider branching out to add richness and nuance to your writing. Here are some examples of synonyms you can use.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
All level 1 and 2 headings should be included in your table of contents . That means the titles of your chapters and the main sections within them.
The contents should also include all appendices and the lists of tables and figures, if applicable, as well as your reference list .
Do not include the acknowledgements or abstract in the table of contents.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, June 08). Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 5 November 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/outline-thesis-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
University Thesis and Dissertation Templates

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Theses and dissertations are already intensive, long-term projects that require a lot of effort and time from their authors. Formatting for submission to the university is often the last thing that graduate students do, and may delay earning the relevant degree if done incorrectly.
Below are some strategies graduate students can use to deal with institutional formatting requirements to earn their degrees on time.
Disciplinary conventions are still paramount.
Scholars in your own discipline are the most common readers of your dissertation; your committee, too, will expect your work to match with their expectations as members of your field. The style guide your field uses most commonly is always the one you should follow, and if your field uses conventions such as including all figures and illustrations at the end of the document, you should do so. After these considerations are met, move on to university formatting. Almost always, university formatting only deals with things like margins, font, numbering of chapters and sections, and illustrations; disciplinary style conventions in content such as APA's directive to use only last names of authors in-text are not interfered with by university formatting at all.
Use your university's formatting guidelines and templates to your advantage.
If your institution has a template for formatting your thesis or dissertation that you can use, do so. Don't look at another student's document and try to replicate it yourself. These templates typically have the necessary section breaks and styles already in the document, and you can copy in your work from your existing draft using the style pane in MS Word to ensure you're using the correct formatting (similarly with software such as Overleaf when writing in LaTeX, templates do a lot of the work for you). It's also often easier for workers in the offices that deal with theses and dissertations to help you with your work if you're using their template — they are familiar with these templates and can often navigate them more proficiently.
These templates also include placeholders for all front matter you will need to include in your thesis or dissertation, and may include guidelines for how to write these. Front matter includes your table of contents, acknowledgements, abstract, abbreviation list, figure list, committee page, and (sometimes) academic history or CV; everything before your introduction is front matter. Since front matter pages such as the author's academic history and dissertation committee are usually for the graduate school and not for your department, your advisor might not remember to have you include them. Knowing about them well before your deposit date means you won't be scrambling to fill in placeholders at the last minute or getting your work returned for revision from the graduate school.
Consider institutional formatting early and often.
Many graduate students leave this aspect of submitting their projects until it's almost too late to work on it, causing delays in obtaining their degree. Simply being aware that this is a task you'll have to complete and making sure you know where templates are, who you can ask for help in your graduate office or your department, and what your institution's guidelines are can help alleviate this issue. Once you know what you'll be expected to do to convert to university formatting, you can set regular check-in times for yourself to do this work in pieces rather than all at once (for instance, when you've completed a chapter and had it approved by your chair).
Consider fair use for images and other third-party content.
Most theses and dissertations are published through ProQuest or another publisher (Harvard, for instance, uses their own open publishing service). For this reason, it may be the case that your institution requires all images or other content obtained from other sources to fall under fair use rules or, if an image is not considered under fair use, you'll have to obtain permission to print it in your dissertation. Your institution should have more guidance on their specific expectations for fair use content; knowing what these guidelines are well in advance of your deposit date means you won't have to make last-minute changes or removals to deposit your work.

Creating an Outline for Your Master’s Thesis
1. introduction.
Your master’s thesis serves to explain the research that you have done during your time as a masters student. For many students, the master’s thesis is the longest document that they’ve ever written, and the length of the document can feel intimidating. The purpose of this CommKit is to cover a key element of writing your thesis: the outline.
2. Criteria for Success
The most important criterion for success is that you’ve shown an outline with your chapter breakdown to your advisor. Your advisor is the one that formally signs off on your thesis as completed, so their feedback is the most important.
Every master’s thesis will have the following elements.
- Introduction – Familiarize the reader with the topic and what gap exists in the field.
- Literature Review – Provide a detailed analysis of similar work in the field and how your work is unique. Master’s thesis literature reviews typically have at least 60 citations throughout the entire document
- Methods – Explain how you produced your results
- Results – Show your results and comment on their significance and implications.
- Conclusion – Summarize the methodology you used to generate results, your key findings, and any future areas of work.
Having an outline for your master’s thesis will help you explain the motivation behind your work, and also connect the different experiments or results that you completed. Furthermore, an outline for your master’s thesis can help break down the larger task of writing the entire thesis into smaller, more manageable chapter-sized subtasks.
4. Analyze Your Audience
The most important audience member for your master’s thesis is your advisor, as they are ultimately the person that signs off on whether or not your thesis is sufficient enough to graduate. The needs of any other audience members are secondary.
Ideally, a good master’s thesis is accessible to people that work in your field. In some cases, master’s theses are passed on to newer students so that that research can continue. In these cases, the thesis is used as a guide to introduce newer students to the research area. If you intend for your thesis to be used as a guide for new students, you may spend more time explaining the state of the field in your introduction and literature review. Additionally, your thesis will be posted publicly on DSpace , MIT’s digital repository for all theses.

5. Best Practices
5.1. identify your claims.
A key element to figuring out the unique structure to your master’s thesis is identifying the claims of your work. A claim is an answer to a research question or gap. Your thesis can have both a higher level claim and also lower level claims that motivate the research projects that you worked on. Identifying your claims will help you spot the key objectives which you want to highlight in the thesis. This will keep your writing on topic.
Some examples are shown below:
Gap/Question : There are no field-portable microplastic sensing technologies to measure their distribution in the environment.
→ Claim : Impedance spectroscopy can be used in a microfluidic device to rapidly distinguish organic matter from polymers.
Gap/Question: How effective are convolutional neural networks for pose estimation during in-space assembly?
→ Claim : Convolutional neural networks can be used to estimate the pose of satellites, but struggle with oversaturated images and images with multiple satellites.
5.2. Support Your Claims
Once you have identified your claim, the next step is to identify evidence that will support it. The structure of your paper will be very dependent on the claim that you make. Figure 1 and 2 demonstrate two different structures to support a claim. In one outline, the claim is best supported by a linear structure that describes the building, testing, and validation of a model. In another outline, the claim is best supported by a trifold structure, where three independent methods are discussed. Depending on the extent of the evidence, you could break this trifold structure into 3 separate chapters, or they could all be discussed in a singular chapter. The value of identifying claims and evidence is that it helps you organize your paper coherently at a high level. The number of chapters that are output as a result of your claim identification is up to you and what you think would be sufficient discussion for a chapter within your thesis.
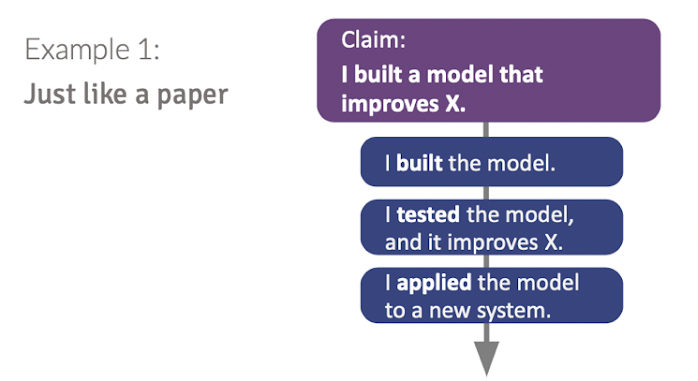
5.3. Connect the Evidence to Your Claims with Reasoning
One common mistake that students make when writing their thesis is treating each chapter as an isolated piece of writing. While it is helpful to break down the actual task of thesis writing into chapter-size pieces, these chapters should have some connection to one another. For your outline, it is ideal to identify what these connections were. Perhaps what made you start on one project was that you realized the weaknesses in your prior work and you wanted to make improvements. For readers who were not doing the research with you, describing the connections between your work in different chapters can help them understand the motivation and value of why you pursued each component.
5.4. Combine Your Claims, Evidence, and Reasoning to Produce Your Outline
Once you have identified your claims, the evidence you have surrounding each claim, and the reasoning that connects each piece of your work, you can now create your full outline, putting the pieces together like a jigsaw puzzle. An example outline is provided as an annotated example.
There are no requirements for minimum or maximum number of chapters that your master’s thesis can have. Therefore, when translating your outline to a literal chapter breakdown, you should feel free to use as many chapters as needed. If your methods section for a claim is extremely long, it may make more sense to have it be a standalone chapter, as shown in the attached annotated pdf.
6. Additional Resources
Every IAP, the Comm Lab hosts a workshop on how to write your master’s thesis. This workshop provides tips for writing each of these sections, and steps you through the process of creating an outline.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Example 1. structure diagram and table of contents, example 2. table of contents.

Step-By-Step Guide To Write Your Thesis Outline
Navigating the intricate maze of thesis writing can be daunting for many students. Unearthing the secrets of creating a coherent structure that communicates complex ideas with clarity is no small task.
Yet, every academic journey hinges on the effective presentation of one’s research, findings, and conclusions. Dive into this comprehensive guide, brimming with insider knowledge, to unravel the mysteries of crafting the perfect thesis outline.
What Is A Thesis Outline?
Thesis Outline is a step-by-step guide that helps you list all the major topics and subtopics in a logical order. For example:
- Introduction : Overview of your research.
- Literature Review : Summary of existing research on the topic.
- Methodology : Research methods employed.
- Chapters : Organise your main ideas, claims, and supporting ideas in sections.
- Conclusion : Conclude your findings, limitations, and future implications.

Chapter 1: Introduction & Thesis Statement
Crafting an impactful introduction and thesis statement is a critical step in the writing process. Having a well-organised introduction and thesis statement can be the roadmap that ensures your research paper flows logically.
Thesis Statement : Often at the end of introduction, it is a specific sentence that states your claims, which you intend to prove with evidence. For instance, “An effective way to prevent youth gang involvement is through community engagement and education.”
Research Question : This guides your thesis or dissertation outline and dictates the scope of your investigation. For instance, “What strategies can communities employ to prevent youth gang involvement?”
Butte College, a reputable academic institution, suggests that thesis statements should remain flexible. As you draft and revise, you might discover new information that could lead to adjustments.
AI tools, like Google Docs, can simplify this iterative process, with features enabling researchers to copy, paste, and reorganise content.
For those unsure where to start, numerous thesis outline templates are available online. Some may even prefer the traditional method of using Roman numerals and capital letters for the organisational structure.
Always remember, your thesis statement and outline are preliminary; as your research unfolds, they should evolve. So, embrace the dynamic nature of the writing process and adapt as necessary.
Chapter 2: Review of Related Literature and Research
To begin, formulate a specific research question and a thesis statement that states your claims. This is the backbone of your literature review, ensuring your content remains focused.
Once you have a draft, critically analyze the content for repetitive elements. Engage in critical thinking: does each sentence and paragraph add value?
As you delve deeper into academic writing, the scope of your literature review might shift. It’s essential to keep your thesis statement flexible and revise it as needed. You may find new information or methodologies that can influence your overview.
Your literature review should also cite previous works effectively. Proper citation:
- Supports your claims
- Gives an overview of the existing research methods.
Every citation and summary should help prove your thesis with evidence. Don’t just copy and paste, understand and integrate.
As you organize your ideas and subtopics, ensure they align with your research methods, offering a clear pathway from introduction to conclusion. For those using the APA format, there are specific guidelines and thesis outline templates available.
Always remember to consult with your supervisor or use AI tools to enhance your literature review’s quality. By maintaining a logical order and clarity, your literature review will form a foundational chapter in your academic thesis or dissertation.
Chapter 3: Methodology
The methodology chapter allows a researcher to outline their specific methods, offering a clear guide for replicating the study if needed. When drafting this chapter:
- You must be precise, presenting content in a logical order to ensure clarity.
- Explain your methodological approach. Did you opt for a quantitative or qualitative method?
- Elaborate on the research question your thesis aims to answer and specify if you collected primary or secondary data.
This forms the foundation of your methodology and provides a framework for your readers.
Next, delve into your methods of data collection. Whether it’s surveys or interviews, detail the research methods, offering a sample paragraph, perhaps.
Organize your ideas and describe the tools and procedures used. In a research paper or thesis document, it’s essential to ensure that another researcher can replicate your methods. Therefore, being specific about:
- Instruments
- Softwares, and
- Sampling method
These information can be invaluable to your future readers.
The subsequent step involves explaining your methods of analysis. For instance, if dealing with numbers, mention any statistical software like SPSS and the specific tests employed. For qualitative data, elucidate how you categorised responses.
Lastly, don’t forget to justify your methodological choices. If certain popular methods weren’t used, provide reasons. An effective way to bolster this section is by referencing similar existing research or citing academic guidelines that support your approach.
Chapter 4: Findings
This chapter should objectively report the results of your research, ensuring the content remains separate from any personal interpretation.
Quantitative Research: Structure this section around your research questions or hypotheses. Include both descriptive (e.g., means, standard deviations) and inferential statistics (like t-scores and p-values).
Consider to incorporate visual aids like graphs and tables only when they genuinely add value for the reader.
Qualitative Research: Findings might revolve around key themes that emerged during data analysis. Here, present general observations and cite specific quotations that resonate with the research question.
You may find it helpful to create an outline, ensuring each theme is explored in a logical order. If you have extensive data, like full interview transcripts, consider adding them to an appendix.
Always draft and revise this chapter in the past tense. And remember, while the findings section provides a summary of your research, refrain from speculative conclusions—these belong in the discussion and conclusion chapters.
Using these guidelines, you’ll ensure your findings are presented in a clear and academic manner.
Chapter 5: Summary, Conclusions, Discussion, and Recommendations
In your thesis, this chapter offers an opportunity to concisely encapsulate your research. It is essential to maintain a logical order while constructing this section. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Summary & Discussion : Synthesise the main findings from your research paper into a summary, addressing how the results provide answers. Consider the implications of your findings and any unexpected insights that arose during the research process.
- Conclusions : It’s the point where you cement the importance of your research. Discuss how your findings either confirm or challenge existing literature review insights. Your conclusion should tie all the chapters together, providing an overview of key points that support your main claims without introducing new data.
- Recommendations : Elaborate on future research implications, ensuring they don’t undermine your work but rather enrich your conclusions. If your research has practical applications, like in policy, frame your suggestions in a way that’s not imperative.
- Final Touches : Once the chapter is drafted, revise it as needed. Utilise thesis outline templates or tools like Google Docs to ensure organisational structure. Always cite sources accurately and check the format.
Remember, this chapter is a reflection of your critical thinking and academic writing abilities. It’s more than a summary; it’s an assertion of your contribution to your field. And if you ever need assistance, consider using AI tools or consult Butte College resources for additional insights.
Wrapping Up: Creating Thesis Outline Is Not Rocket Science
Crafting a thesis outline need not be an overwhelming challenge. This guide simplifies the process, providing clear steps to shape your academic work.
From the foundation of introductions and thesis statements to utilising AI tools for drafts, the path to a coherent and impactful thesis outline is demystified. Hopefully you are now well-equipped to navigate the world of academic writing with confidence.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


How To Write A Dissertation Introduction

I f you’re reading this, you’re probably at the daunting early phases of writing up the introduction chapter of your dissertation or thesis. It can be intimidating, I know.
In this post, we’ll look at the 7 essential ingredients of a strong dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, as well as the essential things you need to keep in mind as you craft each section. We’ll also share some useful tips to help you optimize your approach.
Overview: Writing An Introduction Chapter
- The purpose and function of the intro chapter
- Craft an enticing and engaging opening section
- Provide a background and context to the study
- Clearly define the research problem
- State your research aims, objectives and questions
- Explain the significance of your study
- Identify the limitations of your research
- Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis
A quick sidenote:
You’ll notice that I’ve used the words dissertation and thesis interchangeably. While these terms reflect different levels of research – for example, Masters vs PhD-level research – the introduction chapter generally contains the same 7 essential ingredients regardless of level. So, in this post, dissertation introduction equals thesis introduction.

Start with why.
To craft a high-quality dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, you need to understand exactly what this chapter needs to achieve. In other words, what’s its purpose ? As the name suggests, the introduction chapter needs to introduce the reader to your research so that they understand what you’re trying to figure out, or what problem you’re trying to solve. More specifically, you need to answer four important questions in your introduction chapter.
These questions are:
- What will you be researching? (in other words, your research topic)
- Why is that worthwhile? (in other words, your justification)
- What will the scope of your research be? (in other words, what will you cover and what won’t you cover)
- What will the limitations of your research be? (in other words, what will the potential shortcomings of your research be?)
Simply put, your dissertation’s introduction chapter needs to provide an overview of your planned research , as well as a clear rationale for it. In other words, this chapter has to explain the “what” and the “why” of your research – what’s it all about and why’s that important.
Simple enough, right?
Well, the trick is finding the appropriate depth of information. As the researcher, you’ll be extremely close to your topic and this makes it easy to get caught up in the minor details. While these intricate details might be interesting, you need to write your introduction chapter on more of a “need-to-know” type basis, or it will end up way too lengthy and dense. You need to balance painting a clear picture with keeping things concise. Don’t worry though – you’ll be able to explore all the intricate details in later chapters.

Now that you understand what you need to achieve from your introduction chapter, we can get into the details. While the exact requirements for this chapter can vary from university to university, there are seven core components that most universities will require. We call these the seven essential ingredients .
The 7 Essential Ingredients
- The opening section – where you’ll introduce the reader to your research in high-level terms
- The background to the study – where you’ll explain the context of your project
- The research problem – where you’ll explain the “gap” that exists in the current research
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you’ll clearly state what your research will aim to achieve
- The significance (or justification) – where you’ll explain why your research is worth doing and the value it will provide to the world
- The limitations – where you’ll acknowledge the potential limitations of your project and approach
- The structure – where you’ll briefly outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis to help orient the reader
By incorporating these seven essential ingredients into your introduction chapter, you’ll comprehensively cover both the “ what ” and the “ why ” I mentioned earlier – in other words, you’ll achieve the purpose of the chapter.
Side note – you can also use these 7 ingredients in this order as the structure for your chapter to ensure a smooth, logical flow. This isn’t essential, but, generally speaking, it helps create an engaging narrative that’s easy for your reader to understand. If you’d like, you can also download our free introduction chapter template here.
Alright – let’s look at each of the ingredients now.

#1 – The Opening Section
The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you’ll be covering in the chapter.
This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and digested. If the reader (your marker!) has to struggle through it, they’ll lose interest, which will make it harder for you to earn marks. Just because you’re writing an academic paper doesn’t mean you can ignore the basic principles of engaging writing used by marketers, bloggers, and journalists. At the end of the day, you’re all trying to sell an idea – yours is just a research idea.
So, what goes into this opening section?
Well, while there’s no set formula, it’s a good idea to include the following four foundational sentences in your opening section:
1 – A sentence or two introducing the overall field of your research.
For example:
“Organisational skills development involves identifying current or potential skills gaps within a business and developing programs to resolve these gaps. Management research, including X, Y and Z, has clearly established that organisational skills development is an essential contributor to business growth.”
2 – A sentence introducing your specific research problem.
“However, there are conflicting views and an overall lack of research regarding how best to manage skills development initiatives in highly dynamic environments where subject knowledge is rapidly and continuously evolving – for example, in the website development industry.”
3 – A sentence stating your research aims and objectives.
“This research aims to identify and evaluate skills development approaches and strategies for highly dynamic industries in which subject knowledge is continuously evolving.”.
4 – A sentence outlining the layout of the chapter.
“This chapter will provide an introduction to the study by first discussing the background and context, followed by the research problem, the research aims, objectives and questions, the significance and finally, the limitations.”
As I mentioned, this opening section of your introduction chapter shouldn’t be lengthy . Typically, these four sentences should fit neatly into one or two paragraphs, max. What you’re aiming for here is a clear, concise introduction to your research – not a detailed account.
PS – If some of this terminology sounds unfamiliar, don’t stress – I’ll explain each of the concepts later in this post.
#2 – Background to the study
Now that you’ve provided a high-level overview of your dissertation or thesis, it’s time to go a little deeper and lay a foundation for your research topic. This foundation is what the second ingredient is all about – the background to your study.
So, what is the background section all about?
Well, this section of your introduction chapter should provide a broad overview of the topic area that you’ll be researching, as well as the current contextual factors . This could include, for example, a brief history of the topic, recent developments in the area, key pieces of research in the area and so on. In other words, in this section, you need to provide the relevant background information to give the reader a decent foundational understanding of your research area.
Let’s look at an example to make this a little more concrete.
If we stick with the skills development topic I mentioned earlier, the background to the study section would start by providing an overview of the skills development area and outline the key existing research. Then, it would go on to discuss how the modern-day context has created a new challenge for traditional skills development strategies and approaches. Specifically, that in many industries, technical knowledge is constantly and rapidly evolving, and traditional education providers struggle to keep up with the pace of new technologies.
Importantly, you need to write this section with the assumption that the reader is not an expert in your topic area. So, if there are industry-specific jargon and complex terminology, you should briefly explain that here , so that the reader can understand the rest of your document.
Don’t make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge – in most cases, your markers will not be able to ask you questions if they don’t understand something. So, always err on the safe side and explain anything that’s not common knowledge.

#3 – The research problem
Now that you’ve given your reader an overview of your research area, it’s time to get specific about the research problem that you’ll address in your dissertation or thesis. While the background section would have alluded to a potential research problem (or even multiple research problems), the purpose of this section is to narrow the focus and highlight the specific research problem you’ll focus on.
But, what exactly is a research problem, you ask?
Well, a research problem can be any issue or question for which there isn’t already a well-established and agreed-upon answer in the existing research. In other words, a research problem exists when there’s a need to answer a question (or set of questions), but there’s a gap in the existing literature , or the existing research is conflicting and/or inconsistent.
So, to present your research problem, you need to make it clear what exactly is missing in the current literature and why this is a problem . It’s usually a good idea to structure this discussion into three sections – specifically:
- What’s already well-established in the literature (in other words, the current state of research)
- What’s missing in the literature (in other words, the literature gap)
- Why this is a problem (in other words, why it’s important to fill this gap)
Let’s look at an example of this structure using the skills development topic.
Organisational skills development is critically important for employee satisfaction and company performance (reference). Numerous studies have investigated strategies and approaches to manage skills development programs within organisations (reference).
(this paragraph explains what’s already well-established in the literature)
However, these studies have traditionally focused on relatively slow-paced industries where key skills and knowledge do not change particularly often. This body of theory presents a problem for industries that face a rapidly changing skills landscape – for example, the website development industry – where new platforms, languages and best practices emerge on an extremely frequent basis.
(this paragraph explains what’s missing from the literature)
As a result, the existing research is inadequate for industries in which essential knowledge and skills are constantly and rapidly evolving, as it assumes a slow pace of knowledge development. Industries in such environments, therefore, find themselves ill-equipped in terms of skills development strategies and approaches.
(this paragraph explains why the research gap is problematic)
As you can see in this example, in a few lines, we’ve explained (1) the current state of research, (2) the literature gap and (3) why that gap is problematic. By doing this, the research problem is made crystal clear, which lays the foundation for the next ingredient.
#4 – The research aims, objectives and questions
Now that you’ve clearly identified your research problem, it’s time to identify your research aims and objectives , as well as your research questions . In other words, it’s time to explain what you’re going to do about the research problem.
So, what do you need to do here?
Well, the starting point is to clearly state your research aim (or aims) . The research aim is the main goal or the overarching purpose of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, it’s a high-level statement of what you’re aiming to achieve.
Let’s look at an example, sticking with the skills development topic:
“Given the lack of research regarding organisational skills development in fast-moving industries, this study will aim to identify and evaluate the skills development approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK”.
As you can see in this example, the research aim is clearly outlined, as well as the specific context in which the research will be undertaken (in other words, web development companies in the UK).
Next up is the research objective (or objectives) . While the research aims cover the high-level “what”, the research objectives are a bit more practically oriented, looking at specific things you’ll be doing to achieve those research aims.
Let’s take a look at an example of some research objectives (ROs) to fit the research aim.
- RO1 – To identify common skills development strategies and approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK.
- RO2 – To evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies and approaches.
- RO3 – To compare and contrast these strategies and approaches in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
As you can see from this example, these objectives describe the actions you’ll take and the specific things you’ll investigate in order to achieve your research aims. They break down the research aims into more specific, actionable objectives.
The final step is to state your research questions . Your research questions bring the aims and objectives another level “down to earth”. These are the specific questions that your dissertation or theses will seek to answer. They’re not fluffy, ambiguous or conceptual – they’re very specific and you’ll need to directly answer them in your conclusions chapter .
The research questions typically relate directly to the research objectives and sometimes can look a bit obvious, but they are still extremely important. Let’s take a look at an example of the research questions (RQs) that would flow from the research objectives I mentioned earlier.
- RQ1 – What skills development strategies and approaches are currently being used by web development companies in the UK?
- RQ2 – How effective are each of these strategies and approaches?
- RQ3 – What are the strengths and weaknesses of each of these strategies and approaches?
As you can see, the research questions mimic the research objectives , but they are presented in question format. These questions will act as the driving force throughout your dissertation or thesis – from the literature review to the methodology and onward – so they’re really important.
A final note about this section – it’s really important to be clear about the scope of your study (more technically, the delimitations ). In other words, what you WILL cover and what you WON’T cover. If your research aims, objectives and questions are too broad, you’ll risk losing focus or investigating a problem that is too big to solve within a single dissertation.
Simply put, you need to establish clear boundaries in your research. You can do this, for example, by limiting it to a specific industry, country or time period. That way, you’ll ringfence your research, which will allow you to investigate your topic deeply and thoroughly – which is what earns marks!
Need a helping hand?
#5 – Significance
Now that you’ve made it clear what you’ll be researching, it’s time to make a strong argument regarding your study’s importance and significance . In other words, now that you’ve covered the what, it’s time to cover the why – enter essential ingredient number 5 – significance.
Of course, by this stage, you’ve already briefly alluded to the importance of your study in your background and research problem sections, but you haven’t explicitly stated how your research findings will benefit the world . So, now’s your chance to clearly state how your study will benefit either industry , academia , or – ideally – both . In other words, you need to explain how your research will make a difference and what implications it will have .
Let’s take a look at an example.
“This study will contribute to the body of knowledge on skills development by incorporating skills development strategies and approaches for industries in which knowledge and skills are rapidly and constantly changing. This will help address the current shortage of research in this area and provide real-world value to organisations operating in such dynamic environments.”
As you can see in this example, the paragraph clearly explains how the research will help fill a gap in the literature and also provide practical real-world value to organisations.
This section doesn’t need to be particularly lengthy, but it does need to be convincing . You need to “sell” the value of your research here so that the reader understands why it’s worth committing an entire dissertation or thesis to it. This section needs to be the salesman of your research. So, spend some time thinking about the ways in which your research will make a unique contribution to the world and how the knowledge you create could benefit both academia and industry – and then “sell it” in this section.

#6 – The limitations
Now that you’ve “sold” your research to the reader and hopefully got them excited about what’s coming up in the rest of your dissertation, it’s time to briefly discuss the potential limitations of your research.
But you’re probably thinking, hold up – what limitations? My research is well thought out and carefully designed – why would there be limitations?
Well, no piece of research is perfect . This is especially true for a dissertation or thesis – which typically has a very low or zero budget, tight time constraints and limited researcher experience. Generally, your dissertation will be the first or second formal research project you’ve ever undertaken, so it’s unlikely to win any research awards…
Simply put, your research will invariably have limitations. Don’t stress yourself out though – this is completely acceptable (and expected). Even “professional” research has limitations – as I said, no piece of research is perfect. The key is to recognise the limitations upfront and be completely transparent about them, so that future researchers are aware of them and can improve the study’s design to minimise the limitations and strengthen the findings.
Generally, you’ll want to consider at least the following four common limitations. These are:
- Your scope – for example, perhaps your focus is very narrow and doesn’t consider how certain variables interact with each other.
- Your research methodology – for example, a qualitative methodology could be criticised for being overly subjective, or a quantitative methodology could be criticised for oversimplifying the situation (learn more about methodologies here ).
- Your resources – for example, a lack of time, money, equipment and your own research experience.
- The generalisability of your findings – for example, the findings from the study of a specific industry or country can’t necessarily be generalised to other industries or countries.
Don’t be shy here. There’s no use trying to hide the limitations or weaknesses of your research. In fact, the more critical you can be of your study, the better. The markers want to see that you are aware of the limitations as this demonstrates your understanding of research design – so be brutal.
#7 – The structural outline
Now that you’ve clearly communicated what your research is going to be about, why it’s important and what the limitations of your research will be, the final ingredient is the structural outline.The purpose of this section is simply to provide your reader with a roadmap of what to expect in terms of the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In this section, you’ll need to provide a brief summary of each chapter’s purpose and contents (including the introduction chapter). A sentence or two explaining what you’ll do in each chapter is generally enough to orient the reader. You don’t want to get too detailed here – it’s purely an outline, not a summary of your research.
Let’s look at an example:
In Chapter One, the context of the study has been introduced. The research objectives and questions have been identified, and the value of such research argued. The limitations of the study have also been discussed.
In Chapter Two, the existing literature will be reviewed and a foundation of theory will be laid out to identify key skills development approaches and strategies within the context of fast-moving industries, especially technology-intensive industries.
In Chapter Three, the methodological choices will be explored. Specifically, the adoption of a qualitative, inductive research approach will be justified, and the broader research design will be discussed, including the limitations thereof.
So, as you can see from the example, this section is simply an outline of the chapter structure, allocating a short paragraph to each chapter. Done correctly, the outline will help your reader understand what to expect and reassure them that you’ll address the multiple facets of the study.
By the way – if you’re unsure of how to structure your dissertation or thesis, be sure to check out our video post which explains dissertation structure .
Keep calm and carry on.
Hopefully you feel a bit more prepared for this challenge of crafting your dissertation or thesis introduction chapter now. Take a deep breath and remember that Rome wasn’t built in a day – conquer one ingredient at a time and you’ll be firmly on the path to success.
Let’s quickly recap – the 7 ingredients are:
- The opening section – where you give a brief, high-level overview of what your research will be about.
- The study background – where you introduce the reader to key theory, concepts and terminology, as well as the context of your study.
- The research problem – where you explain what the problem with the current research is. In other words, the research gap.
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you clearly state what your dissertation will investigate.
- The significance – where you explain what value your research will provide to the world.
- The limitations – where you explain what the potential shortcomings and limitations of your research may be.
- The structural outline – where you provide a high-level overview of the structure of your document
If you bake these ingredients into your dissertation introduction chapter, you’ll be well on your way to building an engaging introduction chapter that lays a rock-solid foundation for the rest of your document.
Remember, while we’ve covered the essential ingredients here, there may be some additional components that your university requires, so be sure to double-check your project brief!

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
47 Comments
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident enough in undertaking my thesis on the survey;The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction
Glad to hear that. Good luck with your thesis!
Hi Derek, your article has been really helpful. Samuel. Student, Masters in Communication and Development Studies. Papua New Guinea University of Technology. 2024.
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident now undertaking my thesis; The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction.
Thanks so much for this article. I found myself struggling and wasting a lot of time in my thesis writing but after reading this article and watching some of your youtube videos, I now have a clear understanding of what is required for a thesis.
Thank you Derek, i find your each post so useful. Keep it up.
Thank you so much Derek ,for shedding the light and making it easier for me to handle the daunting task of academic writing .
Thanks do much Dereck for the comprehensive guide. It will assist me queit a lot in my thesis.
thanks a lot for helping
i LOVE the gifs, such a fun way to engage readers. thanks for the advice, much appreciated
Thanks a lot Derek! It will be really useful to the beginner in research!
You’re welcome
This is a well written, easily comprehensible, simple introduction to the basics of a Research Dissertation../the need to keep the reader in mind while writing the dissertation is an important point that is covered../ I appreciate the efforts of the author../
The instruction given are perfect and clear. I was supposed to take the course , unfortunately in Nepal the service is not avaialble.However, I am much more hopeful that you will provide require documents whatever you have produced so far.
Thank you very much
Thanks so much ❤️😘 I feel am ready to start writing my research methodology
This is genuinely the most effective advice I have ever been given regarding academia. Thank you so much!
This is one of the best write up I have seen in my road to PhD thesis. regards, this write up update my knowledge of research
I was looking for some good blogs related to Education hopefully your article will help. Thanks for sharing.
This is an awesome masterpiece. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to writing a Dissertation/Thesis I have seen and read.
You just saved me from going astray in writing a Dissertation for my undergraduate studies. I could not be more grateful for such a relevant guide like this. Thank you so much.
Thank you so much Derek, this has been extremely helpful!!
I do have one question though, in the limitations part do you refer to the scope as the focus of the research on a specific industry/country/chronological period? I assume that in order to talk about whether or not the research could be generalized, the above would need to be already presented and described in the introduction.
Thank you again!
Phew! You have genuinely rescued me. I was stuck how to go about my thesis. Now l have started. Thank you.
This is the very best guide in anything that has to do with thesis or dissertation writing. The numerous blends of examples and detailed insights make it worth a read and in fact, a treasure that is worthy to be bookmarked.
Thanks a lot for this masterpiece!
Powerful insight. I can now take a step
Thank you very much for these valuable introductions to thesis chapters. I saw all your videos about writing the introduction, discussion, and conclusion chapter. Then, I am wondering if we need to explain our research limitations in all three chapters, introduction, discussion, and conclusion? Isn’t it a bit redundant? If not, could you please explain how can we write in different ways? Thank you.
Excellent!!! Thank you…
Thanks for this informative content. I have a question. The research gap is mentioned in both the introduction and literature section. I would like to know how can I demonstrate the research gap in both sections without repeating the contents?
I’m incredibly grateful for this invaluable content. I’ve been dreading compiling my postgrad thesis but breaking each chapter down into sections has made it so much easier for me to engage with the material without feeling overwhelmed. After relying on your guidance, I’m really happy with how I’ve laid out my introduction.
Thank you for the informative content you provided
Hi Derrick and Team, thank you so much for the comprehensive guide on how to write a dissertation or a thesis introduction section. For some of us first-timers, it is a daunting task. However, the instruction with relevant examples makes it clear and easy to follow through. Much appreciated.
It was so helpful. God Bless you. Thanks very much
I thank you Grad coach for your priceless help. I have two questions I have learned from your video the limitations of the research presented in chapter one. but in another video also presented in chapter five. which chapter limitation should be included? If possible, I need your answer since I am doing my thesis. how can I explain If I am asked what is my motivation for this research?
You explain what moment in life caused you to have a peaked interest in the thesis topic. Personal experiences? Or something that had an impact on your life, or others. Something would have caused your drive of topic. Dig deep inside, the answer is within you!
Thank you guys for the great work you are doing. Honestly, you have made the research to be interesting and simplified. Even a novice will easily grasp the ideas you put forward, Thank you once again.
Excellent piece!
I feel like just settling for a good topic is usually the hardest part.
Thank you so much. My confidence has been completely destroyed during my first year of PhD and you have helped me pull myself together again
Happy to help 🙂
I am so glad I ran into your resources and did not waste time doing the wrong this. Research is now making so much sense now.
Gratitude to Derrick and the team I was looking for a solid article that would aid me in drafting the thesis’ introduction. I felt quite happy when I came across the piece you wrote because it was so well-written and insightful. I wish you success in the future.
thank you so much. God Bless you
Thank you so much Grad Coach for these helpful insights. Now I can get started, with a great deal of confidence.
It’s ‘alluded to’ not ‘eluded to’.
This is great!
Thank you for all this information. I feel very confident to complete my dissertation with all the help given. This is awesome and very helpful; I was studying alone with very little supervision and feedback of my thoughts. feelings. aspirations and experiences, with my topic or Kaupapa. It is a topic that very little or few researchers have written a thesis about (from personal experiences). As John Burke said ” unless you are sitting in the front seat and row, up close and personal, you will not understand the difficulties of growing up and living with hearing loss (caused by swimmer’s ears infection, resulting in burst eardrums, unless one denies having a hearing loss. This is from a Māori woman’s cultural perspective. Nga mihi nui kia koutou.
Thanks a lot for this information. The concepts are explained in a simple yet powerful way. They are easy to understand and adopt. Your team played an important role in writing my thesis. A big thank you !!!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to your field.
determine the elements of your dissertation as well as the order of those elements. Dissertations are typically structured as follows: Chapter 1 Introduction (broad overview of the research) Chapter 2 Review of the literature (and conceptual framework) Chapter 3 Methodology Chapter 4 Results or Findings
Thesis outline is a document that outlines the structure and content of a thesis, which is a long-form academic paper that presents an original argument or research on a particular topic.
How do you outline a thesis chapter? Each chapter of your thesis should have its own introduction, the main content or body of the chapter, and a conclusion summarizing what was covered and linking it to the rest of the thesis.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organise your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Use your university's formatting guidelines and templates to your advantage. If your institution has a template for formatting your thesis or dissertation that you can use, do so. Don't look at another student's document and try to replicate it yourself.
Whether you’re writing a master’s thesis or a doctoral dissertation, these foundational steps will help you articulate your ideas and lay the groundwork for a compelling piece of academic writing.
Every master’s thesis will have the following elements. Introduction – Familiarize the reader with the topic and what gap exists in the field. Literature Review – Provide a detailed analysis of similar work in the field and how your work is unique.
Thesis Outline is a step-by-step guide that helps you list all the major topics and subtopics in a logical order. For example: Introduction: Overview of your research. Literature Review: Summary of existing research on the topic. Methodology: Research methods employed. Chapters: Organise your main ideas, claims, and supporting ideas in sections.
Learn how to craft a top-notch dissertation or thesis introduction chapter using the 7 essential ingredients (including loads of examples).